The concept of overhead rate is a crucial aspect of financial management in various industries, particularly in construction, manufacturing, and professional services. It refers to the percentage of indirect costs, such as utilities, rent, and administrative salaries, that are allocated to direct costs, like labor and materials. Understanding and accurately calculating the overhead rate is essential for businesses to ensure profitability, competitiveness, and compliance with financial regulations. In this article, we will explore five ways to calculate and manage overhead rates effectively, highlighting the importance of each method and its applications in different contexts.
Key Points
- Understanding the concept of overhead rate and its significance in financial management
- Calculating overhead rate using the traditional method, activity-based costing, and other approaches
- Applying overhead rates in different industries, such as construction and manufacturing
- Managing overhead costs through efficient allocation and reduction strategies
- Monitoring and adjusting overhead rates to ensure profitability and competitiveness
Traditional Method of Calculating Overhead Rate
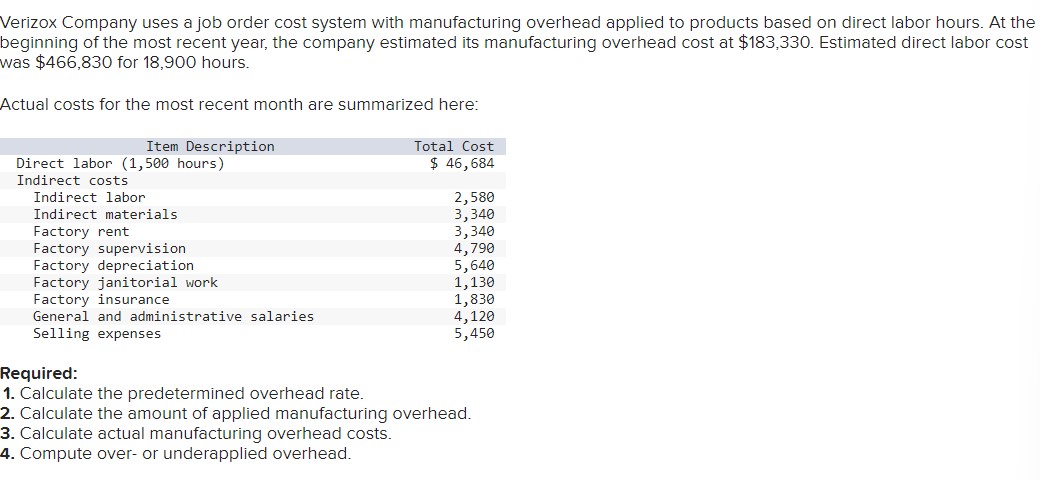
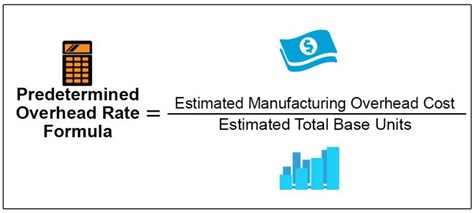
The traditional method of calculating overhead rate involves dividing the total indirect costs by the total direct costs. This approach is straightforward and easy to implement, making it a popular choice among businesses. However, it may not provide an accurate representation of the actual overhead costs, as it does not take into account the varying levels of indirect costs associated with different projects or activities. For instance, a company with a total indirect cost of 100,000 and a total direct cost of 500,000 would have an overhead rate of 20% (100,000 ÷ 500,000).
Activity-Based Costing (ABC) Method
The ABC method is a more advanced approach to calculating overhead rate, which involves assigning indirect costs to specific activities or projects based on their usage. This method provides a more accurate representation of the actual overhead costs, as it takes into account the varying levels of indirect costs associated with different activities. For example, a company that uses ABC method may assign a higher overhead rate to a project that requires more administrative support, such as a construction project with complex regulatory requirements.
| Method | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Method | Overhead Rate = Total Indirect Costs ÷ Total Direct Costs | 20% ($100,000 ÷ $500,000) |
| ABC Method | Overhead Rate = Activity-Based Indirect Costs ÷ Activity-Based Direct Costs | 25% ($50,000 ÷ $200,000) |

Other Methods of Calculating Overhead Rate
Besides the traditional and ABC methods, there are other approaches to calculating overhead rate, such as the job-order costing method and the process costing method. The job-order costing method involves assigning indirect costs to specific jobs or projects, while the process costing method involves assigning indirect costs to specific processes or departments. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of method depends on the specific needs and requirements of the business.
Managing Overhead Costs
Managing overhead costs is crucial to ensuring profitability and competitiveness. Businesses can manage overhead costs by implementing efficient allocation and reduction strategies, such as outsourcing non-core activities, reducing energy consumption, and renegotiating contracts with suppliers. For instance, a company that outsources its administrative functions may be able to reduce its overhead rate by 10%, resulting in significant cost savings.
Applications of Overhead Rate in Different Industries
Overhead rate is a critical concept in various industries, including construction, manufacturing, and professional services. In construction, overhead rate is used to calculate the total cost of a project, including labor, materials, and indirect costs. In manufacturing, overhead rate is used to calculate the total cost of production, including direct and indirect costs. In professional services, overhead rate is used to calculate the total cost of delivering services, including labor, overhead, and profit.
Monitoring and Adjusting Overhead Rates
Monitoring and adjusting overhead rates is essential to ensuring profitability and competitiveness. Businesses should regularly review their overhead rates to ensure that they are accurate and up-to-date. They should also adjust their overhead rates to reflect changes in indirect costs, such as increases in rent or utilities. For example, a company that experiences a 10% increase in rent may need to adjust its overhead rate to reflect this change, resulting in a higher overhead rate.
What is the purpose of calculating overhead rate?
+The purpose of calculating overhead rate is to allocate indirect costs to direct costs, ensuring that businesses accurately reflect their total costs and prices.
How often should overhead rates be reviewed and adjusted?
+Overhead rates should be reviewed and adjusted regularly, ideally on a quarterly or annual basis, to reflect changes in indirect costs and ensure accuracy.
What are the benefits of using activity-based costing (ABC) method?
+The benefits of using ABC method include more accurate allocation of indirect costs, better visibility into cost drivers, and improved decision-making.
In conclusion, calculating and managing overhead rates is a critical aspect of financial management in various industries. By understanding the different methods of calculating overhead rate, including the traditional method, ABC method, and other approaches, businesses can ensure accuracy and profitability. Regular monitoring and adjustment of overhead rates, as well as implementation of efficient allocation and reduction strategies, are essential to maintaining competitiveness and optimizing bottom-line performance.