The Spanish language is renowned for its complex verb conjugations, and the preterite tense is no exception. The verb "llegar," which translates to "to arrive," is a commonly used verb in Spanish that can be challenging to conjugate, especially in the preterite tense. In this article, we will delve into the world of Spanish grammar and explore the 5 ways to conjugate "llegar" in the preterite tense.
Introduction to the Preterite Tense

The preterite tense is used to describe completed actions that occurred in the past. It is a fundamental concept in Spanish grammar, and mastering the preterite tense is essential for effective communication. The verb “llegar” is a regular -ar verb, which means that it follows a specific conjugation pattern in the preterite tense.
Conjugation Patterns
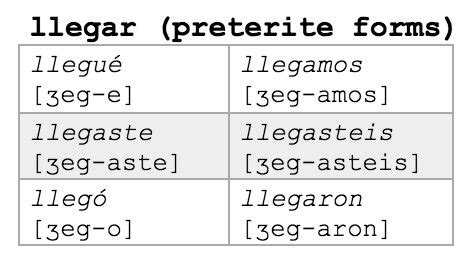
The preterite tense of “llegar” is conjugated as follows:
| Subject | Conjugation |
|---|---|
| Yo | Llegué |
| Tú | Llegaste |
| Él/ella/usted | Llegó |
| Nosotros/as | Llegamos |
| Vosotros/as | Llegasteis |
| Ellos/as | Llegaron |
Key Points
- The preterite tense of "llegar" is used to describe completed actions that occurred in the past.
- The verb "llegar" is a regular -ar verb, which means that it follows a specific conjugation pattern in the preterite tense.
- The conjugation of "llegar" in the preterite tense depends on the subject pronoun.
- Mastering the preterite tense is essential for effective communication in Spanish.
- Practice is key to mastering the conjugation of "llegar" in the preterite tense.
5 Ways to Use Llegar Preterite

Now that we have explored the conjugation patterns of “llegar” in the preterite tense, let’s examine 5 ways to use this verb in context.
1. Describing Arrival Times
The preterite tense of “llegar” can be used to describe the time at which someone arrived at a particular location. For example:
Yo llegué a la fiesta a las 8 pm. (I arrived at the party at 8 pm.)
Tú llegaste a la oficina a las 9 am. (You arrived at the office at 9 am.)
2. Talking About Past Events
The preterite tense of “llegar” can be used to talk about past events that have already occurred. For example:
Nosotros llegamos a la playa y nos dimos un baño. (We arrived at the beach and took a bath.)
Ellos llegaron a la ciudad y se fueron directamente al hotel. (They arrived in the city and went straight to the hotel.)
3. Describing Travel Experiences
The preterite tense of “llegar” can be used to describe travel experiences, such as arriving at a new destination. For example:
Yo llegué a Madrid y me encantó la ciudad. (I arrived in Madrid and loved the city.)
Tú llegaste a París y visitaste la Torre Eiffel. (You arrived in Paris and visited the Eiffel Tower.)
4. Talking About Meetings and Appointments
The preterite tense of “llegar” can be used to talk about meetings and appointments that have already occurred. For example:
Él llegó a la reunión a las 2 pm y dio una presentación. (He arrived at the meeting at 2 pm and gave a presentation.)
Nosotros llegamos a la cita y nos gustó el restaurante. (We arrived at the appointment and liked the restaurant.)
5. Describing Historical Events
The preterite tense of “llegar” can be used to describe historical events that have already occurred. For example:
Los españoles llegaron a América en 1492. (The Spanish arrived in America in 1492.)
Los ingleses llegaron a India en el siglo XVIII. (The English arrived in India in the 18th century.)
What is the difference between the preterite and imperfect tenses in Spanish?
+The preterite tense is used to describe completed actions that occurred in the past, while the imperfect tense is used to describe ongoing or repeated actions in the past.
How do I conjugate "llegar" in the preterite tense?
+The conjugation of "llegar" in the preterite tense depends on the subject pronoun. The conjugations are as follows: yo llegué, tú llegaste, él/ella/usted llegó, nosotros/as llegamos, vosotros/as llegasteis, ellos/as llegaron.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when using the preterite tense of "llegar"?
+Some common mistakes to avoid when using the preterite tense of "llegar" include using the incorrect conjugation for the subject pronoun, confusing the preterite tense with the imperfect tense, and using the wrong verb form for the context.
Meta description suggestion: “Learn how to conjugate the Spanish verb ‘llegar’ in the preterite tense and discover 5 ways to use it in context. Improve your Spanish grammar skills with our expert guide.” (149 characters)