Prime numbers, a fundamental concept in number theory, have fascinated mathematicians and scientists for centuries. These unique numbers, which are divisible only by 1 and themselves, play a crucial role in various mathematical theories and real-world applications. Understanding prime numbers is essential for advancements in cryptography, coding theory, and other fields. In this article, we will delve into the world of prime numbers, exploring their properties, applications, and interesting facts.
Key Points
- Definition and properties of prime numbers, including their role in number theory
- Methods for testing primality, such as trial division and modular arithmetic
- Applications of prime numbers in cryptography, coding theory, and pseudorandom number generation
- Interesting facts and records related to prime numbers, including the largest known prime
- Strategic considerations for working with prime numbers in various mathematical contexts
Introduction to Prime Numbers
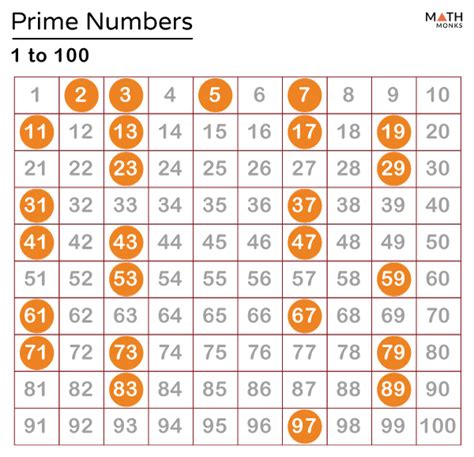
A prime number is a positive integer greater than 1 that has no positive integer divisors other than 1 and itself. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, and 13. Prime numbers are the building blocks of all other numbers, as every positive integer can be expressed as a product of prime numbers in a unique way, known as the prime factorization. This fundamental property makes prime numbers essential for various mathematical and computational applications.
Testing Primality
Testing whether a number is prime or composite is a crucial task in number theory. There are several methods for testing primality, including trial division, modular arithmetic, and probabilistic primality tests. Trial division involves dividing the number by all prime numbers less than or equal to its square root and checking for remainders. Modular arithmetic, on the other hand, uses properties of congruences and orders of numbers to determine primality. Probabilistic primality tests, such as the Miller-Rabin test, use random numbers and modular exponentiation to determine whether a number is likely to be prime.
| Primality Test | Description |
|---|---|
| Trial Division | Divide the number by all prime numbers less than or equal to its square root |
| Modular Arithmetic | Use properties of congruences and orders of numbers to determine primality |
| Miller-Rabin Test | Use random numbers and modular exponentiation to determine whether a number is likely to be prime |
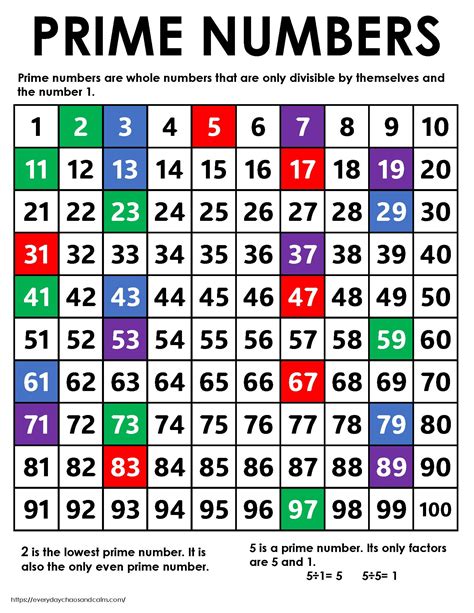
Applications of Prime Numbers
Prime numbers have numerous applications in various fields, including cryptography, coding theory, and pseudorandom number generation. In cryptography, prime numbers are used to create secure encryption algorithms, such as RSA and elliptic curve cryptography. Coding theory relies on prime numbers to construct error-correcting codes, such as Reed-Solomon codes. Pseudorandom number generators, which are essential for simulations and modeling, often use prime numbers to generate random sequences.
Cryptography and Prime Numbers
Cryptography, the practice of secure communication, relies heavily on prime numbers. The RSA algorithm, for example, uses the product of two large prime numbers to create a public-key encryption system. Elliptic curve cryptography, another popular encryption method, uses the properties of elliptic curves over finite fields, which are closely related to prime numbers. The security of these encryption algorithms relies on the difficulty of factoring large composite numbers, which is closely related to the distribution of prime numbers.
What is the largest known prime number?
+The largest known prime number is 2^82,589,933 - 1, which has 24,862,048 digits. It was discovered in 2018 by a team of mathematicians using a distributed computing project.
How are prime numbers used in coding theory?
+Prime numbers are used to construct error-correcting codes, such as Reed-Solomon codes, which are essential for reliable data transmission and storage. These codes use the properties of prime numbers to detect and correct errors in digital data.
What is the importance of prime numbers in pseudorandom number generation?
+Prime numbers are used to generate pseudorandom sequences, which are essential for simulations, modeling, and statistical analysis. These sequences are generated using algorithms that rely on the properties of prime numbers, such as the linear congruential generator.
In conclusion, prime numbers are a fascinating and essential concept in mathematics, with numerous applications in cryptography, coding theory, and pseudorandom number generation. Understanding the properties and applications of prime numbers is crucial for advancements in these fields and for developing new technologies that rely on secure and efficient computational methods.



