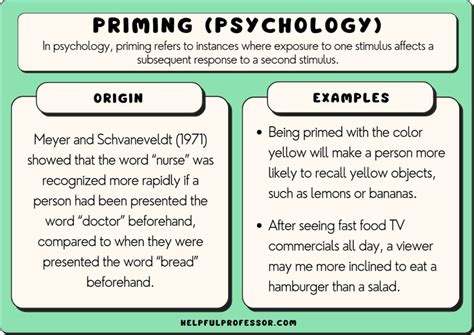
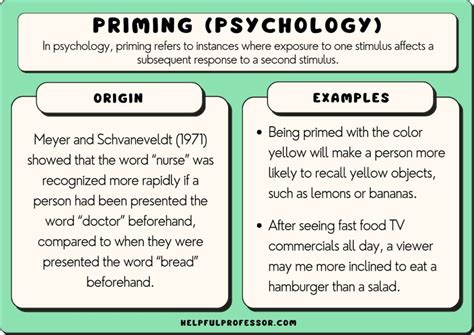
Priming psychology is a fundamental concept in the field of social psychology that refers to the phenomenon where exposure to one stimulus influences an individual's response to a subsequent stimulus. This concept is deeply rooted in the idea that our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are not solely determined by our conscious intentions, but are also shaped by subtle, unconscious cues in our environment. The term "priming" was first introduced by psychologists in the 1960s, and since then, it has become a widely studied and debated topic in the fields of psychology, neuroscience, and marketing.
At its core, priming psychology suggests that our brains are wired to make associations between different concepts, objects, and experiences. When we encounter a particular stimulus, it can activate a network of related concepts and ideas in our minds, which in turn can influence our perceptions, attitudes, and behaviors. For example, if someone is shown a picture of a sunny day, they may be more likely to report feeling happy and optimistic, even if they were not consciously aware of the image's influence. This is because the concept of sunshine is often associated with positive emotions and experiences, and the exposure to the image can "prime" the individual's mind to access these related concepts.
Key Points
- Priming psychology refers to the phenomenon where exposure to one stimulus influences an individual's response to a subsequent stimulus.
- The concept of priming is rooted in the idea that our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are shaped by subtle, unconscious cues in our environment.
- Priming can occur through various forms of stimuli, including visual, auditory, and tactile cues.
- The effects of priming can be short-term or long-term, depending on the strength and duration of the priming stimulus.
- Priming psychology has significant implications for fields such as marketing, education, and social influence.
Types of Priming
There are several types of priming that have been identified in the literature, each with its own unique characteristics and effects. One of the most well-known types of priming is semantic priming, which refers to the activation of related concepts and ideas in memory. For example, if someone is shown a word related to “dog,” such as “bone,” they may be faster to recognize the word “dog” later on. Another type of priming is affective priming, which refers to the influence of emotions and emotional stimuli on subsequent behaviors and attitudes. For instance, if someone is exposed to a positive emotional stimulus, such as a funny video, they may be more likely to exhibit prosocial behaviors later on.
Priming and Consumer Behavior
Priming psychology has significant implications for consumer behavior and marketing. By understanding how priming works, marketers can design more effective advertising campaigns and product placements. For example, if a company wants to promote a new energy drink, they may use priming to associate the product with concepts such as “energy,” “activity,” and “fun.” This can be done through the use of imagery, music, and other sensory stimuli that evoke the desired emotions and associations. By priming consumers with these concepts, the company can increase the likelihood that they will choose their product over competitors.
| Priming Stimulus | Effect on Consumer Behavior |
|---|---|
| Visual cues (e.g. images of happy people) | Increased likelihood of purchasing a product associated with positive emotions |
| Auditory cues (e.g. upbeat music) | Increased energy and activity levels, leading to increased consumption of energy drinks |
| Tactile cues (e.g. soft textures) | Increased feelings of comfort and relaxation, leading to increased preference for luxury products |
Priming and Social Influence
Priming psychology also has significant implications for social influence and persuasion. By priming individuals with certain concepts or attitudes, we can increase the likelihood that they will adopt similar behaviors or attitudes. For example, if someone is primed with the concept of “cooperation,” they may be more likely to engage in cooperative behaviors, such as sharing or volunteering. This can be particularly effective in group settings, where priming can influence the norms and behaviors of the group as a whole.
However, it's essential to note that priming can also have negative effects, particularly if it is used manipulatively or deceptively. For instance, if a company uses priming to associate their product with false or misleading information, it can lead to consumer deception and mistrust. Therefore, it's crucial to use priming in a responsible and ethical manner, with a focus on promoting positive behaviors and attitudes.
What is the difference between priming and persuasion?
+Priming and persuasion are related but distinct concepts. Priming refers to the activation of certain concepts or attitudes in memory, while persuasion refers to the intentional attempt to influence someone's beliefs or behaviors. While priming can be used as a tool for persuasion, it is not the same thing.
Can priming be used to promote positive behaviors?
+Yes, priming can be used to promote positive behaviors, such as cooperation, empathy, and altruism. By priming individuals with concepts and attitudes related to these behaviors, we can increase the likelihood that they will adopt them.
What are the potential risks of priming?
+The potential risks of priming include manipulation, deception, and the promotion of negative behaviors. If priming is used in a manipulative or deceptive manner, it can lead to negative consequences, such as consumer mistrust or the promotion of harmful behaviors.
In conclusion, priming psychology is a powerful and complex phenomenon that has significant implications for our understanding of human behavior and cognition. By recognizing the influence of priming on our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, we can develop more effective strategies for promoting positive behaviors and attitudes, while also avoiding the potential pitfalls of manipulative marketing tactics. As we continue to explore the complexities of priming psychology, it’s essential to approach this topic with a nuanced and critical perspective, recognizing both the benefits and the risks of this powerful phenomenon.