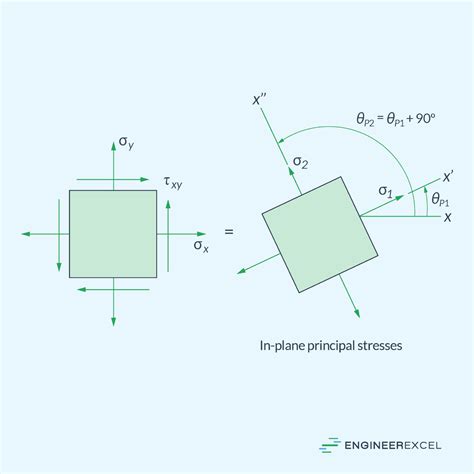
The concept of principal stress is a fundamental aspect of mechanics of materials, a branch of physics and engineering that deals with the behavior of solid objects under various types of loads. Principal stress refers to the maximum and minimum normal stresses that act on a material at a given point, and it plays a crucial role in determining the material's failure criteria. In this article, we will delve into the world of principal stress, exploring its definition, calculation methods, and applications in various fields.
Definition and Calculation of Principal Stress

When a material is subjected to external forces, it undergoes deformation, and the resulting internal forces cause stresses to develop within the material. The state of stress at a point in the material can be described by a set of nine stress components, which can be represented in a 3x3 matrix known as the stress tensor. The principal stresses are the eigenvalues of this stress tensor, and they represent the maximum and minimum normal stresses that act on the material at a given point.
The calculation of principal stress involves finding the eigenvalues of the stress tensor, which can be done using various methods, including the characteristic equation method and the Mohr's circle method. The characteristic equation method involves solving a cubic equation to find the eigenvalues, while the Mohr's circle method involves constructing a graphical representation of the stress state and finding the principal stresses from the intersection points of the circle with the coordinate axes.
Mohr’s Circle Method
Mohr’s circle is a graphical method used to calculate the principal stresses and visualize the state of stress at a point in a material. The method involves plotting the normal and shear stresses on a coordinate system and constructing a circle that represents the state of stress. The intersection points of the circle with the coordinate axes represent the principal stresses, and the angle between the principal axes can be found from the circle.
| Stress Component | Value |
|---|---|
| Normal Stress (σx) | 100 MPa |
| Normal Stress (σy) | 50 MPa |
| Shear Stress (τxy) | 25 MPa |

Applications of Principal Stress

The concept of principal stress has numerous applications in various fields, including engineering, physics, and materials science. Some of the key applications include:
- Design of Mechanical Components: Principal stress is used to determine the failure criteria of mechanical components, such as beams, columns, and shafts.
- Materials Science: Principal stress is used to study the behavior of materials under various types of loads and to develop new materials with improved properties.
- Structural Analysis: Principal stress is used to analyze the behavior of structures, such as bridges, buildings, and dams, under various types of loads.
- Biomechanics: Principal stress is used to study the behavior of biological tissues, such as bone and muscle, under various types of loads.
Key Points
- The principal stress is the maximum and minimum normal stress that acts on a material at a given point.
- The calculation of principal stress involves finding the eigenvalues of the stress tensor.
- Mohr's circle method is a graphical method used to calculate the principal stresses and visualize the state of stress.
- The concept of principal stress has numerous applications in various fields, including engineering, physics, and materials science.
- Principal stress is used to determine the failure criteria of mechanical components and to study the behavior of materials under various types of loads.
Limitations and Challenges
While the concept of principal stress is a powerful tool for analyzing the behavior of materials under various types of loads, it has some limitations and challenges. One of the main limitations is that it assumes a linear elastic behavior of the material, which may not be valid for all materials and loading conditions. Additionally, the calculation of principal stress can be complex and time-consuming, especially for complex stress states.
In recent years, advances in computational methods and software tools have made it possible to calculate the principal stresses more efficiently and accurately. However, the interpretation of the results still requires a deep understanding of the underlying physics and mechanics of the material.
What is the difference between principal stress and von Mises stress?
+The principal stress is the maximum and minimum normal stress that acts on a material at a given point, while the von Mises stress is a scalar value that represents the equivalent stress of the material. The von Mises stress is used to predict the failure of ductile materials, while the principal stress is used to predict the failure of brittle materials.
How is the principal stress calculated in a 3D stress state?
+The principal stress in a 3D stress state is calculated by finding the eigenvalues of the 3x3 stress tensor. This can be done using various methods, including the characteristic equation method and the Mohr's circle method.
What are the applications of principal stress in biomechanics?
+The principal stress is used in biomechanics to study the behavior of biological tissues, such as bone and muscle, under various types of loads. It is also used to develop new biomaterials and medical devices, and to analyze the behavior of implants and prosthetics.
Meta Description: Learn about the concept of principal stress, its calculation methods, and applications in various fields, including engineering, physics, and materials science. Discover the importance of principal stress in determining the failure criteria of mechanical components and the behavior of materials under various types of loads.