The periodic table is a fundamental tool in chemistry, organizing elements in a logical and systematic way. Its significance extends beyond the realm of chemistry, influencing various fields such as physics, biology, and materials science. The periodic table's structure and the relationships it illustrates have been pivotal in understanding the properties and behaviors of elements. Here, we explore five ways the periodic table impacts our understanding and application of chemical principles.
Organizational Framework
The periodic table serves as an organizational framework, arranging elements by their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus), electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. This arrangement allows for the prediction of an element’s properties based on its position in the table, facilitating the identification of patterns and trends among elements. For instance, elements in the same group (vertical column) exhibit similar chemical behaviors due to the same number of electrons in their outermost shell, which is crucial for understanding their reactivity and forming compounds.
Group and Period Trends
One of the key insights provided by the periodic table is the understanding of group and period trends. Moving down a group, elements tend to become more metallic and less electronegative, while moving across a period, elements become less metallic and more electronegative. These trends are essential for predicting the chemical properties and reactivity of elements, which is critical in designing and synthesizing new materials and compounds. For example, the halogens (Group 17) are highly reactive due to their strong tendency to gain an electron and form a stable anion, which is reflected in their position in the periodic table.
| Group | Element Example | Chemical Property |
|---|---|---|
| 1 (Alkali Metals) | Lithium (Li) | Highly reactive, readily lose one electron |
| 17 (Halogens) | Fluorine (F) | Highly electronegative, readily gain one electron |
| 18 (Noble Gases) | Argon (Ar) | Unreactive, full outer energy level |
Predictive Power and New Discoveries
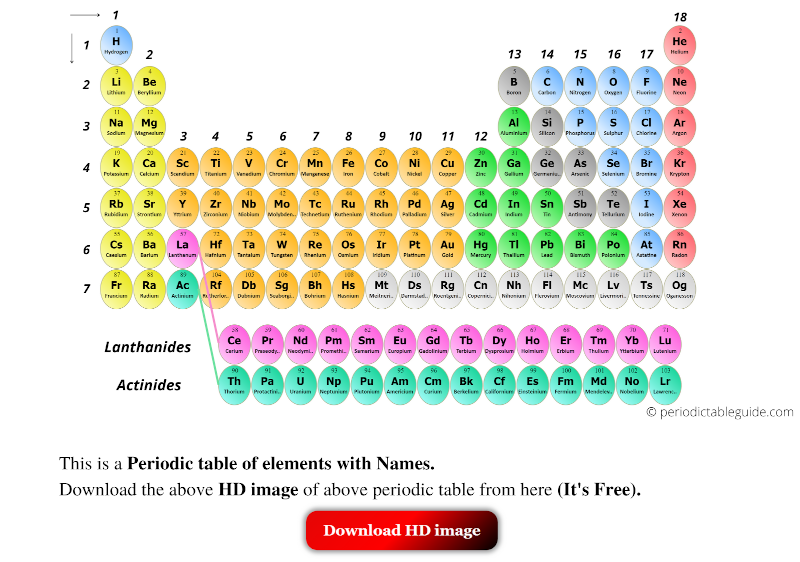
The periodic table has been instrumental in the discovery of new elements. By identifying gaps in the table, scientists have been able to predict the existence and properties of elements that had not yet been discovered. This predictive power has driven the expansion of the periodic table over the years, with new elements being synthesized and added to the table. For example, the discovery of tennessine (Ts) and oganesson (Og) was facilitated by the theoretical predictions based on the periodic table’s structure, demonstrating its role in advancing our understanding of the elemental universe.
Applications in Materials Science
The periodic table plays a crucial role in materials science, guiding the development of new materials with tailored properties. By understanding the relationships between elements and their positions in the periodic table, researchers can design alloys, semiconductors, and other materials with specific characteristics. For instance, the development of high-temperature superconductors relies on understanding the periodic trends and the ability to manipulate the electronic structures of materials, which is fundamentally linked to the elements’ positions in the periodic table.
Key Points
- The periodic table provides a systematic way to organize elements based on their atomic number and chemical properties.
- Understanding group and period trends is crucial for predicting the chemical behavior and reactivity of elements.
- The periodic table has been instrumental in the discovery of new elements by identifying gaps and predicting properties.
- It plays a significant role in materials science, enabling the design of new materials with specific properties.
- The table's structure and the relationships it illustrates have implications for various fields, including physics, biology, and engineering.
Implications for Physics and Biology
Beyond chemistry, the periodic table has implications for physics and biology. In physics, the periodic table underpins our understanding of atomic physics, particularly in the study of electron configurations and the behavior of subatomic particles. In biology, the periodic table is essential for understanding the biochemistry of living organisms, as the properties of elements influence their biological roles and the formation of biomolecules. For example, the essentiality of certain trace elements like zinc and iron for biological functions can be understood through their chemical properties as predicted by the periodic table.
Evolutionary Developments
The periodic table has undergone significant evolutionary developments since its inception. From the early versions developed by Dmitri Mendeleev to the modern table that includes over 118 elements, its structure and understanding have been refined over time. The inclusion of new elements, the refinement of electron configurations, and the deeper understanding of periodic trends have all contributed to its evolution. This evolution reflects our growing understanding of the atomic structure and the chemical properties of elements, underscoring the dynamic and progressive nature of scientific knowledge.
What is the significance of the periodic table in modern chemistry?
+The periodic table is significant because it provides a systematic and logical framework for understanding the properties and behaviors of elements, facilitating predictions and the discovery of new elements and compounds.
How does the periodic table influence materials science?
+The periodic table guides the development of new materials by understanding the relationships between elements and their properties, enabling the design of materials with specific characteristics such as conductivity, strength, and reactivity.
What are some future directions in the study and application of the periodic table?
+Future directions include the synthesis and characterization of new elements, further refinement of the periodic table to accommodate new discoveries, and the application of periodic trends to emerging fields such as nanotechnology and renewable energy.
In conclusion, the periodic table is a cornerstone of modern chemistry, offering a structured approach to understanding the elements and their interactions. Its impact extends beyond the chemical sciences, influencing physics, biology, and materials science. As our understanding of the elements and their properties continues to evolve, the periodic table remains a vital tool, guiding research, discovery, and innovation across disciplines.