Mathematics is replete with identities that serve as the foundation for various mathematical operations and theorems. These identities are equations that remain true regardless of the values assigned to the variables within them. In this article, we will delve into five fundamental math identities that are crucial for understanding and working with algebraic expressions, trigonometric functions, and other areas of mathematics.
Understanding Math Identities
Before exploring the specific identities, it’s essential to understand the significance of math identities. They provide a shorthand way of expressing complex relationships between different mathematical quantities. Identities are used to simplify expressions, solve equations, and prove theorems. They are instrumental in various branches of mathematics, including algebra, geometry, trigonometry, and calculus.
Key Points
- The Pythagorean identity is crucial in geometry and trigonometry.
- The commutative property of addition and multiplication is fundamental in algebra.
- The distributive property is essential for expanding and simplifying expressions.
- The sine and cosine identities are vital in trigonometry for solving equations and proving theorems.
- The identity for the sum of cubes is useful in algebra for factoring expressions.
1. The Pythagorean Identity
The Pythagorean identity, (a^2 + b^2 = c^2), where (c) is the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle, and (a) and (b) are the lengths of the other two sides, is a fundamental concept in geometry. This identity is not only used in geometry but also has applications in trigonometry, particularly in defining the sine, cosine, and tangent functions.
2. The Commutative Property of Addition and Multiplication
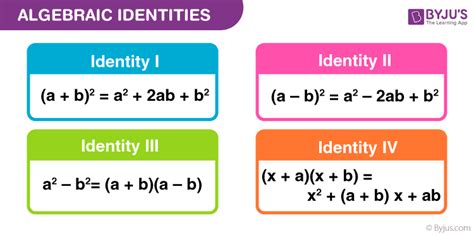
The commutative properties of addition and multiplication, stated as (a + b = b + a) and (a \times b = b \times a), respectively, are basic algebraic identities. These properties are essential for rearranging and simplifying expressions in algebra and are foundational in understanding more complex algebraic concepts.
3. The Distributive Property
The distributive property, expressed as (a(b + c) = ab + ac), is a crucial identity in algebra. It allows for the expansion and simplification of expressions and is fundamental in solving equations and manipulating algebraic expressions.
| Math Operation | Identity |
|---|---|
| Geometry and Trigonometry | a^2 + b^2 = c^2 |
| Algebraic Addition | a + b = b + a |
| Algebraic Multiplication | a \times b = b \times a |
| Expansion and Simplification | a(b + c) = ab + ac |
| Trigonometry | \sin^2(x) + \cos^2(x) = 1 |

4. The Sine and Cosine Identities
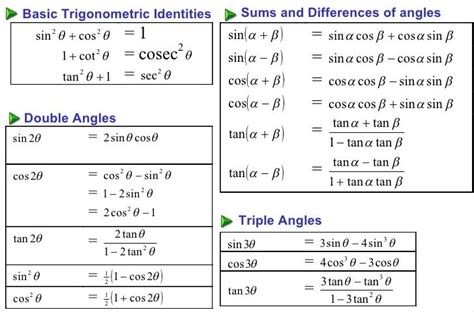
In trigonometry, the identity (\sin^2(x) + \cos^2(x) = 1) is fundamental. This identity, along with others such as (\sin(2x) = 2\sin(x)\cos(x)) and (\cos(2x) = \cos^2(x) - \sin^2(x)), is essential for solving trigonometric equations and understanding the relationships between different trigonometric functions.
5. The Identity for the Sum of Cubes
The identity (a^3 + b^3 = (a + b)(a^2 - ab + b^2)) is useful in algebra for factoring expressions that involve the sum of cubes. This identity, along with its counterpart for the difference of cubes, (a^3 - b^3 = (a - b)(a^2 + ab + b^2)), provides a powerful tool for simplifying and solving cubic equations.
In conclusion, these five math identities are foundational in mathematics, providing the basis for understanding and working with various mathematical concepts and operations. Whether in algebra, geometry, trigonometry, or beyond, mastering these identities is crucial for advancing in mathematical studies and applications.
What is the importance of the Pythagorean identity in mathematics?
+The Pythagorean identity is crucial in geometry for calculating distances and in trigonometry for defining basic trigonometric functions.
How does the distributive property aid in algebraic manipulations?
+The distributive property allows for the expansion and simplification of algebraic expressions, which is essential for solving equations and manipulating expressions in algebra.
What role do trigonometric identities play in solving trigonometric equations?
+Trigonometric identities, such as (\sin^2(x) + \cos^2(x) = 1), are vital for simplifying and solving trigonometric equations, as they provide relationships between different trigonometric functions.