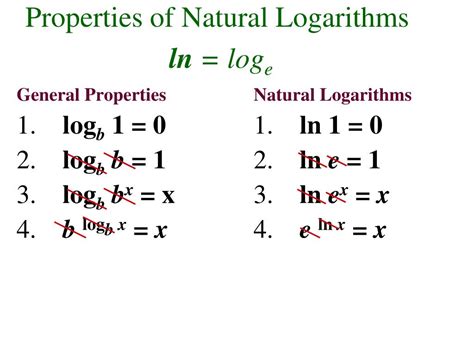
The natural logarithm, denoted as ln, is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in calculus. It is defined as the inverse function of the exponential function, meaning that it returns the power to which the base number e must be raised to produce a given value. In simpler terms, if y = e^x, then x = ln(y). This function has several key properties that make it useful and important in various mathematical and real-world applications.
One of the most basic properties of ln is its domain and range. The domain of the natural logarithm function is all positive real numbers, meaning that the input (or argument) of the function must be greater than zero. This restriction exists because the logarithm of zero or a negative number is undefined in real numbers. On the other hand, the range of the function is all real numbers, indicating that the output of ln(x) can be any real number, positive, negative, or zero.
Key Points
- The natural logarithm is the inverse of the exponential function e^x.
- The domain of ln(x) is all positive real numbers (x > 0).
- The range of ln(x) is all real numbers.
- Ln(1) = 0 because e^0 = 1.
- Ln(e) = 1 because e^1 = e.
Derivative and Integral of Ln
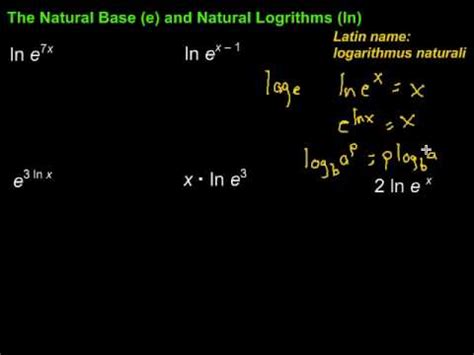
The derivative of the natural logarithm function is 1/x. This is a crucial property for calculus, as it is used in various applications, including optimization problems and the calculation of rates of change. To derive this, one can use the definition of a derivative as a limit and the properties of the exponential function. The integral of ln(x) can be found using integration by parts, which results in x*ln(x) - x + C, where C is the constant of integration.
Product Rule and Chain Rule
In calculus, the product rule and chain rule are essential for differentiating complex functions. The product rule states that if we have a function of the form f(x)*g(x), its derivative is f’(x)*g(x) + f(x)*g’(x). For the chain rule, if we have a composite function f(g(x)), its derivative is f’(g(x))*g’(x). These rules are useful when dealing with functions that involve the natural logarithm, such as ln(x^2) or ln(sin(x)).
| Function | Derivative |
|---|---|
| ln(x) | 1/x |
| ln(x^2) | 2/x |
| ln(sin(x)) | cos(x)/sin(x) |
Applications of Ln
The natural logarithm has numerous applications in mathematics, physics, engineering, and finance. In mathematics, it is used in calculus for differentiation and integration, as mentioned earlier. In physics, the natural logarithm appears in the description of various phenomena, such as population growth, chemical reactions, and the Gaussian distribution in statistics. In finance, logarithmic returns are used to calculate the performance of investments because they are additive, making it easier to aggregate returns over time.
Financial Applications
In finance, the natural logarithm is particularly useful for calculating continuous compounding interest. The formula for continuous compounding is A = Pe^(rt), where A is the amount after t years, P is the principal amount, r is the annual interest rate, and t is the time the money is invested for. The natural logarithm can help in solving for the interest rate or the time period when other variables are known.
What is the domain of the natural logarithm function?
+The domain of the natural logarithm function is all positive real numbers (x > 0).
What is the derivative of ln(x)?
+The derivative of ln(x) is 1/x.
What are some practical applications of the natural logarithm?
+The natural logarithm has applications in calculus, physics, engineering, and finance, including differentiation, integration, population growth models, chemical reactions, Gaussian distribution, and continuous compounding interest.
In conclusion, the natural logarithm function, denoted as ln, is a crucial mathematical concept with various properties and applications. Understanding its domain, range, derivative, and integral, as well as its role in calculus and real-world applications, is essential for advanced mathematical and scientific studies. The natural logarithm’s presence in fields such as finance, physics, and engineering underscores its importance and utility in describing and analyzing a wide range of phenomena.