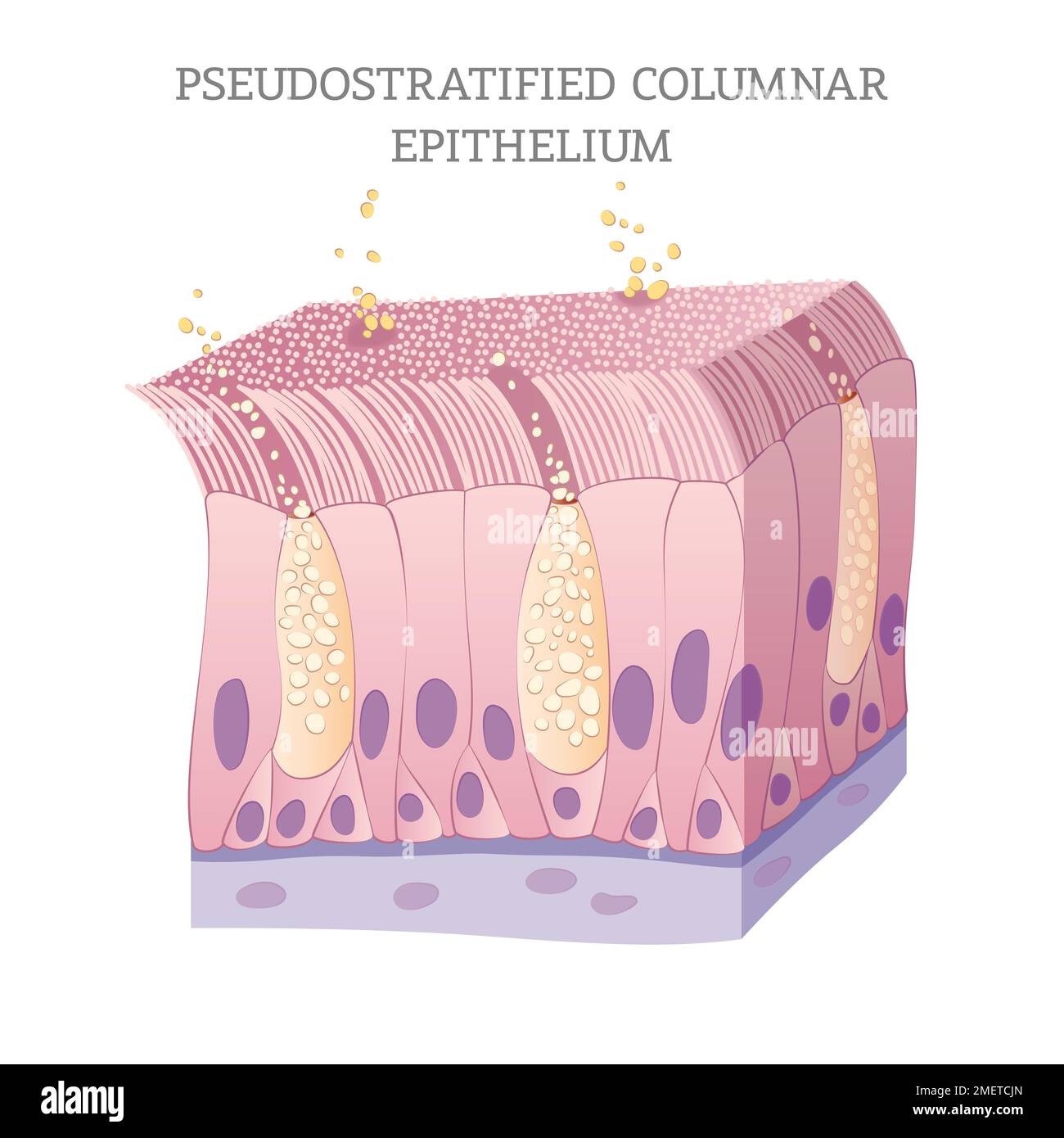
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium is a type of epithelial tissue that lines various parts of the body, including the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive tracts. This complex tissue is characterized by its unique structure and function, which enables it to perform a range of critical tasks. In this article, we will delve into the world of pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium, exploring its key characteristics, functions, and importance in maintaining overall health.
Key Points
- Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium is a type of epithelial tissue that appears to be layered due to the varying heights of its cells.
- This tissue is found in various parts of the body, including the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive tracts.
- The cilia on the surface of the cells play a crucial role in moving mucus, debris, and other substances along the surface of the tissue.
- Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium is sensitive to damage from environmental factors, such as air pollution and cigarette smoke.
- Dysfunction of this tissue has been implicated in various diseases, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma.
Structure and Function of Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium
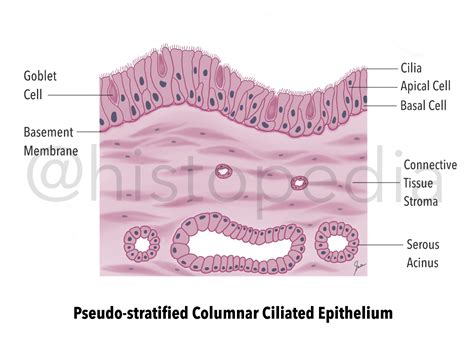
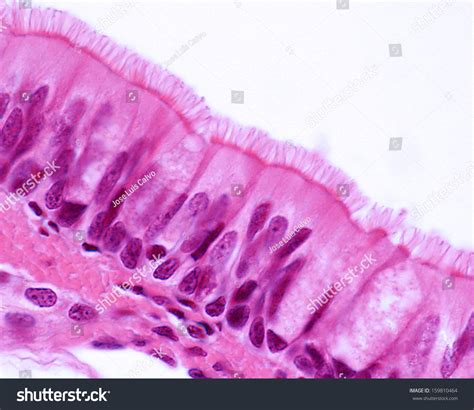
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium is composed of columnar cells that are lined up in a single layer, but appear to be layered due to the varying heights of the cells. The cells are attached to a basement membrane, which provides structural support and separates the epithelium from the underlying connective tissue. The surface of the cells is covered in cilia, which are small, hair-like structures that beat in a coordinated manner to move mucus, debris, and other substances along the surface of the tissue.
Cilia and Mucociliary Clearance
The cilia on the surface of pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium play a crucial role in maintaining the health of the tissue and the surrounding environment. The cilia beat in a coordinated manner to move mucus and debris along the surface of the tissue, a process known as mucociliary clearance. This process is essential for removing harmful substances, such as bacteria and viruses, from the body and preventing infection. In the respiratory tract, for example, the cilia help to move mucus and debris out of the lungs and into the throat, where it can be swallowed or coughed up.
| Location | Function |
|---|---|
| Respiratory Tract | Mucociliary clearance, removal of debris and pathogens |
| Urinary Tract | Prevention of bacterial infection, maintenance of urinary flow |
| Reproductive Tract | Movement of sperm, ovum, and embryos, maintenance of reproductive health |
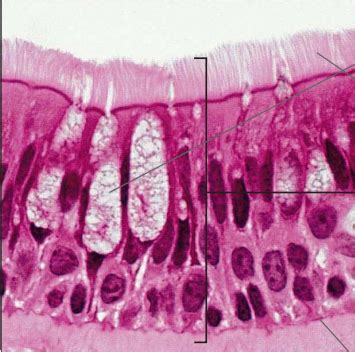
Dysfunction and Disease
Dysfunction of pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium has been implicated in various diseases, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma. In COPD, for example, the cilia on the surface of the cells are damaged, leading to a reduction in mucociliary clearance and an accumulation of mucus and debris in the lungs. This can cause a range of symptoms, including coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Similarly, in asthma, the cilia are often damaged, leading to an overproduction of mucus and an increased risk of infection.
Environmental Factors and Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium is sensitive to damage from environmental factors, such as air pollution and cigarette smoke. Exposure to these substances can cause damage to the cilia and reduce mucociliary clearance, leading to an increased risk of infection and disease. In addition, environmental factors can also cause inflammation and oxidative stress, which can further damage the tissue and reduce its function.
What is pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium?
+Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium is a type of epithelial tissue that appears to be layered due to the varying heights of its cells. It is found in various parts of the body, including the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive tracts.
What is the function of the cilia on the surface of pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium?
+The cilia on the surface of pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium play a crucial role in moving mucus, debris, and other substances along the surface of the tissue. This process is known as mucociliary clearance and is essential for removing harmful substances from the body and preventing infection.
What diseases are associated with dysfunction of pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium?
+Dysfunction of pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium has been implicated in various diseases, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma. In COPD, for example, the cilia on the surface of the cells are damaged, leading to a reduction in mucociliary clearance and an accumulation of mucus and debris in the lungs.
Meta Description: Discover the importance of pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium in maintaining the health of the body. Learn about its unique structure and function, and how dysfunction can lead to disease.