Psychological abuse and emotional abuse are forms of mistreatment that can have devastating effects on an individual's mental health and well-being. These types of abuse can be just as damaging as physical abuse, but they often go unrecognized or unreported due to their subtle and insidious nature. In this article, we will delve into the complexities of psychological and emotional abuse, exploring their definitions, signs, and symptoms, as well as the impact they can have on victims and their loved ones.
Key Points
- Psychological abuse and emotional abuse can be just as damaging as physical abuse, but often go unrecognized or unreported.
- These forms of abuse can lead to anxiety, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and even suicidal thoughts or behaviors.
- Victims of psychological and emotional abuse may experience feelings of shame, guilt, and self-doubt, making it difficult for them to seek help or leave the abusive relationship.
- Abusers may use tactics such as gaslighting, emotional blackmail, and isolation to control and manipulate their victims.
- Support from loved ones, therapy, and self-care are crucial for victims to recover from psychological and emotional abuse.
Understanding Psychological Abuse and Emotional Abuse
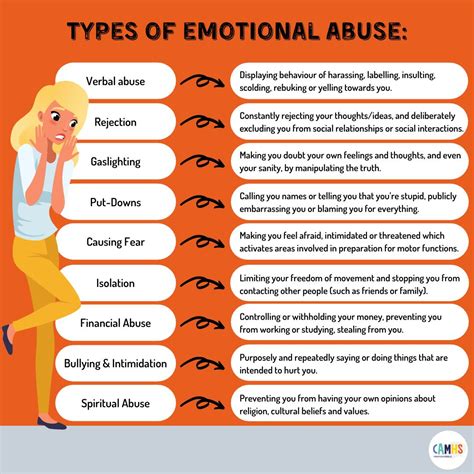
Psychological abuse and emotional abuse are often used interchangeably, but they can have slightly different connotations. Psychological abuse refers to the intentional infliction of mental harm or distress on an individual, often through behaviors such as bullying, harassment, or intimidation. Emotional abuse, on the other hand, encompasses a broader range of behaviors that can damage a person’s emotional well-being, including verbal abuse, emotional manipulation, and neglect.
Both psychological and emotional abuse can be perpetrated by anyone, including intimate partners, family members, friends, or colleagues. The abuse can be overt or covert, with some abusers using subtle tactics to control and manipulate their victims. These tactics can include gaslighting, where the abuser distorts or denies reality to make the victim question their own sanity or memory, or emotional blackmail, where the abuser uses guilt, shame, or self-pity to manipulate the victim into doing their bidding.
Signs and Symptoms of Psychological and Emotional Abuse
Victims of psychological and emotional abuse may exhibit a range of signs and symptoms, including anxiety, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and even suicidal thoughts or behaviors. They may also experience hypervigilance, where they are constantly on edge, waiting for the next abusive incident, or dissociation, where they disconnect from their thoughts, feelings, or bodily sensations as a coping mechanism.
Other signs of psychological and emotional abuse may include:
- Unexplained changes in mood or behavior
- Withdrawal from social activities or relationships
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
- Physical symptoms such as headaches, stomach problems, or sleep disturbances
- Feelings of shame, guilt, or self-doubt
| Abuse Type | Signs and Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Psychological Abuse | Anxiety, depression, PTSD, hypervigilance, dissociation |
| Emotional Abuse | Verbal abuse, emotional manipulation, neglect, gaslighting, emotional blackmail |

Impact of Psychological and Emotional Abuse
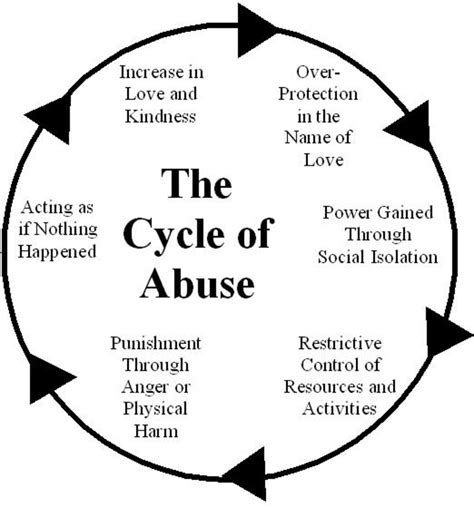
The impact of psychological and emotional abuse can be far-reaching and devastating. Victims may experience long-term effects on their mental health, relationships, and overall well-being. They may struggle with trust issues, finding it challenging to form healthy relationships in the future, or self-esteem problems, where they doubt their own worth or abilities.
In addition to the individual effects, psychological and emotional abuse can also have a broader impact on society. It can contribute to cycles of violence, where abusers learn their behaviors from their own experiences of abuse, and social isolation, where victims become disconnected from their support networks and communities.
Recovery and Support
Recovery from psychological and emotional abuse requires a supportive and non-judgmental environment. Victims may benefit from therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or trauma-focused CBT, to process their experiences and develop coping strategies. They may also require support groups, where they can connect with others who have experienced similar forms of abuse.
In addition to professional support, victims of psychological and emotional abuse may also benefit from self-care activities, such as exercise, meditation, or creative pursuits, to help manage their stress and emotions. They may also need to rebuild their support networks, reconnecting with friends, family, or loved ones who can provide emotional support and validation.
What are the signs of psychological and emotional abuse?
+Signs of psychological and emotional abuse may include anxiety, depression, PTSD, hypervigilance, dissociation, and unexplained changes in mood or behavior.
How can I support a loved one who has experienced psychological or emotional abuse?
+You can support a loved one by listening to their experiences without judgment, validating their emotions, and encouraging them to seek professional help.
What are the long-term effects of psychological and emotional abuse?
+The long-term effects of psychological and emotional abuse can include trust issues, self-esteem problems, and social isolation, as well as increased risk of mental health problems such as anxiety, depression, and PTSD.
In conclusion, psychological and emotional abuse are complex and multifaceted issues that require a comprehensive and supportive approach. By recognizing the signs and symptoms of these forms of abuse, providing a safe and non-judgmental environment, and offering access to professional support and resources, we can help victims recover from the trauma and rebuild their lives. As a society, it’s essential that we acknowledge the impact of psychological and emotional abuse and work together to prevent these forms of mistreatment from occurring in the first place.


