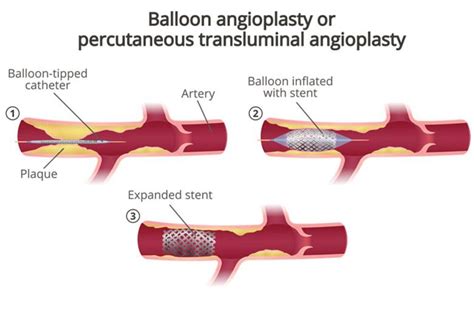
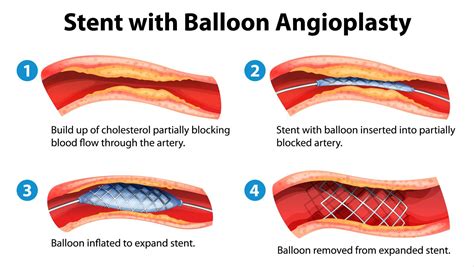
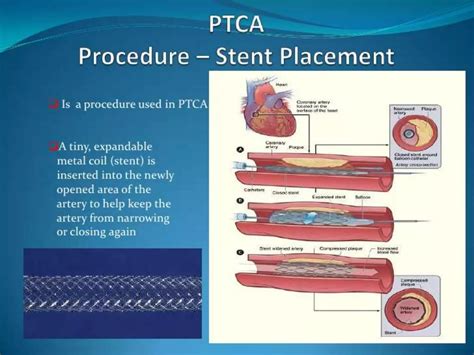
PTCA, a commonly used medical abbreviation, stands for Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty. This procedure is a minimally invasive intervention used to open up blocked coronary arteries, allowing blood to circulate unobstructed to the heart muscle. The PTCA procedure involves the insertion of a catheter (a thin flexible tube) into the narrowed part of the artery. A balloon on the catheter is then inflated to expand the artery, and very often a stent (a small, wire mesh tube) is placed to keep the artery open.
Understanding PTCA: Procedure and Purpose

PTCA is primarily used to treat coronary artery disease, which occurs when the coronary arteries - the major blood vessels that supply blood to the heart - become damaged or diseased. It is usually performed in a catheterization laboratory (cath lab) by a team of healthcare professionals led by an interventional cardiologist. The decision to perform a PTCA is made after a diagnostic angiogram shows that the coronary arteries are narrowed or blocked. This narrowing is typically due to atherosclerosis, a condition in which plaque builds up in the arteries, leading to their hardening and narrowing.
Preparation and Risks
Before undergoing PTCA, patients are usually given medications to prevent blood clots from forming and to reduce the risk of complications. The procedure itself is relatively quick, often lasting about an hour, though preparation and recovery time add to the overall duration. While PTCA is generally safe, as with any medical procedure, there are risks involved, including bleeding, hematoma, or pseudoaneurysm at the catheter site, as well as more serious complications such as coronary artery rupture or the need for emergency coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG). Restenosis, or the re-narrowing of the arteries, is another potential complication, though the use of drug-eluting stents has significantly reduced this risk.
| Complications | Risk Level |
|---|---|
| Bleeding or Hematoma | 1-5% |
| Restenosis (without drug-eluting stent) | 30-50% |
| Death | <1% |
Key Points About PTCA
Understanding the ins and outs of PTCA can help patients and their families navigate the process with confidence. Here are some key points to consider:
Key Points
- PTCA Definition: Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty, a procedure to open blocked coronary arteries.
- Procedure Duration: Typically lasts about an hour, not including preparation and recovery time.
- Common Risks include bleeding, restenosis, and, rarely, death.
- The use of Drug-Eluting Stents has reduced the risk of restenosis.
- Post-procedure Instructions must be followed carefully to minimize complications.
Future of PTCA and Emerging Trends
As medical technology continues to evolve, so too do the techniques and tools used in PTCA. One of the significant advancements has been the development of drug-eluting stents, which release medication to prevent cell proliferation, thereby reducing the rate of restenosis. Further research is focused on improving stent technology, enhancing imaging techniques for better visualization during the procedure, and exploring newer methods for treating coronary artery disease, such as bioresorbable vascular scaffolds.
In conclusion, PTCA remains a vital treatment option for individuals with coronary artery disease, offering a less invasive alternative to surgical interventions like CABG. Its effectiveness, combined with ongoing advancements in medical technology, underscores its importance in the management of heart disease.
What is the primary purpose of PTCA?
+The primary purpose of PTCA is to open up blocked coronary arteries, restoring blood flow to the heart and alleviating symptoms of coronary artery disease such as chest pain (angina) and shortness of breath.
How long does a PTCA procedure typically take?
+The PTCA procedure itself usually lasts about an hour, though the entire process from preparation to recovery can take several hours.
What are the risks associated with PTCA?
+Risks include bleeding, hematoma, restenosis, and, in rare cases, death. However, serious complications are uncommon, and the procedure is generally considered safe when performed by experienced professionals.