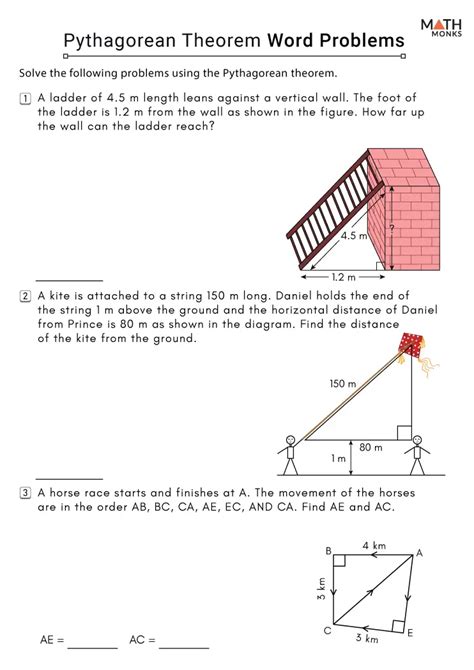
The Pythagorean Theorem is a fundamental concept in geometry, crucial for understanding the relationship between the sides of a right-angled triangle. The theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. This can be expressed as a^2 + b^2 = c^2, where a and b are the lengths of the two legs, and c is the length of the hypotenuse. Mastering the Pythagorean Theorem is essential for various mathematical and real-world applications, including architecture, engineering, and physics.
Understanding the Basics of the Pythagorean Theorem
To apply the Pythagorean Theorem effectively, it’s crucial to understand its components. The theorem is often used to find the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle when the lengths of the other two sides are known, but it can also be used to find the length of a leg when the length of the hypotenuse and the other leg are known. For instance, if you know the lengths of the two legs of a right triangle, you can calculate the length of the hypotenuse by plugging the values into the formula (c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2}). Conversely, if you know the length of the hypotenuse and one leg, you can find the length of the other leg using the formula (a = \sqrt{c^2 - b^2}) or (b = \sqrt{c^2 - a^2}), depending on which leg you’re trying to find.
Applying the Theorem in Real-World Scenarios
The Pythagorean Theorem has numerous practical applications. For example, in construction, it can be used to determine the length of the diagonal of a rectangle (such as a floor or a wall) if the lengths of the sides are known. In physics, it’s used to calculate distances and speeds in problems involving right triangles. Moreover, in computer graphics and game development, the theorem is essential for creating realistic 3D models and for calculating distances and trajectories in game environments.
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Construction | Determining the length of diagonals in buildings or rooms |
| Physics | Calculating distances, speeds, and trajectories in problems involving right triangles |
| Computer Graphics | Creating realistic 3D models and calculating distances in game environments |

Key Points
- The Pythagorean Theorem is expressed as a^2 + b^2 = c^2, where a and b are the lengths of the legs, and c is the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle.
- The theorem can be used to find the length of the hypotenuse or the length of a leg in a right triangle, given sufficient information.
- It has practical applications in construction, physics, computer graphics, and other fields involving spatial measurements and calculations.
- Ensuring the triangle is a right triangle is crucial for the theorem's applicability.
- Understanding and applying the Pythagorean Theorem is fundamental for problem-solving in geometry and various real-world scenarios.
As a fundamental principle in geometry, the Pythagorean Theorem offers a powerful tool for solving problems involving right triangles. Its applications are diverse, ranging from the mundane, such as calculating room dimensions, to the complex, such as modeling trajectories in physics. By mastering the theorem and understanding its limitations and applications, individuals can enhance their problem-solving skills in mathematics and apply these skills effectively in real-world contexts.
What is the primary use of the Pythagorean Theorem?
+The primary use of the Pythagorean Theorem is to find the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle when the lengths of the other two sides are known, or to find the length of a leg when the length of the hypotenuse and the other leg are known.
Can the Pythagorean Theorem be applied to non-right triangles?
+No, the Pythagorean Theorem is specifically designed for right triangles. For non-right triangles, other trigonometric methods such as the law of cosines or the law of sines must be used.
What are some real-world applications of the Pythagorean Theorem?
+The Pythagorean Theorem has applications in construction, physics, computer graphics, and other fields where spatial measurements and calculations are necessary. It’s used for determining distances, speeds, and trajectories, as well as for creating realistic models in computer graphics.