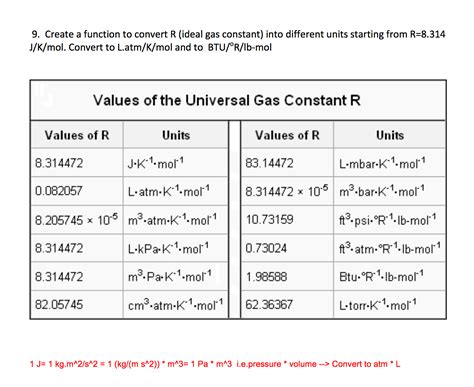
The ideal gas law, a fundamental principle in physics and chemistry, is often expressed as PV = nRT, where P is the pressure of the gas, V is the volume, n is the number of moles of gas, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin. The gas constant, R, is a crucial component of this equation, relating the energy of a gas to its temperature. In this article, we will explore 5 ways the R gas constant is utilized across different scientific disciplines and its significance in understanding various phenomena.
Introduction to the Gas Constant
The gas constant, denoted by R, has a value of approximately 8.3145 J/(mol·K). This constant is essential for calculating the behavior of ideal gases, which do not exist in reality but serve as a useful model for real gases under many conditions. The gas constant is derived from the Boltzmann constant (kB) and the Avogadro constant (NA) through the relationship R = NAkB. Understanding the gas constant is vital for predicting the physical behavior of gases, including their expansion, compression, and the relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature.
Key Points
- The gas constant (R) is a fundamental constant in the ideal gas law, PV = nRT.
- R has a value of approximately 8.3145 J/(mol·K) and is used to relate the energy of a gas to its temperature.
- The gas constant is crucial in chemistry for calculations involving the behavior of gases.
- In physics, R is used to understand the thermal properties of gases and to derive other important constants.
- The gas constant plays a significant role in engineering, particularly in the design of systems involving gas flow and thermal energy transfer.
Applications in Chemistry

In chemistry, the gas constant is indispensable for calculating the behavior of gases under various conditions. For instance, in the study of chemical reactions involving gases, understanding how the reactants and products behave under different temperatures and pressures is crucial. The gas constant is used in these calculations to predict the direction and feasibility of reactions. Moreover, in the field of chemical engineering, R is vital for the design of processes and equipment, such as reactors and separation units, where gases play a significant role.
Calculating Reaction Feasibility
Chemists often use the gas constant in conjunction with other thermodynamic constants to assess the feasibility of chemical reactions. For example, the change in Gibbs free energy (ΔG) of a reaction, which determines whether a reaction is spontaneous, can be calculated using the equation ΔG = ΔH - TΔS, where ΔH is the change in enthalpy, T is the temperature in Kelvin, and ΔS is the change in entropy. The gas constant is implicitly involved in these calculations through its role in defining the entropy change of gases.
| Thermodynamic Property | Formula | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Change in Gibbs Free Energy (ΔG) | ΔG = ΔH - TΔS | J/mol |
| Change in Enthalpy (ΔH) | ΔH = U + PΔV | J/mol |
| Change in Entropy (ΔS) | ΔS = Q / T | J/(mol·K) |
Physical and Engineering Applications
Beyond chemistry, the gas constant has profound implications in physics and engineering. In physics, R is used to derive other important constants and to understand the thermal properties of gases. The gas constant is also critical in the study of the behavior of real gases, which deviate from ideal gas behavior, especially at high pressures and low temperatures. In engineering, particularly in mechanical and aerospace engineering, the gas constant is essential for designing systems that involve gas flow and thermal energy transfer, such as internal combustion engines, gas turbines, and refrigeration systems.
Designing Efficient Systems
Engineers utilize the gas constant in the design of efficient systems that involve the expansion and compression of gases. For example, in the design of steam turbines, understanding how the properties of steam (a gas) change with temperature and pressure is crucial. The gas constant is used in these calculations to predict the performance of the turbine under various operating conditions. Similarly, in the design of refrigeration systems, R is essential for understanding the thermodynamic cycle of the refrigerant, ensuring the system’s efficiency and safety.
In conclusion, the R gas constant is a fundamental constant that plays a pivotal role across various scientific disciplines, including chemistry, physics, and engineering. Its applications range from calculating the behavior of gases in chemical reactions to designing efficient systems in engineering. Understanding the gas constant and its implications is essential for advancing our knowledge in these fields and for developing innovative technologies that rely on the principles of thermodynamics.
What is the significance of the gas constant in chemistry?
+The gas constant is crucial in chemistry for calculating the behavior of gases under various conditions, including predicting the direction and feasibility of chemical reactions involving gases.
How is the gas constant used in engineering?
+In engineering, the gas constant is used in the design of systems that involve gas flow and thermal energy transfer, such as internal combustion engines, gas turbines, and refrigeration systems, to predict performance and efficiency under various operating conditions.
What is the value of the gas constant?
+The gas constant ® has a value of approximately 8.3145 J/(mol·K).