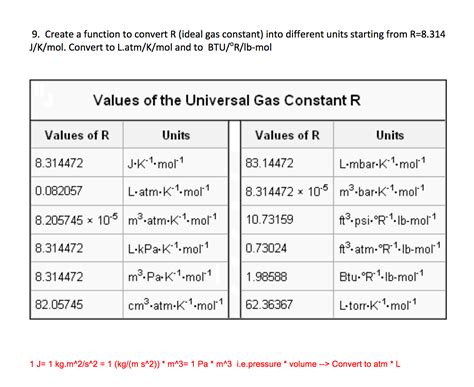
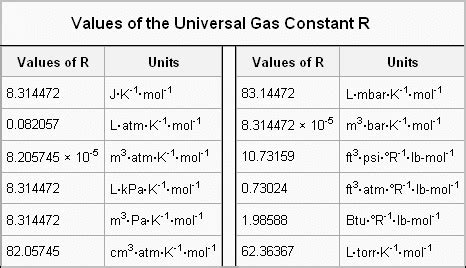
The Ideal Gas Constant, denoted by the symbol R, is a fundamental constant in physics and chemistry that relates the energy of a gas to its temperature. It is a crucial component in the ideal gas law, which describes the behavior of ideal gases. The ideal gas law is given by the equation PV = nRT, where P is the pressure of the gas, V is the volume, n is the number of moles of gas, and T is the temperature in Kelvin. The Ideal Gas Constant is a proportionality constant that allows us to calculate the energy of a gas based on its temperature and other properties.
The value of the Ideal Gas Constant is approximately 8.3145 J/(mol·K), although it can vary slightly depending on the specific definition and measurement method used. This constant is a universal value that applies to all ideal gases, regardless of their composition or properties. It is a key concept in thermodynamics, which is the study of the relationships between heat, work, and energy. The Ideal Gas Constant is used in a wide range of applications, including chemistry, physics, engineering, and materials science.
Key Points
- The Ideal Gas Constant is a fundamental constant in physics and chemistry that relates the energy of a gas to its temperature.
- The value of the Ideal Gas Constant is approximately 8.3145 J/(mol·K).
- The Ideal Gas Constant is a universal value that applies to all ideal gases, regardless of their composition or properties.
- The Ideal Gas Constant is used in a wide range of applications, including chemistry, physics, engineering, and materials science.
- The Ideal Gas Constant is a crucial component in the ideal gas law, which describes the behavior of ideal gases.
History and Development of the Ideal Gas Constant

The concept of the Ideal Gas Constant has its roots in the work of scientists such as Robert Boyle, Jacques Charles, and Gay-Lussac, who studied the properties of gases in the 17th and 18th centuries. The ideal gas law, which includes the Ideal Gas Constant, was first formulated by Émile Clapeyron in the early 19th century. Over time, the value of the Ideal Gas Constant has been refined through experiments and measurements, and it is now recognized as a fundamental constant in physics and chemistry.
Measurements and Definitions
The Ideal Gas Constant can be measured in several ways, including through the use of gas thermometers, which measure the temperature of a gas based on its pressure and volume. The value of the Ideal Gas Constant can also be calculated using theoretical models, such as the kinetic theory of gases. There are several definitions of the Ideal Gas Constant, including the molar gas constant, which is defined as the constant of proportionality between the pressure and temperature of a gas, and the specific gas constant, which is defined as the constant of proportionality between the pressure and temperature of a gas per unit mass.
| Constant | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molar Gas Constant | 8.3145 | J/(mol·K) |
| Specific Gas Constant | 287.058 | J/(kg·K) |
Applications and Implications

The Ideal Gas Constant has a wide range of applications in chemistry, physics, engineering, and materials science. It is used to calculate the energy of a gas, predict the behavior of gases under different conditions, and design and optimize systems that involve gases. The Ideal Gas Constant is also used in the study of thermodynamics, which is the study of the relationships between heat, work, and energy.
Real-World Examples
The Ideal Gas Constant is used in many real-world applications, including the design of power plants, refrigeration systems, and chemical synthesis processes. For example, the Ideal Gas Constant is used to calculate the energy required to compress a gas, which is essential for the design of efficient and safe compression systems. The Ideal Gas Constant is also used in the study of atmospheric science, where it is used to model the behavior of gases in the atmosphere and predict climate patterns.
In conclusion, the Ideal Gas Constant is a fundamental constant in physics and chemistry that relates the energy of a gas to its temperature. It is a crucial component in the ideal gas law, which describes the behavior of ideal gases. The Ideal Gas Constant has a wide range of applications in chemistry, physics, engineering, and materials science, and it is used to calculate the energy of a gas, predict the behavior of gases under different conditions, and design and optimize systems that involve gases.
What is the Ideal Gas Constant?
+The Ideal Gas Constant is a fundamental constant in physics and chemistry that relates the energy of a gas to its temperature. It is a proportionality constant that allows us to calculate the energy of a gas based on its temperature and other properties.
What is the value of the Ideal Gas Constant?
+The value of the Ideal Gas Constant is approximately 8.3145 J/(mol·K), although it can vary slightly depending on the specific definition and measurement method used.
What are the applications of the Ideal Gas Constant?
+The Ideal Gas Constant has a wide range of applications in chemistry, physics, engineering, and materials science. It is used to calculate the energy of a gas, predict the behavior of gases under different conditions, and design and optimize systems that involve gases.