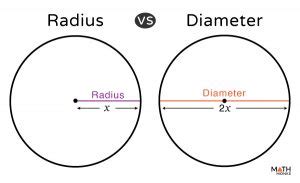
When discussing the concept of radius, it's essential to understand its foundational role in geometry and various mathematical applications. The radius, which is the distance from the center of a circle or sphere to its edge, plays a crucial role in determining the area, circumference, and volume of these geometric shapes. In this article, we will delve into five key tips related to the radius, exploring its significance, applications, and how to work with it in different mathematical contexts.
Key Points
- Understanding the definition and role of the radius in geometry
- Calculating the area and circumference of a circle using the radius
- Applying the radius in real-world problems, such as architecture and engineering
- Using the radius to calculate the volume of a sphere
- Integrating the concept of radius into more complex geometric calculations
Understanding the Radius and Its Applications
The radius of a circle or sphere is a fundamental concept in geometry. It is defined as the distance from the center of the circle or sphere to any point on its circumference or surface. This distance is crucial for calculating various properties of the circle or sphere, including its area, circumference, and volume. For instance, the formula for the area of a circle, A = πr^2, where A is the area and r is the radius, demonstrates how the radius is used to determine the size of a circle.
Calculating the Area and Circumference of a Circle
To calculate the area and circumference of a circle, one must know the radius. The formulas for these calculations are A = πr^2 for the area and C = 2πr for the circumference, where C is the circumference. These formulas highlight the importance of the radius in basic geometric calculations. For example, if the radius of a circle is 5 cm, its area would be A = π(5)^2 = 25π cm^2, and its circumference would be C = 2π(5) = 10π cm.
| Geometric Property | Formula | Example (with r = 5 cm) |
|---|---|---|
| Area | A = πr^2 | 25π cm^2 |
| Circumference | C = 2πr | 10π cm |
Applying the Radius in Real-World Problems

The concept of radius extends beyond theoretical mathematics, with practical applications in fields such as architecture, engineering, and design. For instance, architects use the radius to design circular structures, ensuring stability and aesthetic appeal. Engineers apply the radius in the construction of tunnels, pipelines, and other infrastructural projects, where precise calculations are critical for safety and functionality.
Calculating the Volume of a Sphere
The radius is also essential for calculating the volume of a sphere, which is given by the formula V = (4⁄3)πr^3, where V is the volume. This formula demonstrates how the radius influences the volume of a three-dimensional object. For example, if the radius of a sphere is 3 cm, its volume would be V = (4⁄3)π(3)^3 = 36π cm^3.
In conclusion, the radius is a foundational concept in geometry with far-reaching implications in various fields. Understanding its definition, applications, and how to work with it in different mathematical contexts is essential for solving problems and making informed decisions in real-world scenarios.
What is the formula for the area of a circle using the radius?
+The formula for the area of a circle is A = πr^2, where A is the area and r is the radius.
How do architects apply the concept of radius in their designs?
+Architects use the radius to design circular structures, ensuring stability and aesthetic appeal. They apply the radius in calculating the area, circumference, and other properties of circular elements in their designs.
What is the formula for the volume of a sphere using the radius?
+The formula for the volume of a sphere is V = (4⁄3)πr^3, where V is the volume and r is the radius.