The rain shadow effect is a fascinating phenomenon that has captivated the imagination of meteorologists, geologists, and environmental scientists for centuries. This complex process occurs when a mountain range or a high terrain feature blocks the path of prevailing winds, resulting in a significant reduction in precipitation on the leeward side. The rain shadow effect has far-reaching implications for the climate, ecosystem, and human activities in the affected regions. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the rain shadow effect, exploring its causes, consequences, and real-world examples.
Key Points
- The rain shadow effect is caused by the blocking of prevailing winds by a mountain range or high terrain feature.
- The resulting reduction in precipitation on the leeward side can lead to the formation of deserts, dry lakes, and unique ecosystems.
- The rain shadow effect has significant implications for climate, agriculture, and human settlement patterns.
- Understanding the rain shadow effect is crucial for predicting weather patterns, managing water resources, and mitigating the effects of climate change.
- Examples of the rain shadow effect can be observed in various regions around the world, including the Atacama Desert, the Great Basin, and the Himalayan Mountains.
Causes of the Rain Shadow Effect

The rain shadow effect is primarily caused by the interaction between prevailing winds and mountain ranges. When prevailing winds, which are winds that blow from a consistent direction over a particular region, encounter a mountain range, they are forced to rise, cool, and condense, resulting in the formation of clouds and precipitation. As the winds continue to move over the mountain range, they eventually descend on the leeward side, where the air is drier and warmer. This descent of dry air leads to a significant reduction in precipitation, resulting in a rain shadow effect.
Factors Influencing the Rain Shadow Effect
Several factors can influence the intensity and extent of the rain shadow effect. These include the height and orientation of the mountain range, the strength and direction of the prevailing winds, and the presence of other terrain features such as valleys and plateaus. For example, a mountain range that is perpendicular to the prevailing winds will have a more pronounced rain shadow effect than one that is parallel. Additionally, the presence of a valley or plateau on the leeward side can further enhance the rain shadow effect by trapping the dry air and preventing it from rising and cooling.
| Mountain Range | Rain Shadow Effect |
|---|---|
| Atacama Mountains | Atacama Desert, one of the driest places on Earth |
| Great Basin Mountains | Great Basin Desert, a cold desert region in North America |
| Himalayan Mountains | Tibetan Plateau, a high-altitude desert region in Asia |

Consequences of the Rain Shadow Effect
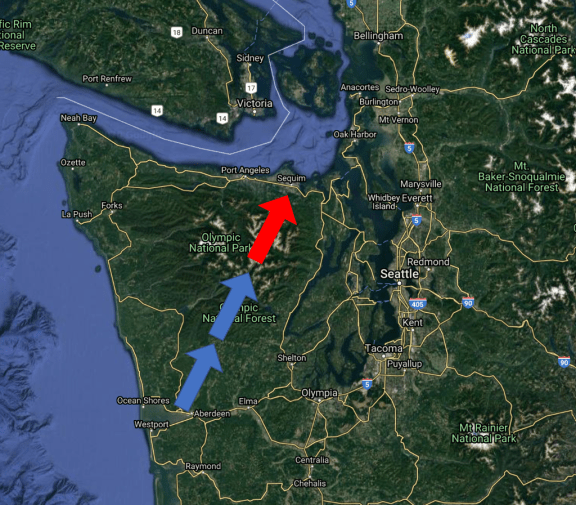
The rain shadow effect has far-reaching consequences for the climate, ecosystem, and human activities in the affected regions. The reduction in precipitation on the leeward side can lead to the formation of deserts, dry lakes, and unique ecosystems that are adapted to the arid conditions. For example, the Atacama Desert in Chile is one of the driest places on Earth, with some areas receiving as little as 0.01 inches of rainfall per year. The rain shadow effect also has significant implications for agriculture, as the reduced precipitation can limit crop growth and make irrigation essential.
Real-World Examples of the Rain Shadow Effect
Examples of the rain shadow effect can be observed in various regions around the world. The Great Basin Desert in North America, the Tibetan Plateau in Asia, and the Australian Outback are all regions that experience a significant rain shadow effect. The Himalayan Mountains, for example, create a rain shadow effect that results in the formation of the Tibetan Plateau, a high-altitude desert region that is home to several unique and adapted ecosystems.
In conclusion, the rain shadow effect is a complex and fascinating phenomenon that has significant implications for the climate, ecosystem, and human activities in the affected regions. By understanding the causes and consequences of the rain shadow effect, scientists can better predict precipitation patterns, manage water resources, and mitigate the effects of climate change.
What is the primary cause of the rain shadow effect?
+The primary cause of the rain shadow effect is the blocking of prevailing winds by a mountain range or high terrain feature.
What are the consequences of the rain shadow effect?
+The consequences of the rain shadow effect include the formation of deserts, dry lakes, and unique ecosystems, as well as significant implications for climate, agriculture, and human settlement patterns.
Can the rain shadow effect be observed in different regions around the world?
+Yes, the rain shadow effect can be observed in various regions around the world, including the Atacama Desert, the Great Basin, and the Himalayan Mountains.
Meta Description: The rain shadow effect is a complex phenomenon caused by the blocking of prevailing winds by a mountain range or high terrain feature, resulting in a significant reduction in precipitation on the leeward side. (150 characters)