The rainforest, often referred to as the lungs of the Earth, is a complex and vibrant ecosystem that supports a vast array of plant and animal life. One of the most fascinating aspects of the rainforest is its food chain, which is comprised of a delicate balance of predators and prey. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the rainforest food chain, exploring the various levels of the chain and the interconnected relationships between the different species that inhabit this unique ecosystem.
Key Points
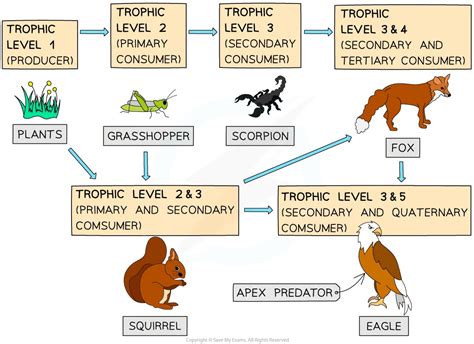
- The rainforest food chain is comprised of primary producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, and tertiary consumers.
- Primary producers, such as plants and algae, form the base of the food chain and provide energy for the entire ecosystem.
- Herbivores, such as insects and mammals, feed on primary producers and are an essential link in the food chain.
- Carnivores, such as birds and reptiles, feed on herbivores and other carnivores, playing a crucial role in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem.
- Decomposers, such as fungi and bacteria, break down dead organic matter and recycle nutrients, completing the cycle of the food chain.
Primary Producers: The Foundation of the Rainforest Food Chain

Primary producers, such as plants and algae, are the foundation of the rainforest food chain. These organisms are capable of producing their own food through photosynthesis, using energy from the sun to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. The primary producers in the rainforest include towering trees, such as the kapok and the ceiba, as well as a vast array of smaller plants, including ferns, flowers, and grasses. These plants provide the energy and nutrients that support the entire food chain, and are the starting point for the complex web of relationships that exist within the rainforest ecosystem.
Primary Consumers: Herbivores in the Rainforest
Primary consumers, such as insects and mammals, feed on primary producers and are an essential link in the food chain. These herbivores play a crucial role in regulating the growth and distribution of plant species, and help to maintain the balance of the ecosystem. Some examples of primary consumers in the rainforest include insects, such as butterflies and beetles, as well as mammals, such as sloths and monkeys. These animals feed on the leaves, fruits, and flowers of the primary producers, and in turn provide energy and nutrients for the next level of the food chain.
| Trophic Level | Example Species |
|---|---|
| Primary Producer | Kapok Tree, Ceiba Tree |
| Primary Consumer | Butterfly, Sloth, Monkey |
| Secondary Consumer | Bird, Reptile, Small Mammal |
| Tertiary Consumer | Large Mammal, Top Predator |
Secondary Consumers: Carnivores in the Rainforest
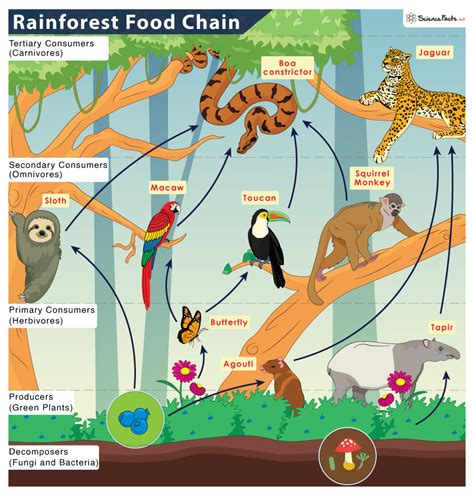
Secondary consumers, such as birds and reptiles, feed on primary consumers and are a crucial link in the food chain. These carnivores play a vital role in regulating the populations of herbivores, and help to maintain the balance of the ecosystem. Some examples of secondary consumers in the rainforest include birds, such as eagles and hawks, as well as reptiles, such as snakes and lizards. These animals feed on the primary consumers, and in turn provide energy and nutrients for the next level of the food chain.
Tertiary Consumers: Top Predators in the Rainforest
Tertiary consumers, such as large mammals and top predators, feed on secondary consumers and are the apex of the food chain. These animals play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem, and are often referred to as keystone species. Some examples of tertiary consumers in the rainforest include large mammals, such as jaguars and pumas, as well as top predators, such as anacondas and boa constrictors. These animals feed on the secondary consumers, and help to regulate the populations of the lower trophic levels.
What is the role of decomposers in the rainforest food chain?
+Decomposers, such as fungi and bacteria, play a crucial role in the rainforest food chain by breaking down dead organic matter and recycling nutrients. This process helps to maintain the balance of the ecosystem and ensures that nutrients are available for the primary producers.
How do human activities impact the rainforest food chain?
+Human activities, such as deforestation and habitat fragmentation, can have a significant impact on the rainforest food chain. These activities can lead to the loss of biodiversity, disrupt the balance of the ecosystem, and threaten the long-term sustainability of the rainforest.
What can be done to conserve the rainforest food chain?
+Conservation efforts, such as protected areas and sustainable forest management, can help to conserve the rainforest food chain. Additionally, reducing human impact through activities such as reforestation and habitat restoration can help to maintain the balance of the ecosystem and ensure the long-term sustainability of the rainforest.
In conclusion, the rainforest food chain is a complex and dynamic system that is essential for maintaining the balance of the ecosystem. Understanding the relationships between the different trophic levels and the role of each species in the food chain is crucial for appreciating the beauty and importance of this unique ecosystem. By recognizing the interconnectedness of the rainforest food chain and taking steps to conserve and protect it, we can help to ensure the long-term sustainability of this vital ecosystem.