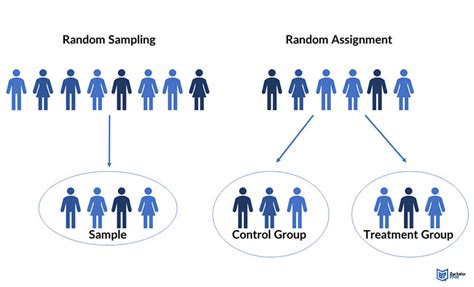
Random assignment is a fundamental concept in psychology research, ensuring that participants are allocated to different conditions or groups in a study by chance, rather than by any systematic or intentional method. This technique is crucial for establishing cause-and-effect relationships between variables and for reducing biases in research findings. In the context of psychology, random assignment helps to minimize confounding variables, which are factors other than the independent variable that could influence the outcome of the study. By randomly assigning participants to different conditions, researchers can increase the internal validity of their study, which refers to the extent to which the study measures what it is supposed to measure.
One of the primary reasons random assignment is essential in psychology research is that it helps to distribute participant characteristics, such as age, gender, and personality traits, evenly across different conditions. This distribution ensures that any differences found between groups can be attributed to the independent variable, rather than to pre-existing differences between the groups. For instance, in a study examining the effect of cognitive-behavioral therapy on anxiety, random assignment would ensure that participants with similar levels of anxiety are distributed evenly across the therapy and control groups. This even distribution allows researchers to isolate the effect of the therapy on anxiety, rather than being confounded by pre-existing differences in anxiety levels between the groups.
Key Points
- Random assignment ensures that participants are allocated to different conditions by chance, reducing biases in research findings.
- This technique helps to minimize confounding variables and increases the internal validity of a study.
- Random assignment distributes participant characteristics evenly across different conditions, allowing researchers to isolate the effect of the independent variable.
- In psychology research, random assignment is crucial for establishing cause-and-effect relationships between variables.
- By using random assignment, researchers can increase the generalizability of their findings to the larger population.
Types of Random Assignment
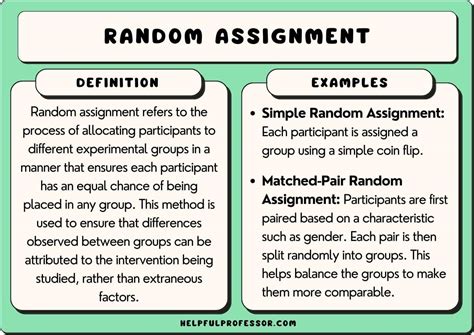
There are several types of random assignment used in psychology research, each with its own strengths and limitations. Simple random assignment involves allocating participants to different conditions using a random method, such as flipping a coin or using a random number generator. Stratified random assignment involves dividing participants into subgroups based on certain characteristics, such as age or gender, and then randomly assigning participants within each subgroup to different conditions. Cluster random assignment involves randomly assigning groups of participants, rather than individual participants, to different conditions. This type of random assignment is often used in studies where it is not possible or practical to assign individual participants to different conditions, such as in studies examining the effect of a new teaching method on student outcomes.
Benefits of Random Assignment
The benefits of random assignment in psychology research are numerous. By reducing biases and confounding variables, random assignment increases the internal validity of a study, allowing researchers to draw more accurate conclusions about the relationships between variables. Random assignment also increases the generalizability of findings to the larger population, as the sample is more likely to be representative of the population. Additionally, random assignment helps to reduce the risk of researcher bias, as participants are allocated to different conditions by chance, rather than by the researcher’s intentional assignment. For example, in a study examining the effect of a new medication on symptoms of depression, random assignment would ensure that participants are allocated to the treatment or control group by chance, rather than by the researcher’s expectation of how the participant will respond to the medication.
| Type of Random Assignment | Description |
|---|---|
| Simple Random Assignment | Allocating participants to different conditions using a random method. |
| Stratified Random Assignment | Dividing participants into subgroups based on certain characteristics and then randomly assigning participants within each subgroup to different conditions. |
| Cluster Random Assignment | Randomly assigning groups of participants to different conditions. |
Limitations of Random Assignment
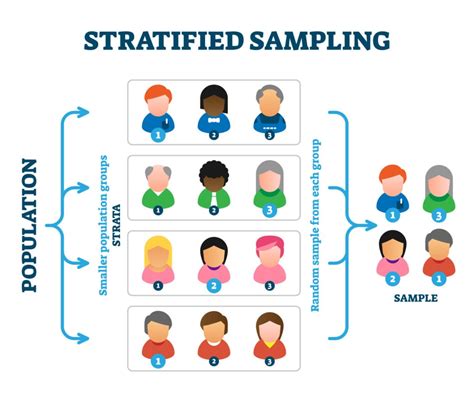
While random assignment is a powerful technique for reducing biases and increasing the internal validity of a study, it is not without its limitations. One of the primary limitations of random assignment is that it may not always be possible or practical to implement. For example, in studies examining the effect of a new policy on a population, it may not be possible to randomly assign participants to different conditions. Additionally, random assignment may not always be successful in distributing participant characteristics evenly across different conditions, particularly in studies with small sample sizes. Furthermore, random assignment may not account for unknown or unmeasured confounding variables, which can still influence the outcome of the study.
Real-World Applications of Random Assignment
Random assignment has numerous real-world applications in psychology research. For instance, in clinical trials, random assignment is used to evaluate the effectiveness of new medications or therapies. In educational research, random assignment is used to evaluate the effectiveness of different teaching methods or programs. In social psychology research, random assignment is used to examine the effect of different social influences on behavior. By using random assignment, researchers can increase the accuracy of their findings and provide more effective interventions and treatments for various psychological disorders.
What is the purpose of random assignment in psychology research?
+The purpose of random assignment is to reduce biases and confounding variables, increasing the internal validity of a study and allowing researchers to draw more accurate conclusions about the relationships between variables.
What are the benefits of random assignment in psychology research?
+The benefits of random assignment include increasing the internal validity of a study, reducing biases and confounding variables, and increasing the generalizability of findings to the larger population.
What are the limitations of random assignment in psychology research?
+The limitations of random assignment include the possibility that it may not always be possible or practical to implement, and that it may not always be successful in distributing participant characteristics evenly across different conditions.