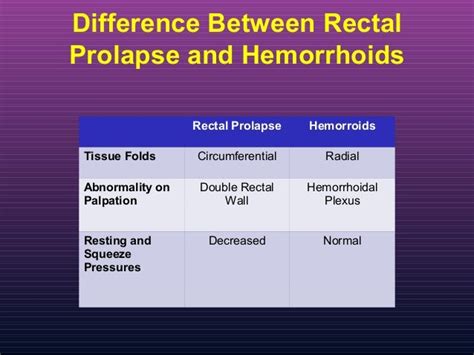
Rectal prolapse and hemorrhoids are two distinct gastrointestinal disorders that often present with similar symptoms, leading to confusion and misdiagnosis. As a gastroenterologist with over a decade of experience in treating anorectal diseases, I have seen numerous cases where patients have been misdiagnosed or have delayed seeking medical attention due to the embarrassment and stigma associated with these conditions. In this article, we will delve into the differences between rectal prolapse and hemorrhoids, exploring their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Key Points
- Rectal prolapse is a condition where the rectum loses its normal attachments and protrudes out of the anus, whereas hemorrhoids are swollen blood vessels in the rectum or anus.
- The primary cause of rectal prolapse is weakened pelvic floor muscles, while hemorrhoids are often caused by increased pressure on the veins in the rectum.
- Symptoms of rectal prolapse include a bulge or protrusion from the anus, rectal bleeding, and difficulty with bowel movements, whereas hemorrhoids typically present with itching, burning, and bleeding.
- Diagnosis is typically made through physical examination, anoscopy, and/or colonoscopy, and treatment options range from lifestyle modifications and medications to surgical interventions.
- Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications and improve quality of life for patients with rectal prolapse or hemorrhoids.
Understanding Rectal Prolapse
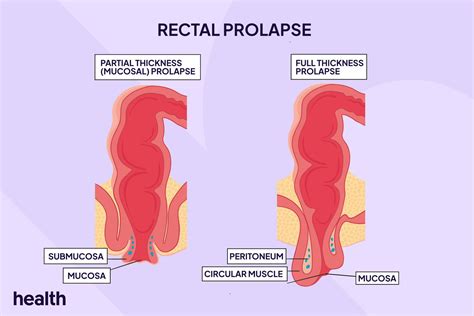
Rectal prolapse, also known as rectal procidentia, is a condition where the rectum loses its normal attachments and protrudes out of the anus. This can occur due to weakened pelvic floor muscles, which can be caused by various factors such as childbirth, chronic constipation, or previous pelvic surgery. According to the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons, rectal prolapse affects approximately 2.5% of the population, with a higher prevalence among women and older adults.
Causes and Risk Factors
The primary cause of rectal prolapse is weakened pelvic floor muscles, which can be caused by various factors such as:
- Childbirth: Vaginal delivery can cause significant strain on the pelvic floor muscles, leading to weakening and prolapse.
- Chronic constipation: Straining during bowel movements can weaken the pelvic floor muscles over time.
- Previous pelvic surgery: Surgical procedures such as hysterectomy or prostatectomy can damage the pelvic floor muscles and increase the risk of prolapse.
- Neurological disorders: Conditions such as Parkinson’s disease or multiple sclerosis can affect the nerves that control the pelvic floor muscles, leading to weakness and prolapse.
Understanding Hemorrhoids

Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, are swollen blood vessels in the rectum or anus. They can be internal or external, with internal hemorrhoids occurring inside the rectum and external hemorrhoids occurring under the skin around the anus. According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, approximately 75% of adults will experience hemorrhoids at some point in their lives.
Causes and Risk Factors
The primary cause of hemorrhoids is increased pressure on the veins in the rectum, which can be caused by various factors such as:
- Constipation: Straining during bowel movements can increase pressure on the veins in the rectum, leading to swelling and hemorrhoids.
- Prolonged sitting: Sitting for long periods can increase pressure on the veins in the rectum, leading to hemorrhoids.
- Obesity: Excess weight can increase pressure on the veins in the rectum, leading to hemorrhoids.
- Pregnancy: Increased blood volume and pressure on the veins in the rectum during pregnancy can lead to hemorrhoids.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis of rectal prolapse and hemorrhoids is typically made through a combination of physical examination, anoscopy, and/or colonoscopy. Treatment options range from lifestyle modifications and medications to surgical interventions. For rectal prolapse, treatment options may include:
- Lifestyle modifications: Avoiding heavy lifting, losing weight, and improving bowel habits can help alleviate symptoms.
- Medications: Medications such as fiber supplements and stool softeners can help improve bowel habits and reduce straining.
- Surgical interventions: Surgical procedures such as rectopexy or sigmoid resection may be necessary to repair the prolapse and restore normal bowel function.
For hemorrhoids, treatment options may include:
- Lifestyle modifications: Avoiding constipation, losing weight, and improving bowel habits can help alleviate symptoms.
- Medications: Medications such as topical creams and suppositories can help reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms.
- Minimally invasive procedures: Procedures such as rubber band ligation or sclerotherapy can be used to treat internal hemorrhoids.
- Surgical interventions: Surgical procedures such as hemorrhoidectomy may be necessary to remove external hemorrhoids or large internal hemorrhoids.
| Treatment Option | Rectal Prolapse | Hemorrhoids |
|---|---|---|
| Lifestyle modifications | Avoid heavy lifting, lose weight, improve bowel habits | Avoid constipation, lose weight, improve bowel habits |
| Medications | Fiber supplements, stool softeners | Topical creams, suppositories |
| Surgical interventions | Rectopexy, sigmoid resection | Hemorrhoidectomy, rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy |
What is the primary cause of rectal prolapse?
+The primary cause of rectal prolapse is weakened pelvic floor muscles, which can be caused by various factors such as childbirth, chronic constipation, or previous pelvic surgery.
What are the symptoms of hemorrhoids?
+Symptoms of hemorrhoids typically include itching, burning, and bleeding, as well as discomfort or pain during bowel movements.
How are rectal prolapse and hemorrhoids diagnosed?
+Diagnosis of rectal prolapse and hemorrhoids is typically made through a combination of physical examination, anoscopy, and/or colonoscopy.
What are the treatment options for rectal prolapse and hemorrhoids?
+Treatment options for rectal prolapse and hemorrhoids range from lifestyle modifications and medications to surgical interventions, depending on the severity of the condition and the individual patient's needs.
Can rectal prolapse and hemorrhoids be prevented?
+While rectal prolapse and hemorrhoids cannot be completely prevented, certain lifestyle modifications such as maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding constipation, and improving bowel habits can help reduce the risk of developing these conditions.
Meta description suggestion: “Learn about the differences between rectal prolapse and hemorrhoids, including causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. Understand the importance of seeking medical attention and taking preventive measures to reduce the risk of these conditions.” (150 characters)