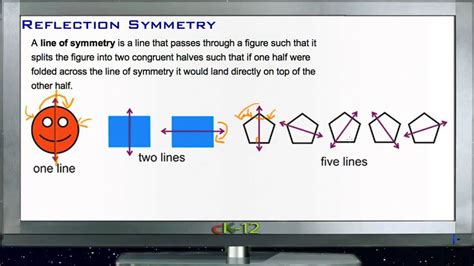
Reflection in mathematics is a fundamental concept that involves the transformation of a figure or a point across a line of reflection, resulting in a mirror image. This concept is crucial in various branches of mathematics, including geometry, algebra, and trigonometry. The line of reflection acts as a mirror, and the original figure is transformed into its image, with each point on the original figure having a corresponding point on the reflected image. Reflections can be performed across different types of lines, including horizontal, vertical, and diagonal lines, and can also be applied to three-dimensional objects.
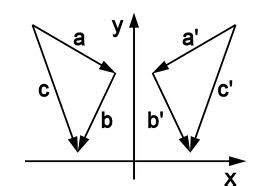
The definition of reflection in mathematics is often formalized using the concept of distance and midpoint. Specifically, given a point P and a line of reflection L, the reflection of P across L is the point P' such that L is the perpendicular bisector of the line segment PP'. This means that the distance from P to L is equal to the distance from P' to L, and the midpoint of the line segment PP' lies on L. This definition provides a precise and rigorous framework for understanding and working with reflections in mathematics.
Key Points
- Reflection in mathematics involves the transformation of a figure or point across a line of reflection, resulting in a mirror image.
- The line of reflection acts as a mirror, and the original figure is transformed into its image, with each point on the original figure having a corresponding point on the reflected image.
- Reflections can be performed across different types of lines, including horizontal, vertical, and diagonal lines, and can also be applied to three-dimensional objects.
- The definition of reflection in mathematics is often formalized using the concept of distance and midpoint.
- Reflections have numerous applications in mathematics, including geometry, algebra, and trigonometry, as well as in physics, engineering, and computer science.
Types of Reflections

There are several types of reflections in mathematics, including line reflections, point reflections, and glide reflections. A line reflection involves reflecting a figure across a line, while a point reflection involves reflecting a figure across a point. A glide reflection involves reflecting a figure across a line and then translating it by a certain distance. Each type of reflection has its own unique properties and applications, and understanding these different types of reflections is essential for working with reflections in mathematics.
Line Reflections
A line reflection is a type of reflection that involves reflecting a figure across a line. This type of reflection is often used in geometry and trigonometry to solve problems involving symmetry and congruence. For example, if a triangle is reflected across a line, the resulting triangle will be congruent to the original triangle, with the same size and shape. Line reflections can be performed across different types of lines, including horizontal, vertical, and diagonal lines.
| Type of Reflection | Description |
|---|---|
| Line Reflection | Reflecting a figure across a line |
| Point Reflection | Reflecting a figure across a point |
| Glide Reflection | Reflecting a figure across a line and then translating it by a certain distance |
Applications of Reflections
Reflections have numerous applications in mathematics, including geometry, algebra, and trigonometry, as well as in physics, engineering, and computer science. In geometry, reflections are used to solve problems involving symmetry and congruence, while in algebra, reflections are used to solve equations and graph functions. In physics, reflections are used to model the behavior of light and sound waves, while in engineering, reflections are used to design and optimize systems. In computer science, reflections are used in computer graphics and game development to create realistic and engaging visual effects.
The application of reflections in mathematics and science is diverse and widespread, and reflections play a critical role in many different fields. By understanding the properties and applications of reflections, mathematicians and scientists can use reflections to solve problems, model real-world phenomena, and create innovative solutions.
Reflections in Geometry
In geometry, reflections are used to solve problems involving symmetry and congruence. For example, if a triangle is reflected across a line, the resulting triangle will be congruent to the original triangle, with the same size and shape. Geometers use reflections to solve problems involving symmetry, including finding the symmetries of a figure and determining whether two figures are congruent.
What is the definition of reflection in mathematics?
+Reflection in mathematics is a fundamental concept that involves the transformation of a figure or a point across a line of reflection, resulting in a mirror image.
What are the different types of reflections in mathematics?
+There are several types of reflections in mathematics, including line reflections, point reflections, and glide reflections.
What are some applications of reflections in mathematics and science?
+Reflections have numerous applications in mathematics, including geometry, algebra, and trigonometry, as well as in physics, engineering, and computer science.
In conclusion, reflections are a fundamental concept in mathematics, with numerous applications in geometry, algebra, and trigonometry, as well as in physics, engineering, and computer science. By understanding the properties and applications of reflections, mathematicians and scientists can use reflections to solve problems, model real-world phenomena, and create innovative solutions. Whether in the context of geometry, algebra, or physics, reflections play a critical role in many different fields, and their study and application continue to be an active area of research and development.



