Regression to the mean is a fundamental concept in statistics and probability theory that describes the tendency of extreme values to return to a more average or normal value over time. This phenomenon is observed in a wide range of fields, including finance, sports, medicine, and social sciences. At its core, regression to the mean is a statistical principle that helps explain why exceptional events or outcomes are often followed by more typical ones. In this article, we will delve into the concept of regression to the mean, its underlying causes, and its applications in various domains.
Key Points
- Regression to the mean is a statistical principle that describes the tendency of extreme values to return to a more average value over time.
- The concept is often observed in fields such as finance, sports, medicine, and social sciences.
- Regression to the mean is caused by chance and the influence of multiple factors on outcomes.
- Understanding regression to the mean is essential for making informed decisions and avoiding misconceptions.
- The concept has significant implications for fields such as finance, where it can help investors make more informed decisions.
Understanding Regression to the Mean

To understand regression to the mean, consider a simple example. Imagine a basketball player who scores an unusually high number of points in a single game. While it’s possible that the player has suddenly improved their skills, it’s more likely that the high score is due to a combination of factors, such as luck, favorable matchups, and temporary hot streaks. In subsequent games, the player’s performance is likely to return to their average level, as the unusual factors that contributed to the high score are unlikely to be repeated. This is an example of regression to the mean, where an extreme value (the high score) returns to a more average value (the player’s typical performance) over time.
Causes of Regression to the Mean
Regression to the mean is caused by the influence of multiple factors on outcomes, as well as the role of chance. When an extreme value occurs, it’s often the result of a combination of factors, some of which may be temporary or unusual. As these factors change or return to their normal state, the outcome is likely to revert to its average value. For instance, in finance, a stock’s price may fluctuate due to a variety of factors, including economic conditions, industry trends, and investor sentiment. When the stock’s price reaches an extreme value, it’s likely to return to its average value as the influencing factors change or stabilize.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Chance | The random and unpredictable nature of events |
| Multiple Influencing Factors | The combination of various factors that contribute to an outcome |
| Temporary Conditions | Unusual or short-term factors that influence an outcome |
Applications of Regression to the Mean
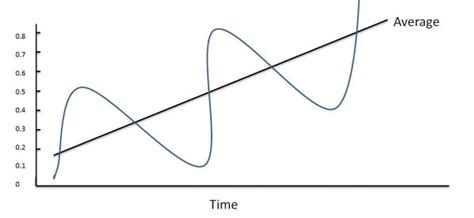
Regression to the mean has significant implications for various fields, including finance, sports, and medicine. In finance, understanding regression to the mean can help investors make more informed decisions by recognizing that extreme stock prices or returns are likely to revert to their average values over time. In sports, coaches and analysts can use regression to the mean to evaluate player performance and make more accurate predictions about future outcomes. In medicine, regression to the mean can help researchers and clinicians understand the natural progression of diseases and the effectiveness of treatments.
Implications for Decision-Making
Regression to the mean has important implications for decision-making in various contexts. By recognizing the tendency of extreme values to return to their average values, individuals can avoid making decisions based on misconceptions or temporary conditions. For instance, an investor who observes a stock’s price soaring may be tempted to buy, assuming that the stock will continue to rise. However, if the investor understands regression to the mean, they may recognize that the stock’s price is likely to return to its average value, making it a less attractive investment opportunity.
What is regression to the mean, and how does it occur?
+Regression to the mean is a statistical principle that describes the tendency of extreme values to return to a more average value over time. It occurs due to the influence of multiple factors on outcomes, as well as the role of chance.
How can regression to the mean be applied in finance?
+Understanding regression to the mean can help investors make more informed decisions by recognizing that extreme stock prices or returns are likely to revert to their average values over time.
What are the implications of regression to the mean for decision-making?
+Regression to the mean has important implications for decision-making, as it can help individuals avoid making decisions based on misconceptions or temporary conditions. By recognizing the tendency of extreme values to return to their average values, individuals can make more informed decisions.
In conclusion, regression to the mean is a fundamental concept in statistics and probability theory that describes the tendency of extreme values to return to a more average value over time. By understanding this concept, individuals can make more informed decisions, avoid misconceptions, and recognize the natural progression of events in various contexts. Whether in finance, sports, medicine, or other fields, regression to the mean is an essential principle that can help us better understand the world around us.