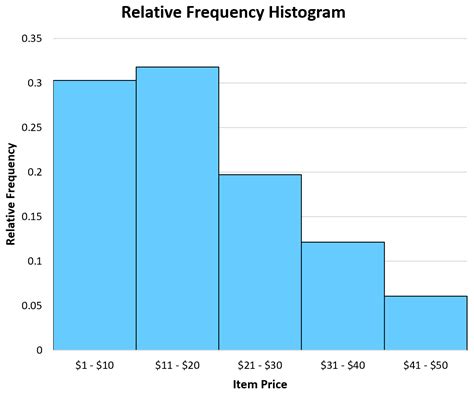
Relative frequency charts are a fundamental tool in data analysis, providing a clear and concise way to visualize the distribution of data points across different categories or intervals. By understanding how to create and interpret these charts, individuals can gain valuable insights into the characteristics of their data, making informed decisions based on empirical evidence. In this article, we will explore five ways relative frequency charts can be utilized, highlighting their versatility and importance in statistical analysis.
Introduction to Relative Frequency Charts
A relative frequency chart, often presented as a histogram or a bar chart, displays the proportion or percentage of data points that fall into each category or interval. This visualization technique is particularly useful for understanding the shape of the data distribution, identifying outliers, and comparing the frequency of different categories. For instance, in a study examining the grades of students in a class, a relative frequency chart could show the proportion of students who received each possible grade, providing a quick snapshot of academic performance.
Constructing a Relative Frequency Chart
To construct a relative frequency chart, one must first categorize the data into appropriate intervals or categories. The choice of interval width is crucial, as it affects the appearance and interpretability of the chart. Generally, the intervals should be mutually exclusive and exhaustive, ensuring that every data point falls into exactly one category. After categorizing the data, calculate the frequency of each category and then divide by the total number of data points to find the relative frequency. This process can be efficiently managed using spreadsheet software or statistical analysis programs.
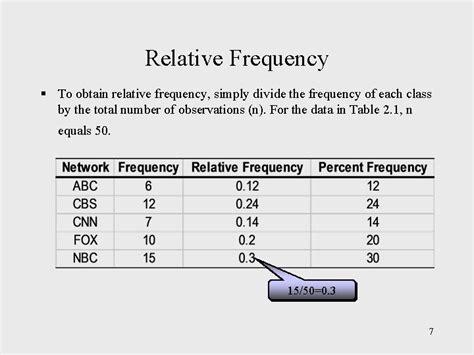
| Category | Frequency | Relative Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| A | 10 | 0.2 |
| B | 20 | 0.4 |
| C | 30 | 0.6 |
5 Ways to Utilize Relative Frequency Charts
Relative frequency charts offer a multitude of applications across various fields, from business and economics to healthcare and education. Here are five ways these charts can be utilized:
1. Data Distribution Analysis
One of the primary uses of relative frequency charts is to analyze the distribution of data. By visualizing the proportion of data points in each category, analysts can determine if the data follows a normal distribution or if it is skewed. This information is critical for selecting appropriate statistical tests and models for further analysis.
2. Identifying Trends and Patterns
Relative frequency charts are also invaluable for identifying trends and patterns within the data. For instance, in market research, these charts can help identify the most popular product categories or consumer preferences, guiding business strategies and marketing campaigns.
3. Quality Control and Assurance
In manufacturing and production, relative frequency charts play a key role in quality control and assurance. By monitoring the distribution of product characteristics, such as size, weight, or performance, manufacturers can quickly identify any deviations from the expected standards, allowing for prompt corrective actions.
4. Educational Assessment and Evaluation
In education, relative frequency charts can be used to evaluate student performance across different subjects or topics. Teachers and educators can use these charts to identify areas where students may need additional support, tailoring their teaching strategies to better meet the needs of their students.
5. Healthcare and Medical Research
Finally, in healthcare and medical research, relative frequency charts can be used to analyze the incidence of diseases, the effectiveness of treatments, or the distribution of health-related characteristics among different populations. This information is crucial for developing public health policies, designing clinical trials, and improving patient outcomes.
Key Points
- Relative frequency charts are a powerful tool for data analysis, offering insights into the distribution and characteristics of the data.
- These charts are versatile and can be applied across various fields, including business, education, healthcare, and quality control.
- Understanding how to construct and interpret relative frequency charts is essential for making informed decisions based on data analysis.
- The choice of interval width in constructing relative frequency charts can significantly affect the interpretability of the results.
- Relative frequency charts can help identify trends, patterns, and outliers in the data, guiding further analysis and decision-making processes.
In conclusion, relative frequency charts are a fundamental component of statistical analysis, providing a visual representation of how data points are distributed across different categories or intervals. By understanding the construction and interpretation of these charts, individuals can unlock the full potential of their data, making informed decisions that are grounded in empirical evidence. Whether in business, education, healthcare, or any other field, the ability to analyze and interpret relative frequency charts is a critical skill for anyone looking to derive meaningful insights from data.
What is the primary purpose of a relative frequency chart?
+The primary purpose of a relative frequency chart is to visualize the distribution of data points across different categories or intervals, helping to identify patterns, trends, and outliers.
How do you construct a relative frequency chart?
+To construct a relative frequency chart, categorize the data into appropriate intervals, calculate the frequency of each category, and then divide by the total number of data points to find the relative frequency.
What are some common applications of relative frequency charts?
+Relative frequency charts have applications in data distribution analysis, identifying trends and patterns, quality control, educational assessment, and healthcare research, among others.