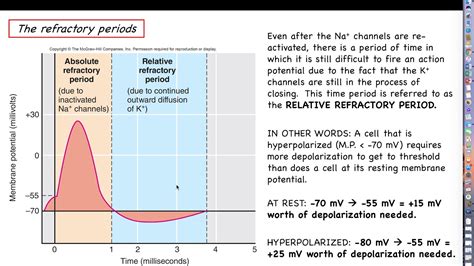
The refractory period, a critical component of the human sexual response cycle, has been a subject of interest for both researchers and the general public alike. This period, characterized by a temporary inability to achieve another orgasm after a previous one, varies significantly among individuals and is influenced by a multitude of factors. Understanding the refractory period is essential for sexual health and satisfaction, as it impacts the frequency and quality of sexual encounters. Here, we will delve into five key facts about the refractory period, exploring its definition, duration, influencing factors, and implications for sexual health.
Key Points
- The refractory period is a temporary phase after orgasm during which it's difficult to achieve another orgasm.
- The duration of the refractory period varies widely among individuals and can be influenced by age, sexual activity frequency, and overall health.
- Hormonal changes, particularly the release of oxytocin and prolactin, play a significant role in the onset and duration of the refractory period.
- There are strategies to potentially shorten the refractory period, including frequent sexual activity, a healthy lifestyle, and certain dietary supplements.
- Understanding and discussing the refractory period openly with partners can enhance sexual satisfaction and relationship intimacy.
Definition and Duration of the Refractory Period
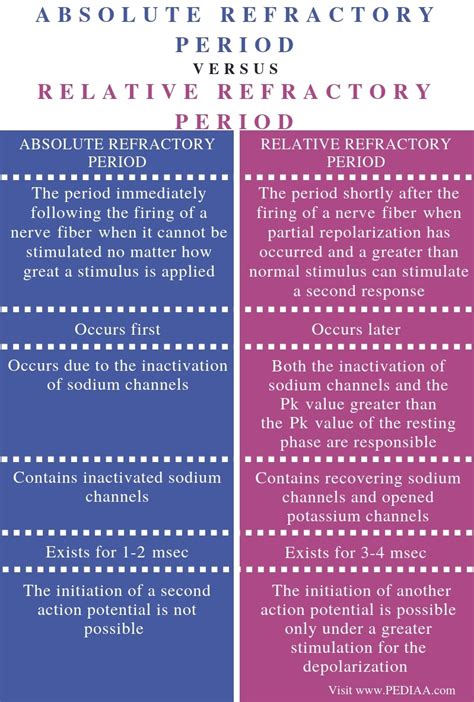
The refractory period is characterized by two phases: the absolute refractory period, during which orgasm is impossible, and the relative refractory period, where achieving orgasm is more difficult but not impossible. The duration of the refractory period can vary significantly, from a few minutes to several hours or even days, depending on the individual and their specific circumstances.
Influencing Factors of the Refractory Period
Several factors influence the length and intensity of the refractory period. Age is a significant factor, with younger individuals typically experiencing shorter refractory periods. The frequency of sexual activity also plays a role, as more frequent sexual engagement can lead to shorter refractory periods over time. Additionally, overall physical and mental health, including factors like stress levels and hormonal balance, can impact the refractory period.
| Factor | Influence on Refractory Period |
|---|---|
| Age | Generally, younger individuals have shorter refractory periods. |
| Sexual Activity Frequency | Frequent sexual activity can lead to shorter refractory periods. |
| Physical and Mental Health | Good health tends to result in shorter refractory periods; poor health can extend them. |
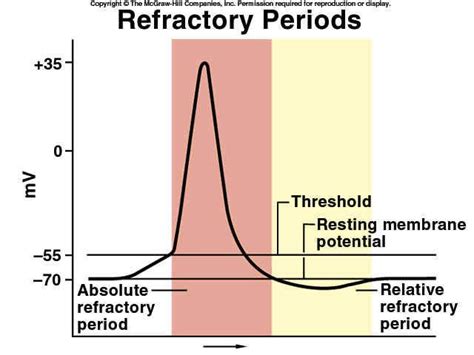
Strategies to Shorten the Refractory Period

While the refractory period is a natural part of the sexual response cycle, there are strategies that may help shorten its duration. Engaging in frequent sexual activity can help reduce the refractory period over time. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep, can also contribute to improved sexual health and potentially shorter refractory periods. Certain dietary supplements, such as those aimed at enhancing overall sexual health, may also offer benefits, though their effectiveness can vary and should be approached with caution.
Implications for Sexual Health and Relationships
Understanding the refractory period and its implications can significantly impact sexual satisfaction and relationship intimacy. Open communication with sexual partners about desires, needs, and the refractory period can help manage expectations and enhance the overall sexual experience. Recognizing the variability and normalcy of the refractory period can reduce anxiety and improve sexual health outcomes.
What is the average duration of the refractory period in men and women?
+The refractory period varies significantly among individuals. In men, it can range from a few minutes to several hours or even days, generally increasing with age. Women typically experience a shorter refractory period or may not experience one at all, allowing for the potential of multiple orgasms in a short time frame.
Can the refractory period be influenced by psychological factors?
+Yes, psychological factors such as stress, anxiety, and relationship issues can influence the refractory period. High levels of stress or anxiety can extend the refractory period, while a healthy and fulfilling relationship can potentially shorten it.
Are there any medical conditions that can affect the refractory period?
+Yes, certain medical conditions and medications can impact the refractory period. For example, hormonal imbalances, erectile dysfunction, and the use of certain antidepressants can affect sexual response and the duration of the refractory period.
In conclusion, the refractory period is a complex and multifaceted aspect of human sexuality, influenced by a wide range of factors including age, health, and psychological state. By understanding and discussing the refractory period openly, individuals can better navigate their sexual health, improve intimacy with their partners, and enhance their overall sexual satisfaction.