The removal of a chalazion, a small bump on the eyelid caused by a blocked oil gland, is a relatively common procedure that can be performed in various settings, ranging from a doctor's office to an outpatient surgical facility. A chalazion is different from a stye, which is usually smaller and more painful, and is typically found at the edge of the eyelid. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for chalazion is essential for individuals seeking to manage or remove these benign but sometimes bothersome growths.
Understanding Chalazion
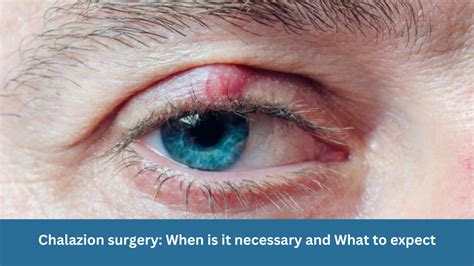
A chalazion occurs when the meibomian gland in the eyelid becomes clogged. The meibomian glands produce the oily layer of the tear film, which helps to lubricate and protect the eyes. If the gland becomes blocked, the oil can accumulate and cause inflammation, leading to a chalazion. These growths are usually painless but can cause discomfort due to their size and location. In some cases, a chalazion may resolve on its own with warm compresses and good eyelid hygiene. However, if it persists, grows larger, or becomes painful, medical intervention may be necessary.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing a chalazion. These include poor eyelid hygiene, blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelids), rosacea, and meibomian gland dysfunction. Individuals with a history of chalazia or styes may also be more prone to developing these growths. Understanding and addressing the underlying causes can help in managing and preventing future occurrences.
Key Points
- A chalazion is a benign growth caused by a blocked oil gland in the eyelid.
- It is different from a stye and is usually painless but can cause discomfort due to its size.
- Warm compresses and good eyelid hygiene may help resolve a chalazion, but medical intervention is sometimes necessary.
- Risk factors include poor eyelid hygiene, blepharitis, rosacea, and meibomian gland dysfunction.
- Preventive measures focus on maintaining good eyelid hygiene and addressing underlying conditions.
Treatment Options for Chalazion Removal
Treatment for a chalazion typically starts with conservative measures such as warm compresses applied several times a day to help the blockage clear on its own. If this approach fails, a doctor may prescribe antibiotics or steroid injections to reduce inflammation. In cases where the chalazion is large, persistent, or is causing significant discomfort, surgical removal may be recommended.
Surgical Removal Procedure
The surgical removal of a chalazion, known as incision and curettage, is a minor procedure usually performed under local anesthesia. The doctor makes a small incision on the inside of the eyelid to avoid a visible scar, and then removes the contents of the chalazion with a curette. The procedure is relatively quick, and patients can usually resume normal activities shortly after. It’s essential to follow post-operative instructions carefully to ensure proper healing and minimize the risk of complications.
| Treatment Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Warm Compresses | Applying warm compresses to the affected area to help clear the blockage. |
| Antibiotics or Steroid Injections | Prescribing antibiotics or steroid injections to reduce inflammation if the chalazion becomes infected or significantly inflamed. |
| Surgical Removal | Performing incision and curettage under local anesthesia to remove the chalazion. |
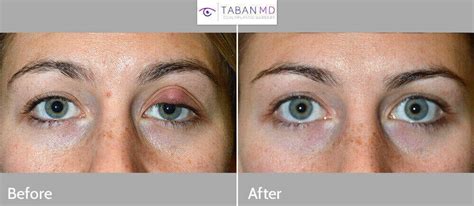
Post-Operative Care and Prevention
After the removal of a chalazion, it’s essential to follow the doctor’s instructions for post-operative care. This may include applying antibiotic ointment to the affected area, using warm compresses to promote healing, and avoiding rubbing or touching the eyes. Preventive measures such as maintaining good eyelid hygiene, avoiding excessive makeup use around the eyes, and managing underlying conditions like blepharitis or rosacea can help reduce the risk of future occurrences.
Long-Term Outcomes and Complications
While the removal of a chalazion is generally a safe procedure, there are potential risks and complications, including infection, scarring, and recurrence. Rarely, a chalazion can be a sign of an underlying condition that requires further investigation. Therefore, it’s crucial to work closely with a healthcare provider to address any concerns and ensure the best possible outcomes.
What is the difference between a chalazion and a stye?
+A chalazion is a small bump on the eyelid caused by a blocked oil gland and is usually painless, whereas a stye is an infection of the oil glands in the eyelid and is typically smaller and more painful.
How long does it take to recover from chalazion removal surgery?
+Recovery from chalazion removal surgery is generally quick, with most patients able to resume normal activities shortly after the procedure. However, it's essential to follow the doctor's instructions for post-operative care to ensure proper healing.
Can a chalazion be prevented?
+While not all cases can be prevented, maintaining good eyelid hygiene, avoiding excessive makeup use around the eyes, and managing underlying conditions like blepharitis or rosacea can help reduce the risk of developing a chalazion.
In conclusion, the removal of a chalazion is a procedure that can be effectively managed with the right approach. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking appropriate medical care when necessary are key to addressing these growths. By following post-operative care instructions and taking preventive measures, individuals can reduce the risk of future occurrences and maintain the health and comfort of their eyes.