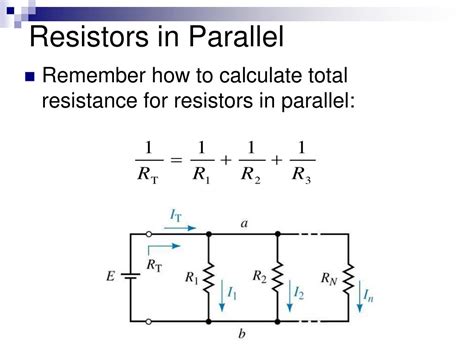
When dealing with resistors in parallel, many individuals may find themselves overwhelmed by the complexity of the calculations involved. However, understanding how to calculate the total resistance of resistors connected in parallel is a fundamental concept in electronics. In this article, we will delve into the world of resistors in parallel, exploring the underlying principles, formulas, and practical applications to make this concept easy to grasp.
To begin with, let's establish a solid foundation by defining what resistors in parallel mean. When two or more resistors are connected between the same two points, they are said to be in parallel. This configuration allows the current to flow through each resistor independently, which has a significant impact on the total resistance of the circuit. The total resistance (R_total) of resistors in parallel is always less than the resistance of any individual resistor in the circuit.
Key Points
- The total resistance of resistors in parallel is less than any individual resistor's resistance.
- The formula to calculate total resistance in a parallel circuit is 1/R_total = 1/R1 + 1/R2 +... + 1/Rn.
- Parallel circuits are useful for increasing the current capacity and reducing the total resistance of a circuit.
- Calculating the voltage across each resistor in a parallel circuit involves understanding that the voltage across each resistor is the same.
- Current through each resistor in a parallel circuit can be found using Ohm's Law, I = V/R, where V is the voltage across the resistor and R is the resistance of the resistor.
Understanding the Formula for Resistors in Parallel
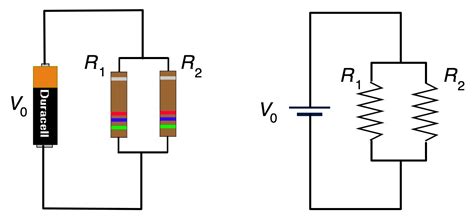
The formula for calculating the total resistance of resistors in parallel is given by 1/R_total = 1/R1 + 1/R2 +… + 1/Rn, where R1, R2,…, Rn are the resistances of the individual resistors. This formula is derived from the principle that the reciprocal of the total resistance is equal to the sum of the reciprocals of the individual resistances. To find the total resistance, you simply take the reciprocal of the sum of the reciprocals of the individual resistances.
Calculating Total Resistance in a Parallel Circuit
Let’s consider a practical example to illustrate how this formula works. Suppose we have two resistors, R1 = 10 ohms and R2 = 20 ohms, connected in parallel. To find the total resistance, we apply the formula: 1/R_total = 1⁄10 + 1⁄20. Simplifying, we get 1/R_total = 0.1 + 0.05 = 0.15. Therefore, R_total = 1⁄0.15 = 6.67 ohms. As expected, the total resistance (6.67 ohms) is less than the resistance of either individual resistor.
| Resistor | Resistance (Ohms) | Reciprocal Resistance (1/Ohms) |
|---|---|---|
| R1 | 10 | 0.1 |
| R2 | 20 | 0.05 |
| Total | 6.67 | 0.15 |
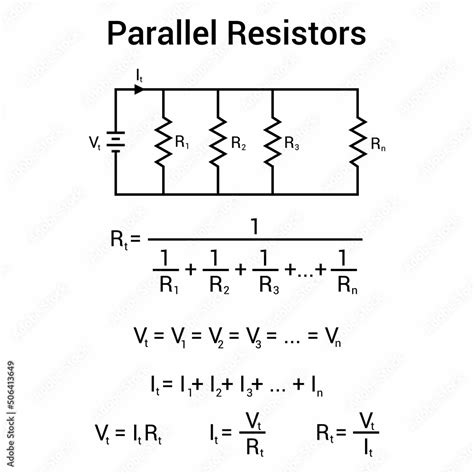
Practical Applications of Resistors in Parallel

Resistors in parallel have numerous practical applications in electronics. One of the primary advantages of parallel circuits is the ability to increase the current capacity of a circuit. By connecting resistors in parallel, you can reduce the total resistance of the circuit, allowing more current to flow. This is particularly useful in applications where high current is required, such as in power supplies and audio amplifiers.
Voltage and Current in Parallel Circuits
In a parallel circuit, the voltage across each resistor is the same. This means that if you have a 12-volt power source connected to a parallel circuit, each resistor in the circuit will have 12 volts across it. However, the current through each resistor can be different and is determined by the resistance of each resistor and the voltage across it, according to Ohm’s Law (I = V/R). Understanding how voltage and current behave in parallel circuits is crucial for designing and analyzing electronic circuits.
In conclusion, resistors in parallel are a fundamental concept in electronics, and understanding how they work is essential for designing and analyzing electronic circuits. By grasping the formula for calculating total resistance in a parallel circuit and understanding the behavior of voltage and current, you can unlock the full potential of parallel circuits in your electronic projects.
What is the main advantage of connecting resistors in parallel?
+The main advantage of connecting resistors in parallel is that it reduces the total resistance of the circuit, allowing more current to flow. This is particularly useful in applications where high current is required.
How do you calculate the total resistance of resistors in parallel?
+The total resistance of resistors in parallel is calculated using the formula 1/R_total = 1/R1 + 1/R2 +... + 1/Rn, where R1, R2,..., Rn are the resistances of the individual resistors.
Is the voltage across each resistor in a parallel circuit the same?
+Yes, the voltage across each resistor in a parallel circuit is the same. However, the current through each resistor can vary based on its resistance.
What is the significance of Ohm's Law in parallel circuits?
+Ohm's Law (I = V/R) is significant in parallel circuits because it allows you to calculate the current through each resistor, given the voltage across it and its resistance.
Can you increase the current capacity of a circuit by connecting resistors in parallel?
+Yes, connecting resistors in parallel can increase the current capacity of a circuit by reducing the total resistance of the circuit.
Meta Description: Learn how to calculate the total resistance of resistors in parallel and understand the practical applications of parallel circuits in electronics, including increasing current capacity and reducing total resistance.