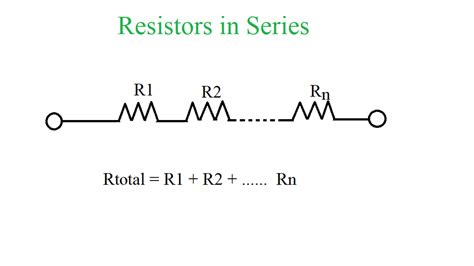
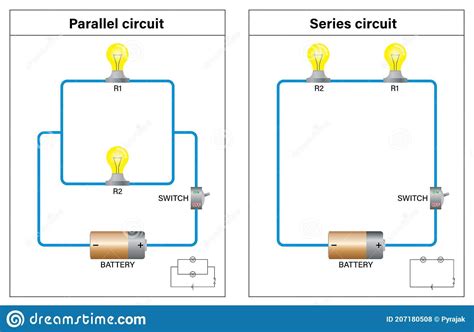
Resistors in series are a fundamental concept in electronics, where two or more resistors are connected end-to-end to form a single circuit. This configuration is commonly used in a wide range of applications, from simple voltage dividers to complex electronic circuits. Understanding the basics of resistors in series is crucial for designing and analyzing electronic circuits, as it allows engineers to calculate the total resistance, voltage drop, and current flow in the circuit.
In a series circuit, the current flows through each resistor in sequence, and the voltage drop across each resistor is proportional to its resistance value. The total resistance of the circuit is the sum of the individual resistances, and the total voltage drop is the sum of the voltage drops across each resistor. This is based on Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL), which states that the sum of the voltage changes around a closed loop in a circuit must be zero. By applying KVL to a series circuit, we can derive the fundamental equations that govern the behavior of resistors in series.
Key Points
- The total resistance of a series circuit is the sum of the individual resistances.
- The voltage drop across each resistor is proportional to its resistance value.
- The current flow through each resistor is the same, as there is only one path for the current to flow.
- Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL) is used to derive the equations that govern the behavior of resistors in series.
- Resistors in series are commonly used in voltage dividers, current limiters, and other electronic circuits.
Calculating Total Resistance
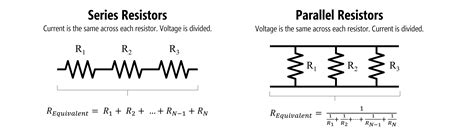
The total resistance of a series circuit can be calculated using the formula: R_total = R1 + R2 +… + Rn, where R_total is the total resistance and R1, R2,…, Rn are the individual resistances. This formula is derived from the fact that the voltage drop across each resistor is proportional to its resistance value, and the total voltage drop is the sum of the voltage drops across each resistor. For example, if we have two resistors in series, R1 = 10 ohms and R2 = 20 ohms, the total resistance would be R_total = 10 + 20 = 30 ohms.
Voltage Drop and Current Flow
The voltage drop across each resistor can be calculated using Ohm’s law, V = IR, where V is the voltage drop, I is the current flow, and R is the resistance. Since the current flow through each resistor is the same, we can use the total resistance and total voltage to calculate the current flow. For example, if we have a series circuit with a total resistance of 30 ohms and a total voltage of 12 volts, the current flow would be I = V_total / R_total = 12 / 30 = 0.4 amps.
| Resistor | Resistance (ohms) | Voltage Drop (volts) |
|---|---|---|
| R1 | 10 | 4 |
| R2 | 20 | 8 |
| Total | 30 | 12 |
Practical Applications
Resistors in series have numerous practical applications in electronics, including voltage dividers, current limiters, and impedance matching networks. A voltage divider, for example, uses two resistors in series to divide a voltage signal into a lower voltage signal. The ratio of the resistance values determines the voltage division ratio, and the total resistance determines the current flow. Current limiters, on the other hand, use a series resistor to limit the current flow in a circuit, protecting the circuit from excessive current or voltage.
Design Considerations
When designing a series circuit, it’s essential to consider the tolerance of the resistors, as well as the temperature coefficient of resistance. The tolerance of a resistor refers to the acceptable variation in its resistance value, and the temperature coefficient of resistance refers to the change in resistance value with temperature. These factors can affect the accuracy and reliability of the circuit, and should be carefully considered in the design process.
What is the main advantage of using resistors in series?
+The main advantage of using resistors in series is that it allows for the creation of a voltage divider or current limiter, which can be used to protect the circuit from excessive voltage or current.
How do you calculate the total resistance of a series circuit?
+The total resistance of a series circuit can be calculated using the formula: R_total = R1 + R2 +... + Rn, where R_total is the total resistance and R1, R2,..., Rn are the individual resistances.
What is the effect of temperature on resistors in series?
+The temperature coefficient of resistance can affect the resistance value of each resistor, which can in turn affect the total resistance and voltage drop of the circuit. It's essential to consider the temperature coefficient of resistance when designing a series circuit.
In conclusion, resistors in series are a fundamental concept in electronics, and understanding their behavior is crucial for designing and analyzing electronic circuits. By considering the total resistance, voltage drop, and current flow, as well as the tolerance and temperature coefficient of resistance, engineers can create reliable and efficient circuits that meet the required specifications.