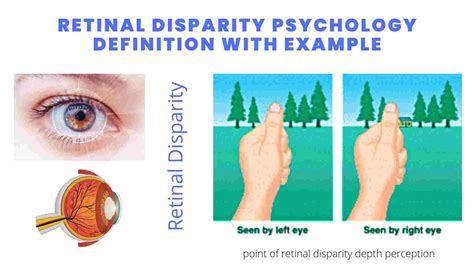
Retinal disparity, a fundamental concept in psychology, plays a crucial role in our ability to perceive depth and distance in the visual world. This phenomenon, also known as binocular disparity, refers to the difference in the images seen by each eye due to their slightly different viewpoints. As we navigate through our environment, our brains process this disparity to create a three-dimensional representation of the world, allowing us to judge distances, depths, and spatial relationships with remarkable accuracy. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of retinal disparity, exploring its underlying mechanisms, psychological implications, and the fascinating ways in which our brains interpret visual information.
Key Points
- Retinal disparity is the difference in images seen by each eye due to their slightly different viewpoints, crucial for depth perception.
- The brain processes retinal disparity to create a three-dimensional representation of the world, enabling accurate judgment of distances and depths.
- Binocular vision, which involves the coordination of both eyes, is essential for retinal disparity and depth perception.
- Psychological factors, such as attention and past experiences, can influence how retinal disparity is interpreted and perceived.
- Understanding retinal disparity has significant implications for fields like optometry, ophthalmology, and computer vision.
Understanding Retinal Disparity
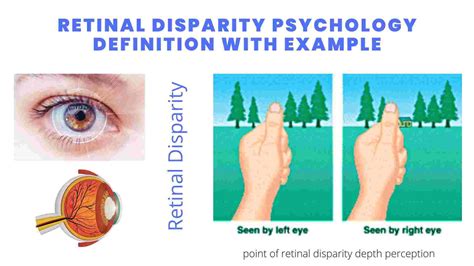
To comprehend retinal disparity, it’s essential to consider the anatomy of the human visual system. Each eye has a slightly different viewpoint, resulting in a disparity between the images projected onto the retinas. This disparity is most pronounced for objects that are close to the observer, as the angle of view between the two eyes is more significant. The brain, however, is able to take this disparity into account, using it to calculate depth and distance. This process, known as stereopsis, is a critical component of binocular vision, allowing us to perceive the world in three dimensions.
The Role of Binocular Vision
Binocular vision, which involves the coordination of both eyes, is essential for retinal disparity and depth perception. When both eyes are working together, the brain is able to combine the images from each eye, creating a single, unified perception of the visual world. This process, known as binocular fusion, allows us to perceive depth and distance with remarkable accuracy. In individuals with impaired binocular vision, such as those with strabismus or amblyopia, depth perception can be significantly impaired, highlighting the importance of binocular vision in retinal disparity.
| Condition | Description | Impact on Depth Perception |
|---|---|---|
| Strabismus | Misalignment of the eyes, resulting in impaired binocular vision | Significant impairment of depth perception |
| Amblyopia | Reduced vision in one eye, often due to abnormal binocular vision development | Impaired depth perception, particularly in situations requiring binocular vision |
| Anisometropia | Significant difference in refractive error between the two eyes | Potential impairment of depth perception, depending on the degree of anisometropia |
Psychological Implications of Retinal Disparity

Retinal disparity has significant psychological implications, influencing our perception of the visual world and our interactions with it. For example, research has shown that retinal disparity can affect our judgment of distances and depths, with individuals who are more sensitive to retinal disparity tend to be more accurate in their depth judgments. Additionally, retinal disparity can influence our perception of shape and form, with the brain using disparity information to create a more detailed and nuanced representation of the visual world.
Attention and Retinal Disparity
Attention also plays a critical role in retinal disparity, with focused attention enhancing the processing of disparity information. When we attend to a particular object or region of space, our brains are able to process the disparity information more efficiently, allowing us to perceive depth and distance with greater accuracy. This highlights the importance of attention in modulating the processing of visual information and demonstrates the complex interplay between attention, perception, and retinal disparity.
Applications and Implications of Retinal Disparity
Understanding retinal disparity has significant implications for a range of fields, from optometry and ophthalmology to computer vision and robotics. For example, clinicians can use retinal disparity to diagnose and treat conditions such as strabismus and amblyopia, while computer vision researchers can develop more sophisticated algorithms for depth perception and 3D reconstruction. Additionally, understanding retinal disparity can inform the development of more effective virtual reality systems, allowing users to perceive depth and distance in a more realistic and immersive way.
What is retinal disparity, and how does it contribute to depth perception?
+Retinal disparity refers to the difference in images seen by each eye due to their slightly different viewpoints. This disparity is processed by the brain to create a three-dimensional representation of the world, allowing us to perceive depth and distance.
How does binocular vision relate to retinal disparity?
+Binocular vision, which involves the coordination of both eyes, is essential for retinal disparity and depth perception. When both eyes are working together, the brain is able to combine the images from each eye, creating a single, unified perception of the visual world.
What are some potential applications of retinal disparity research?
+Understanding retinal disparity has significant implications for fields such as optometry, ophthalmology, computer vision, and robotics. Clinicians can use retinal disparity to diagnose and treat conditions such as strabismus and amblyopia, while computer vision researchers can develop more sophisticated algorithms for depth perception and 3D reconstruction.
In conclusion, retinal disparity is a fundamental concept in psychology, playing a critical role in our ability to perceive depth and distance in the visual world. By understanding the mechanisms underlying retinal disparity, we can gain insights into the complex and multifaceted nature of human perception, and develop more effective treatments for individuals with impaired depth perception. As research in this field continues to evolve, we can expect to see significant advances in our understanding of retinal disparity and its applications in a range of fields.