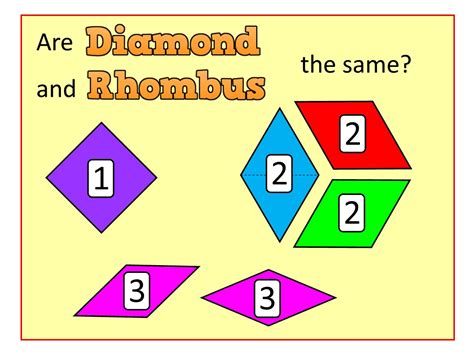
The terms "diamond" and "rhombus" are often used interchangeably in everyday language, but in the realm of geometry, they have distinct meanings. A diamond is a quadrilateral with all sides of equal length, where the opposite sides are parallel, and the opposite angles are equal. On the other hand, a rhombus is a special type of quadrilateral where all four sides are of equal length. While these definitions might seem similar, there are key differences between the two shapes. In this article, we will delve into the world of geometry and explore five essential facts that differentiate diamonds from rhombi.
Key Points
- The definition and properties of a diamond in geometry, highlighting its unique characteristics.
- The distinction between a diamond and a rhombus, focusing on their respective geometric properties.
- The types of angles and side lengths found in diamonds and rhombi, and how these affect their overall shape.
- Real-world applications of diamonds and rhombi in architecture, design, and nature.
- The historical development of geometric concepts, including the study of diamonds and rhombi.
Definition and Properties of Diamonds and Rhombi

A diamond, in geometric terms, refers to a quadrilateral with all sides of equal length, where the opposite sides are parallel, and the opposite angles are equal. This means that a diamond has the properties of both a parallelogram and a rhombus. A rhombus, as mentioned earlier, is a quadrilateral with all sides of equal length. However, unlike a diamond, a rhombus does not necessarily have parallel opposite sides or equal opposite angles. These distinctions are crucial in understanding the unique characteristics of each shape.
Angles and Side Lengths in Diamonds and Rhombi
One of the primary differences between diamonds and rhombi lies in their angles and side lengths. A diamond, by definition, has opposite angles that are equal, which means that the sum of the interior angles of a diamond is always 360 degrees. In contrast, a rhombus has equal side lengths, but its angles can vary. The properties of these shapes have significant implications for their applications in various fields, including architecture, design, and engineering.
| Shape | Side Lengths | Angles |
|---|---|---|
| Diamond | All sides equal | Opposite angles equal |
| Rhombus | All sides equal | Angles can vary |

Real-World Applications of Diamonds and Rhombi

Diamonds and rhombi appear in various aspects of our lives, from the architecture of buildings to the design of textiles. In nature, the diamond shape is found in the structure of certain crystals, while rhombi are seen in the patterns of some tilings and the shapes of certain leaves. The unique properties of these shapes make them ideal for specific applications, such as providing stability in construction or creating visually appealing patterns in design.
Historical Development of Geometric Concepts
The study of geometry, including the concepts of diamonds and rhombi, has a rich history that spans thousands of years. From ancient civilizations like the Egyptians and Greeks to modern mathematicians, the understanding of geometric shapes has evolved significantly. The development of geometric concepts has not only deepened our understanding of the physical world but has also inspired innovation in fields like architecture, engineering, and art.
What is the primary difference between a diamond and a rhombus in geometry?
+The primary difference lies in their properties: a diamond has all sides of equal length with parallel opposite sides and equal opposite angles, whereas a rhombus has all sides of equal length but does not necessarily have parallel opposite sides or equal opposite angles.
How are diamonds and rhombi used in real-world applications?
+Diamonds and rhombi are used in architecture for their stability, in design for their aesthetic appeal, and in nature, their patterns and structures are observed in crystals, tilings, and certain types of leaves.
What is the significance of understanding the properties of diamonds and rhombi?
+Understanding the properties of diamonds and rhombi is crucial for creating structures that are both aesthetically pleasing and structurally sound. It also contributes to the advancement of geometric knowledge and its applications across various disciplines.
In conclusion, the distinction between diamonds and rhombi is more than just a matter of terminology; it reflects fundamental differences in their geometric properties and real-world applications. By exploring these differences and understanding the unique characteristics of each shape, we can appreciate the complexity and beauty of geometry and its role in shaping our world.