The formation of rocks is a complex and multifaceted process that has captivated the imagination of geologists and the general public alike for centuries. Rocks are the building blocks of our planet, and their formation is a crucial aspect of the Earth's geological history. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of rock formation, exploring the five primary ways in which rocks are created. From the intense heat and pressure of magma to the gradual accumulation of sediments, we will examine the diverse processes that shape our planet's geology.
Key Points
- Igneous rocks form from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava
- Sedimentary rocks are created through the accumulation and compression of sediments
- Metamorphic rocks are formed through the transformation of existing rocks under high pressure and temperature
- Hydrothermal rocks are created through the interaction of hot water and minerals
- Biogenic rocks are formed through the accumulation of organic matter, such as shells or skeletons
Igneous Rock Formation

Igneous rocks are formed from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. This process can occur either beneath the Earth’s surface, resulting in intrusive rocks, or above the surface, resulting in extrusive rocks. The rate of cooling and the composition of the magma determine the texture and mineralogy of the resulting rock. For example, granite is a type of igneous rock that forms from the slow cooling of magma deep within the Earth’s crust, resulting in a coarse-grained texture and a characteristic speckled appearance.
Magma Composition and Rock Type
The composition of magma plays a crucial role in determining the type of igneous rock that forms. Magma with a high silica content, for example, will produce rocks with a higher proportion of quartz and feldspar minerals, such as granite or rhyolite. In contrast, magma with a low silica content will produce rocks with a higher proportion of olivine and pyroxene minerals, such as basalt or gabbro. The study of magma composition and its relationship to rock type is a key area of research in igneous petrology.
| Rock Type | Magma Composition | Texture |
|---|---|---|
| Granite | High silica content | Coarse-grained |
| Basalt | Low silica content | Fine-grained |
| Rhyolite | High silica content | Porphyritic |

Sedimentary Rock Formation

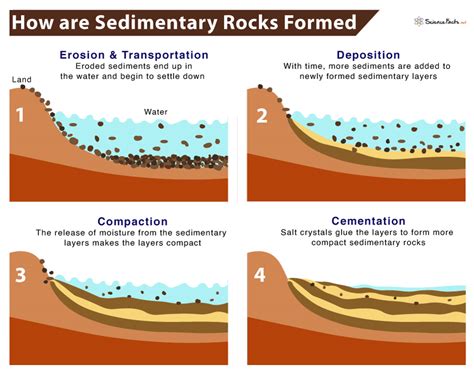
Sedimentary rocks are formed through the accumulation and compression of sediments, such as sand, silt, or clay. This process can occur through a variety of mechanisms, including erosion, weathering, and deposition. Sedimentary rocks can be further divided into three main categories: clastic, chemical, and organic. Clastic sedimentary rocks, such as conglomerate or sandstone, are formed from the accumulation of pre-existing rocks or minerals. Chemical sedimentary rocks, such as limestone or rock salt, are formed through the precipitation of minerals from a solution. Organic sedimentary rocks, such as coal or oil shale, are formed from the accumulation of organic matter.
Sediment Transport and Deposition
The transport and deposition of sediments play a crucial role in the formation of sedimentary rocks. Sediments can be transported through a variety of mechanisms, including water, wind, or ice. The distance and mode of transport determine the size, shape, and composition of the sediments, which in turn affect the resulting rock type. For example, sediments transported by water will tend to be rounded and smoothed, resulting in rocks with a more uniform texture and composition.
Metamorphic Rock Formation
Metamorphic rocks are formed through the transformation of existing rocks under high pressure and temperature. This process can occur through a variety of mechanisms, including mountain building, faulting, or contact metamorphism. Metamorphic rocks can be further divided into two main categories: foliated and non-foliated. Foliated metamorphic rocks, such as slate or schist, are characterized by a layered or banded structure, resulting from the alignment of minerals under directed pressure. Non-foliated metamorphic rocks, such as marble or quartzite, lack a layered structure and are formed through the recrystallization of minerals under high pressure and temperature.
Hydrothermal Rock Formation
Hydrothermal rocks are formed through the interaction of hot water and minerals. This process can occur through a variety of mechanisms, including the circulation of hot water through rocks or the deposition of minerals from a hydrothermal solution. Hydrothermal rocks can be further divided into two main categories: veins and alteration zones. Veins are formed through the deposition of minerals in fractures or faults, resulting in rocks with a characteristic linear or tabular shape. Alteration zones are formed through the interaction of hot water and rocks, resulting in rocks with a characteristic zoned or patchy appearance.
Biogenic Rock Formation
Biogenic rocks are formed through the accumulation of organic matter, such as shells, skeletons, or plant material. This process can occur through a variety of mechanisms, including the growth of organisms, the accumulation of dead organisms, or the transformation of organic matter into rock. Biogenic rocks can be further divided into two main categories: skeletal and non-skeletal. Skeletal biogenic rocks, such as limestone or chalk, are formed from the accumulation of shells or skeletons. Non-skeletal biogenic rocks, such as coal or oil shale, are formed from the accumulation of plant material or other organic matter.
What is the difference between igneous and sedimentary rocks?
+Igneous rocks are formed from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava, while sedimentary rocks are formed through the accumulation and compression of sediments.
What is the process of metamorphic rock formation?
+Metamorphic rocks are formed through the transformation of existing rocks under high pressure and temperature, resulting in changes to the rock's mineralogy and texture.
What is the role of hydrothermal activity in rock formation?
+Hydrothermal activity plays a crucial role in the formation of hydrothermal rocks, which are formed through the interaction of hot water and minerals.
In conclusion, the formation of rocks is a complex and multifaceted process that involves a variety of mechanisms and processes. From the intense heat and pressure of magma to the gradual accumulation of sediments, each type of rock formation provides a unique window into the Earth’s geological history. By studying the different types of rock formation, geologists can gain a deeper understanding of the Earth’s evolution and the processes that have shaped our planet over millions of years.