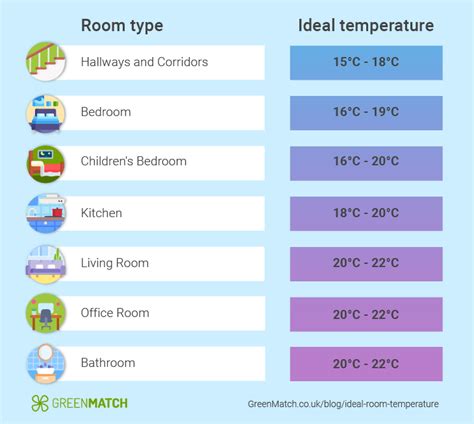
Room temperature, a term commonly used to describe the temperature range that is comfortable for human occupancy, varies slightly depending on the source and context. However, it is generally accepted that room temperature falls within a specific range in Celsius. To understand this range, it's essential to consider the historical and practical contexts in which room temperature has been defined.
Historically, the concept of room temperature emerged as a standard for comfort and productivity in indoor environments. The ideal temperature range has been debated, but a commonly cited figure for room temperature in Celsius is between 20°C and 25°C. This range is not only comfortable for most people but also conducive to efficient work and relaxation. The lower end of this spectrum, around 20°C, is often preferred for more sedentary activities or in cooler climates, while the upper end, around 25°C, might be more comfortable in warmer climates or for individuals who prefer a slightly warmer environment.
Key Points
- The generally accepted range for room temperature is between 20°C and 25°C.
- This range is considered comfortable for most individuals and suitable for both work and leisure activities.
- Personal preferences, climate, and activity levels can influence the ideal room temperature.
- Historical and cultural factors have played a role in defining comfort temperatures.
- Technological advancements have made it easier to maintain optimal room temperatures with precision.
Natural Variations in Room Temperature Preferences
It’s worth noting that preferences for room temperature can vary significantly among individuals due to factors such as age, health, clothing, and activity level. For instance, older adults or those with certain health conditions might prefer warmer temperatures, while younger, more active individuals might find cooler temperatures more comfortable. Moreover, cultural and regional differences play a significant role in determining what is considered an ideal room temperature, reflecting local climate conditions, architectural traditions, and societal norms.
Technical Specifications and Climate Control
From a technical standpoint, maintaining an optimal room temperature involves understanding the principles of thermodynamics and employing appropriate climate control measures. This can range from simple heating and cooling systems to more sophisticated technologies like radiant floor heating, air conditioning, and smart home temperature control systems. The choice of heating or cooling method can significantly impact energy efficiency, indoor air quality, and overall comfort. For example, a well-insulated building can maintain a stable room temperature with minimal external heating or cooling, reducing energy consumption and environmental impact.
| Temperature Range | Comfort Level |
|---|---|
| Below 18°C | Cool to Cold |
| 18°C - 22°C | Comfortable for Most |
| 22°C - 25°C | Warm for Some |
| Above 25°C | Hot for Most |
Practical Applications and Considerations
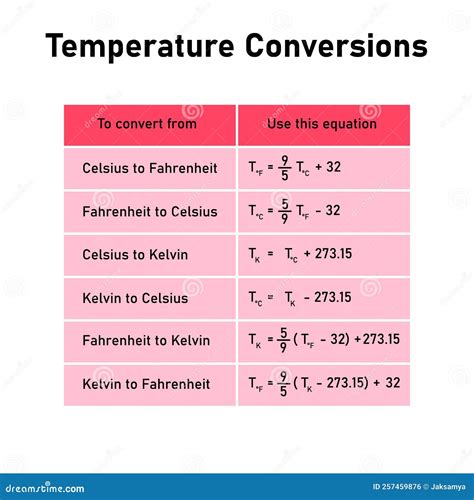
In practical terms, understanding and managing room temperature is crucial for various settings, including residential homes, offices, and public spaces. For instance, in workplaces, maintaining a comfortable room temperature can improve employee satisfaction and productivity. In healthcare settings, precise temperature control is vital for patient comfort and recovery. Furthermore, with the increasing focus on energy efficiency and sustainability, selecting heating and cooling systems that minimize environmental impact while maintaining comfort is a significant consideration.
Evidence-Based Analysis
Studies have shown that room temperature significantly affects human performance and health. For example, temperatures that are too high or too low can lead to decreased productivity, increased fatigue, and even health issues such as heatstroke or hypothermia. Therefore, it’s essential to strike a balance that caters to the majority while considering individual variations. This can be achieved through flexible temperature control systems and adaptive thermal comfort models that take into account factors like air movement, humidity, and personal factors.
What is the ideal room temperature for sleeping?
+The ideal room temperature for sleeping is often considered to be around 16°C to 19°C, as this range promotes better sleep quality by regulating body temperature effectively.
How does room temperature affect productivity?
+Room temperature significantly affects productivity. Temperatures that are too low or too high can decrease productivity, while temperatures within the comfortable range (around 22°C to 25°C) can boost performance and efficiency.
What factors influence personal preferences for room temperature?
+Personal preferences for room temperature are influenced by factors such as age, health, activity level, clothing, and cultural background. For instance, older individuals might prefer warmer temperatures, while younger, active individuals might prefer cooler temperatures.
In conclusion, the concept of room temperature in Celsius is multifaceted, influenced by personal, cultural, and technological factors. Understanding these dynamics is essential for creating comfortable, productive, and sustainable indoor environments. By considering the intricacies of human comfort and the capabilities of modern climate control systems, individuals and organizations can optimize room temperatures to enhance well-being, efficiency, and environmental stewardship.