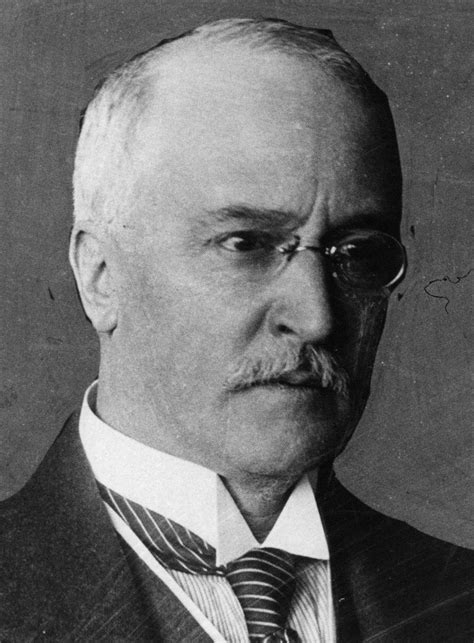The story of Rudolf Diesel, the inventor of the Diesel engine, is a fascinating tale of innovation, perseverance, and tragedy. Born on March 18, 1858, in Paris, France, to German parents, Diesel's early life was marked by a passion for engineering and a desire to make a name for himself in the field. His father, Theodor Diesel, was a leather goods manufacturer, and the family moved to Augsburg, Germany, when Rudolf was just a child. It was in Augsburg that Diesel developed a strong interest in engineering, which would eventually lead him to create one of the most revolutionary engines of the 20th century.
Diesel's educational background was rooted in engineering, and he attended the Technical University of Munich, where he studied mechanical engineering. After completing his studies, he worked for several companies, including the Linde Refrigeration Machine Company, where he developed a deep understanding of thermodynamics and heat transfer. This knowledge would later prove crucial in the development of his iconic engine. In 1890, Diesel patented his design for a "new rational heat engine," which would eventually become known as the Diesel engine.
Key Points
- Rudolf Diesel was born in Paris, France, in 1858 to German parents.
- He developed a passion for engineering at a young age and attended the Technical University of Munich.
- Diesel patented his design for a "new rational heat engine" in 1890, which would later become known as the Diesel engine.
- The Diesel engine uses a combination of air compression and fuel injection to ignite the fuel, increasing efficiency and power output.
- Diesel's invention revolutionized the transportation industry, enabling the development of more efficient and powerful vehicles.
The Development of the Diesel Engine
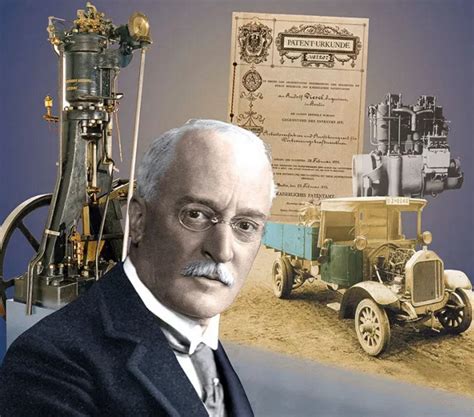

The Diesel engine, as we know it today, is a type of internal combustion engine that uses a combination of air compression and fuel injection to ignite the fuel. This design allows for a more efficient and powerful engine, which has made it a staple in the transportation industry. Diesel’s engine used a unique combination of air compression and fuel injection to achieve this efficiency, which was a significant improvement over the traditional gasoline engines of the time. The engine’s operating cycle, known as the Diesel cycle, involves four stages: intake, compression, power, and exhaust.
The Diesel Cycle
The Diesel cycle is a four-stage process that allows the engine to operate efficiently and effectively. The first stage, intake, involves drawing air into the cylinder through the intake valve. The second stage, compression, involves compressing the air to a high pressure, which increases the temperature of the air. The third stage, power, involves injecting fuel into the cylinder, which ignites and produces power. The final stage, exhaust, involves releasing the exhaust gases from the cylinder through the exhaust valve. This cycle allows the Diesel engine to achieve high efficiency and power output, making it a popular choice for transportation and industrial applications.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Intake | Air is drawn into the cylinder through the intake valve. |
| Compression | Air is compressed to a high pressure, increasing the temperature. |
| Power | Fuel is injected into the cylinder, igniting and producing power. |
| Exhaust | Exhaust gases are released from the cylinder through the exhaust valve. |

Impact of the Diesel Engine

The Diesel engine has had a profound impact on the transportation industry, enabling the development of more efficient and powerful vehicles. The engine’s high efficiency and power output make it a popular choice for trucks, buses, and other heavy-duty vehicles. Additionally, the Diesel engine has been used in a variety of industrial applications, including generators, pumps, and compressors. The engine’s reliability and durability have made it a trusted choice for many industries, and its impact can still be felt today.
Applications of the Diesel Engine
The Diesel engine has a wide range of applications, including transportation, industrial, and recreational uses. In the transportation industry, the Diesel engine is used in trucks, buses, and other heavy-duty vehicles. In industrial applications, the engine is used in generators, pumps, and compressors. Additionally, the Diesel engine is used in recreational vehicles, such as boats and RVs. The engine’s versatility and reliability have made it a popular choice for many applications, and its impact can still be felt today.
What is the main difference between a Diesel engine and a gasoline engine?
+The main difference between a Diesel engine and a gasoline engine is the way they ignite the fuel. A Diesel engine uses compression to ignite the fuel, while a gasoline engine uses a spark plug.
What are the advantages of using a Diesel engine?
+The advantages of using a Diesel engine include higher efficiency, more power output, and longer engine life. Diesel engines are also more reliable and durable than gasoline engines.
What are some common applications of the Diesel engine?
+Some common applications of the Diesel engine include transportation, industrial, and recreational uses. The engine is used in trucks, buses, generators, pumps, and compressors, as well as in boats and RVs.
Meta Description: Learn about the life and work of Rudolf Diesel, the inventor of the Diesel engine, and how his innovative design revolutionized the transportation industry.