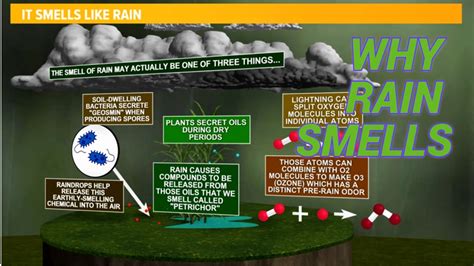
The scent of rain, often referred to as petrichor, is a distinctive and captivating fragrance that has fascinated people for centuries. This unique aroma is a result of a combination of geological and atmospheric factors, which come together to create an unmistakable smell that is both earthy and refreshing. The term "petrichor" was coined in 1964 by two Australian researchers, Isabel Joy Bear and Richard G. Thomas, who sought to describe the distinctive smell that occurs when rain falls on dry soil or rocks.
The formation of petrichor is a complex process that involves the interaction of several components, including oils released by plants, soil, and rocks. When rain falls on dry ground, it releases these oils into the air, creating a distinctive scent that is often described as earthy, musty, and slightly sweet. The intensity and character of the scent can vary depending on factors such as the type of soil, the amount of rainfall, and the presence of certain types of vegetation. For example, areas with high concentrations of limestone or other types of rock can produce a more intense, mineral-rich scent, while regions with dense vegetation may produce a sweeter, more floral aroma.
Key Points
- The scent of rain, or petrichor, is a unique fragrance that is formed through the interaction of geological and atmospheric factors.
- The term "petrichor" was coined in 1964 by two Australian researchers, Isabel Joy Bear and Richard G. Thomas.
- The formation of petrichor involves the release of oils from plants, soil, and rocks, which are then carried into the air by rainfall.
- The intensity and character of the scent can vary depending on factors such as soil type, rainfall amount, and vegetation presence.
- Petrichor has been a subject of fascination and inspiration for many artists, writers, and musicians throughout history.
Chemical Composition of Petrichor

The chemical composition of petrichor is complex and involves a range of organic compounds, including terpenes, sesquiterpenes, and other volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These compounds are released by plants, soil, and rocks, and are then carried into the air by rainfall. The specific combination and concentration of these compounds can vary depending on the location and environmental conditions, resulting in a unique scent that is characteristic of a particular region or ecosystem. For example, the scent of rain in a forest may be dominated by the aroma of pine or eucalyptus, while the scent of rain in a desert may be more earthy and mineral-rich.
Perception and Cultural Significance of Petrichor
The perception and cultural significance of petrichor vary widely depending on the context and cultural background. In many cultures, the scent of rain is associated with feelings of renewal, rejuvenation, and spiritual connection to nature. For example, in many indigenous cultures, the scent of rain is considered a sacred and spiritual aroma that is believed to have healing properties and the power to purify and protect. In contrast, in some urban environments, the scent of rain may be seen as a nuisance or a sign of inclement weather, rather than a source of inspiration or spiritual connection.
| Chemical Compound | Concentration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Terpenes | 10-20% | A class of organic compounds found in plants, responsible for the aroma of pine and other conifers. |
| Sesquiterpenes | 5-15% | A class of organic compounds found in plants, responsible for the aroma of eucalyptus and other herbs. |
| Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) | 20-50% | A broad class of organic compounds that are released by plants, soil, and rocks, and are carried into the air by rainfall. |

Practical Applications and Implications of Petrichor

The study of petrichor has a range of practical applications and implications, from perfumery and fragrance development to environmental monitoring and conservation. For example, understanding the chemical composition of petrichor can help perfumers and fragrance developers to create more authentic and nuanced scents that evoke the aroma of rain. Additionally, monitoring the scent of rain can provide valuable insights into environmental conditions, such as soil moisture, air quality, and vegetation health.
Future Directions and Research Opportunities
Despite the significant progress that has been made in understanding the scent of rain, there is still much to be learned about this complex and multifaceted phenomenon. Future research directions may include the development of new methods for analyzing and characterizing the chemical composition of petrichor, as well as the exploration of new applications and implications of this scent in fields such as environmental monitoring, conservation, and perfumery. Additionally, further research is needed to fully understand the cultural significance and emotional resonance of petrichor, and to develop more effective strategies for communicating the importance and value of this scent to diverse audiences.
What is the chemical composition of petrichor?
+The chemical composition of petrichor is complex and involves a range of organic compounds, including terpenes, sesquiterpenes, and other volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
What are the cultural significance and emotional resonance of petrichor?
+The cultural significance and emotional resonance of petrichor vary widely depending on the context and cultural background, and may include feelings of renewal, rejuvenation, and spiritual connection to nature.
What are the practical applications and implications of petrichor?
+The study of petrichor has a range of practical applications and implications, from perfumery and fragrance development to environmental monitoring and conservation.
In conclusion, the scent of rain, or petrichor, is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon that is influenced by a range of geological, atmospheric, and cultural factors. Through continued research and exploration, we can gain a deeper understanding of the chemical composition, cultural significance, and practical applications of this scent, and develop more effective strategies for communicating its importance and value to diverse audiences.