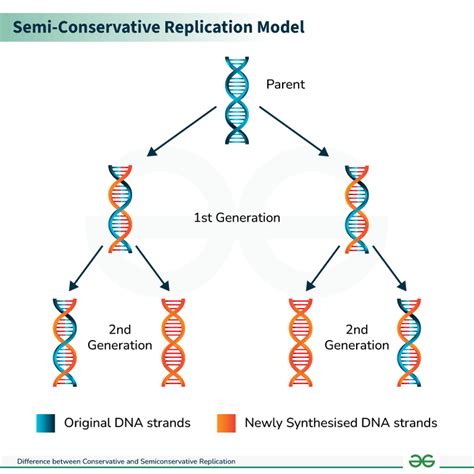
Semi-conservative replication is a fundamental concept in molecular biology that describes the process by which DNA makes a copy of itself during cell division. This process is crucial for the transmission of genetic information from one generation of cells to the next. In semi-conservative replication, the double helix structure of DNA is unwound, and each strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand. This results in two daughter DNA molecules, each consisting of one old strand (the template) and one newly synthesized strand.
The concept of semi-conservative replication was first proposed by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953, based on their model of the DNA double helix. Their proposal was later confirmed through a series of experiments conducted by Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl in 1958. These experiments involved labeling DNA with heavy isotopes and then observing how the labels were distributed in the daughter molecules after replication. The results supported the semi-conservative model, showing that each daughter molecule contained one old strand and one new strand.
Key Points
- Semi-conservative replication is the process by which DNA makes a copy of itself during cell division.
- The process involves unwinding the double helix structure of DNA and using each strand as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand.
- Each daughter DNA molecule consists of one old strand (the template) and one newly synthesized strand.
- The concept of semi-conservative replication was first proposed by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953.
- The Meselson-Stahl experiments in 1958 provided conclusive evidence for the semi-conservative model of DNA replication.
The Process of Semi-Conservative Replication
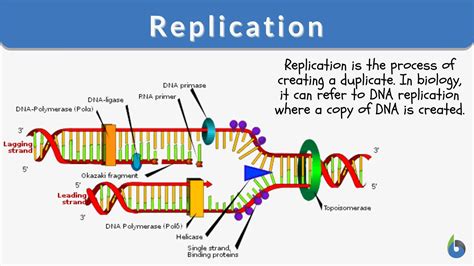
The process of semi-conservative replication can be divided into several stages. First, the double helix structure of DNA is unwound by an enzyme called helicase. This creates a replication fork, where the two strands of DNA are separated. Next, an enzyme called primase adds short RNA primers to the template strands at specific regions called origin of replication. These primers provide a starting point for DNA synthesis.
Once the primers are in place, an enzyme called DNA polymerase begins to synthesize new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to the primers. DNA polymerase reads the template strands and matches the incoming nucleotides to the base pairing rules (A-T and G-C). This process continues until the entire genome has been replicated. Finally, the RNA primers are removed and replaced with DNA, and the new DNA molecules are sealed by an enzyme called DNA ligase.
Importance of Semi-Conservative Replication
Semi-conservative replication is essential for the transmission of genetic information from one generation of cells to the next. It ensures that each daughter cell receives a complete and accurate copy of the genome, which is necessary for proper cellular function and development. Additionally, semi-conservative replication allows for the repair of damaged DNA through a process called mismatch repair, which helps to maintain the integrity of the genome.
| Stage of Replication | Description |
|---|---|
| Initiation | Unwinding of DNA double helix and addition of RNA primers |
| Elongation | Synthesis of new DNA strands by DNA polymerase |
| Termination | Removal of RNA primers and sealing of new DNA molecules |
Challenges and Limitations of Semi-Conservative Replication
While semi-conservative replication is a highly accurate process, it is not perfect and can be affected by various factors. For example, errors can occur during DNA synthesis, resulting in mutations that can have significant consequences for the cell. Additionally, the process of replication can be disrupted by environmental factors, such as radiation and chemical mutagens, which can cause damage to the DNA template.
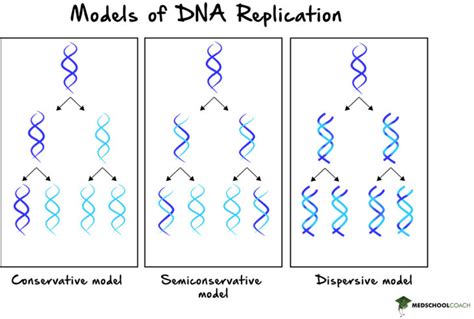
Furthermore, the semi-conservative model of DNA replication has been challenged by alternative models, such as the conservative and dispersive models. However, these models have been largely discredited by experimental evidence, and the semi-conservative model remains the most widely accepted explanation for DNA replication.
Future Directions and Implications
Our understanding of semi-conservative replication has significant implications for various fields, including genetics, molecular biology, and medicine. For example, the development of cancer therapies often relies on an understanding of DNA replication and the mechanisms that regulate it. Additionally, the study of semi-conservative replication can provide insights into the evolution of life on Earth and the development of new technologies, such as genetic engineering and gene editing.
In conclusion, semi-conservative replication is a fundamental process that underlies the transmission of genetic information from one generation of cells to the next. Its importance extends beyond the basic understanding of DNA replication, as it has implications for our understanding of genetic inheritance, mutation, and the development of diseases. Further research into the mechanisms and regulation of semi-conservative replication will continue to provide valuable insights into the biology of living organisms and the development of new technologies and therapies.
What is the difference between semi-conservative and conservative replication?
+In semi-conservative replication, each daughter molecule contains one old strand and one new strand. In contrast, conservative replication would result in one daughter molecule containing two old strands and the other daughter molecule containing two new strands.
How does semi-conservative replication ensure the accuracy of genetic information?
+Semi-conservative replication ensures the accuracy of genetic information through the use of proofreading and editing mechanisms, such as mismatch repair, which helps to correct errors that occur during DNA synthesis.
What are the implications of semi-conservative replication for our understanding of genetic inheritance?
+The semi-conservative model of DNA replication provides a mechanism for the transmission of genetic information from one generation of cells to the next, which is essential for our understanding of genetic inheritance and the development of traits and diseases.