Understanding the geometry of molecules is crucial in chemistry, as it helps predict the physical and chemical properties of substances. One molecule that has garnered significant attention due to its unique properties and applications is sulfur hexafluoride, or SF6. SF6 is a synthetic gas that is widely used in various industries, including electrical engineering, medical research, and more, due to its inertness and high dielectric strength. The geometry of SF6 is a key factor in its stability and chemical inertness, making it an interesting subject for study.
Introduction to SF6 Geometry
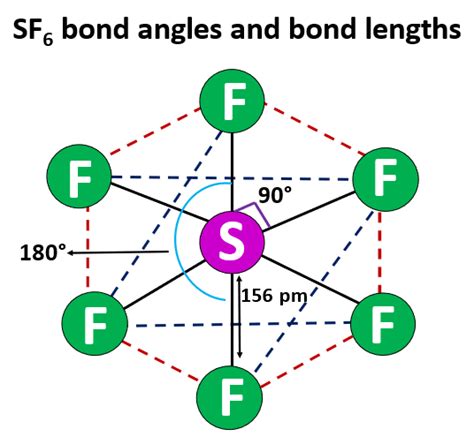
SF6, or sulfur hexafluoride, consists of one sulfur atom bonded to six fluorine atoms. The sulfur atom is at the center, and the fluorine atoms are arranged around it in a symmetrical fashion. This arrangement is not random but follows specific rules of molecular geometry, which are determined by the repulsions between the electron pairs around the central atom. Understanding the geometry of SF6 requires knowledge of the VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) theory, which predicts the shape of molecules based on the number of electron pairs (bonding and non-bonding) around the central atom.
VSEPR Theory and SF6
According to the VSEPR theory, the shape of a molecule is determined by the repulsion between electron pairs. In the case of SF6, the sulfur atom has six bonding electron pairs (one from each fluorine atom) and no lone pairs. These six electron pairs arrange themselves to maximize the distance between each pair, which results in an octahedral geometry. This means that the six fluorine atoms are positioned at the vertices of an octahedron, with the sulfur atom at the center. The octahedral arrangement is the most stable configuration for SF6 because it minimizes the repulsion between the electron pairs, leading to a highly stable molecule.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | SF6 |
| Geometry | Octahedral |
| Bond Angle | 90 degrees (between each F-S-F bond) |
| Polarity | Non-polar |
Applications of SF6

The unique properties of SF6, including its high dielectric strength, chemical inertness, and non-toxicity, make it an essential gas in various industries. In electrical engineering, SF6 is used as an insulating gas in high-voltage equipment such as circuit breakers, switchgear, and transformers. Its high dielectric strength ensures that electrical discharges are safely contained, preventing short circuits and electrical fires. In medical research, SF6 is used as a contrast agent in ultrasound imaging due to its ability to enhance the contrast of images, allowing for better diagnosis of certain conditions.
Environmental Considerations
Despite its useful applications, SF6 has a significant environmental impact. It is a potent greenhouse gas, with a global warming potential about 22,800 times that of carbon dioxide over a 100-year time frame. The release of SF6 into the atmosphere contributes to climate change, and efforts are being made to reduce its emission and find alternative gases with lower environmental impact. The handling and disposal of SF6 require careful consideration to minimize its release into the environment.
Key Points
- The geometry of SF6 is octahedral, determined by the arrangement of six fluorine atoms around a central sulfur atom to minimize electron pair repulsion.
- SF6 is highly stable and chemically inert due to its symmetrical geometry, making it suitable for various industrial applications.
- The molecule has a high dielectric strength, is non-toxic, and is used in electrical engineering and medical research.
- SF6 is a potent greenhouse gas, and its release into the atmosphere contributes to climate change, necessitating careful handling and disposal.
- Understanding the geometry of SF6 is crucial for predicting its physical and chemical properties and for developing strategies to minimize its environmental impact.
Conclusion and Future Perspectives
In conclusion, the geometry of SF6 plays a critical role in its physical and chemical properties, making it a valuable molecule for various applications. However, its significant environmental impact necessitates the development of strategies to reduce its emission and to find alternative gases. Further research into the properties of SF6 and the development of new technologies for its safe handling and disposal are essential for minimizing its environmental footprint. As our understanding of molecular geometry and its implications for molecular properties continues to evolve, we can expect to see the development of new materials and technologies that are more environmentally friendly.
What is the molecular geometry of SF6?
+The molecular geometry of SF6 is octahedral, with six fluorine atoms arranged around a central sulfur atom.
Why is SF6 used in electrical engineering?
+SF6 is used in electrical engineering due to its high dielectric strength, which makes it an excellent insulator for high-voltage equipment.
What is the environmental impact of SF6?
+SF6 is a potent greenhouse gas, with a global warming potential significantly higher than carbon dioxide, contributing to climate change.



