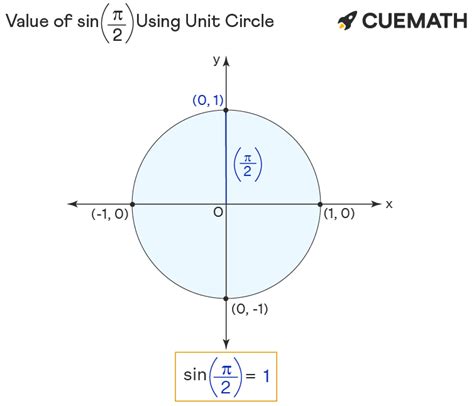
The concept of sine, pi, and their relationship is fundamental in mathematics, particularly in trigonometry and geometry. The sine of an angle in a right-angled triangle is defined as the ratio of the length of the side opposite the angle to the length of the hypotenuse. Pi (π), on the other hand, is a mathematical constant representing the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter. When we discuss "sin pi/2," we are referring to the sine of the angle pi/2 radians, which is equivalent to 90 degrees. The sine of pi/2 is 1, as the angle pi/2 radians corresponds to the point (0,1) on the unit circle. This concept has numerous applications and implications across various fields. Let's explore five key aspects or applications related to the sine function, particularly focusing on its value at pi/2, and the broader context of pi itself.
Understanding the Sine Function and Pi/2
The sine function is periodic with a period of 2π, meaning its values repeat every 2π radians. At π/2, the sine function reaches its maximum value, which is 1. This is because, on the unit circle, the point corresponding to π/2 radians has coordinates (0,1), where the y-coordinate represents the sine of the angle. The significance of π/2 as an angle is not just mathematical; it has practical implications in fields like physics, engineering, and computer science, particularly in the description of wave phenomena and the modeling of periodic systems.
Mathematical Derivations and Proofs
Mathematicians and students alike often delve into the proofs and derivations that establish the value of sin(π/2) as 1. These involve understanding the unit circle, trigonometric identities, and the geometric interpretation of sine and cosine. For instance, the Pythagorean trigonometric identity, sin^2(x) + cos^2(x) = 1, can be used to derive the value of sin(π/2) by considering the coordinates of the point on the unit circle at π/2 radians. Such mathematical explorations not only solidify the understanding of these concepts but also highlight the interconnectedness of mathematical principles.
| Angle in Radians | Sine Value |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| π/2 | 1 |
| π | 0 |
| 3π/2 | -1 |
Applications in Physics and Engineering
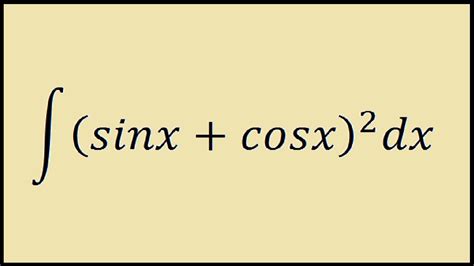
The sine of π/2 and the broader sine function play significant roles in physics and engineering, particularly in the description of simple harmonic motion, wave propagation, and electrical circuits. For example, in AC circuits, the voltage and current can be described using sine waves, with phases that can be represented by angles like π/2, indicating a 90-degree phase shift. This understanding is vital for designing and analyzing electrical systems, from power grids to electronic devices.
Computational Aspects and Programming
In computer science, the sine function, including its value at π/2, is used in various applications, such as graphics rendering, game development, and scientific simulations. Programmers often utilize libraries that provide implementations of trigonometric functions, including sine, to perform tasks like rotating objects in 3D space or modeling physical phenomena. The accuracy and efficiency of these implementations can significantly impact the performance and realism of simulations and visual effects.
Key Points
- The sine of π/2 radians is 1, which is a fundamental concept in trigonometry and has numerous applications.
- Understanding the sine function and its periodic nature is crucial for problem-solving in mathematics, physics, and engineering.
- The value of sin(π/2) and the sine function's properties are used in mathematical derivations and proofs to establish trigonometric identities and principles.
- Applications of the sine function, including at π/2, are found in physics and engineering, particularly in the study of wave phenomena and electrical circuits.
- Computational aspects of the sine function are important in computer science, affecting the performance and realism of simulations and graphics.
In conclusion, the concept of sin(π/2) and its value being 1 is a cornerstone of trigonometry and has far-reaching implications across various disciplines. From mathematical derivations to practical applications in physics, engineering, and computer science, understanding the sine function and its properties is essential for advancing in these fields. As technology continues to evolve, the importance of these fundamental mathematical concepts will only continue to grow, underlining the need for a deep and nuanced understanding of mathematics and its applications.
What is the significance of sin(π/2) in trigonometry?
+The significance of sin(π/2) in trigonometry lies in its value being 1, which is the maximum value of the sine function. This is crucial for understanding the periodic nature of the sine function and its applications in various mathematical and scientific contexts.
How is the sine function used in physics and engineering?
+The sine function is used in physics and engineering to describe wave phenomena, simple harmonic motion, and electrical circuits, among other applications. Its periodic nature and specific values at key angles like π/2 are essential for these descriptions and analyses.
What role does the sine function play in computer science?
+In computer science, the sine function is utilized in graphics rendering, game development, and scientific simulations. It is crucial for tasks such as rotating objects in 3D space and modeling physical phenomena, contributing to the realism and performance of simulations and visual effects.