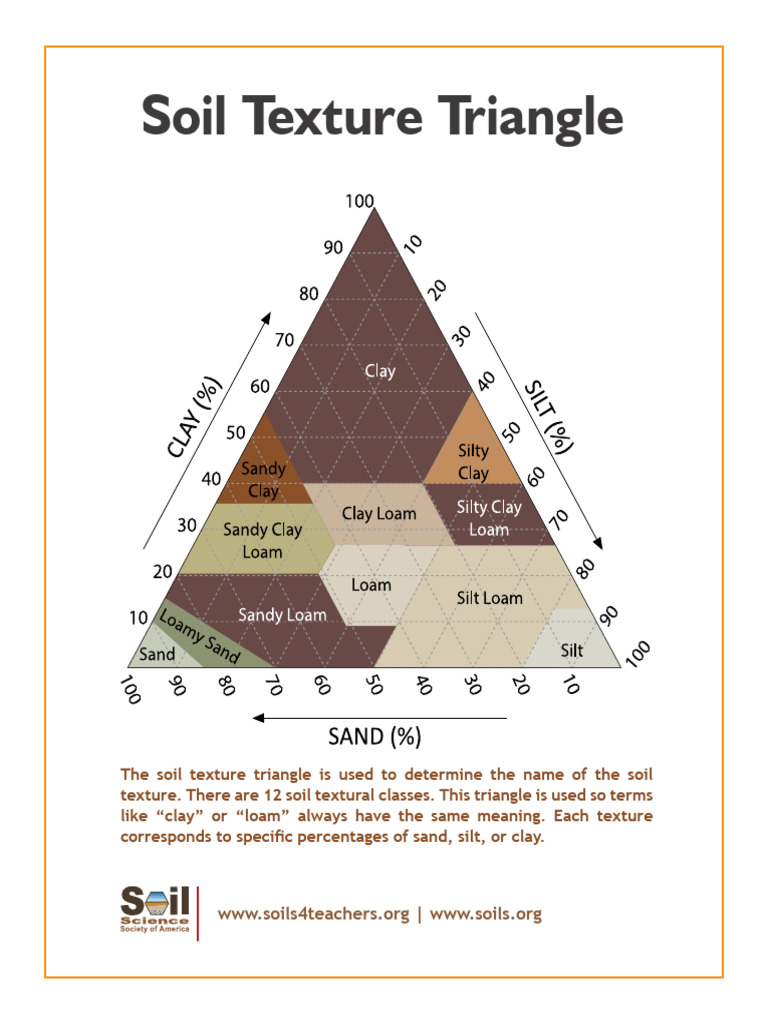
The soil texture triangle, also known as the soil texture diagram, is a graphical representation used to determine the texture of soil based on the proportion of sand, silt, and clay particles. This fundamental concept in soil science is crucial for understanding the physical and chemical properties of soils, which in turn affects plant growth, water infiltration, and soil erosion. The triangle is a simple yet powerful tool that has been widely adopted in agriculture, engineering, and environmental sciences.
To understand the soil texture triangle, it's essential to know the definitions of sand, silt, and clay. Sand particles are the largest, with diameters ranging from 0.05 to 2 millimeters. Silt particles are smaller, with diameters between 0.002 and 0.05 millimeters. Clay particles are the smallest, with diameters less than 0.002 millimeters. The proportion of these particles in a soil sample determines its texture, which can range from sandy to clayey, with various combinations in between.
Key Points
- The soil texture triangle is a graphical representation of the proportion of sand, silt, and clay particles in a soil sample.
- The triangle is divided into 12 textural classes, including sandy loam, loam, clay loam, and others.
- Soil texture affects plant growth, water infiltration, and soil erosion.
- The triangle is a simple yet powerful tool for understanding soil properties and behavior.
- Soil texture can be determined using various methods, including the feel method, sedimentation method, and hydrometer method.
How the Soil Texture Triangle Works
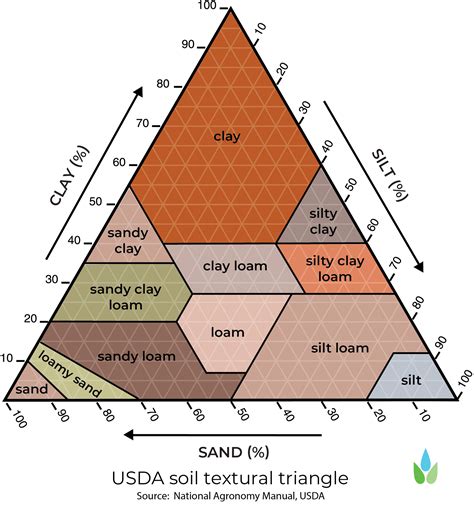
The soil texture triangle is a triangular graph with sand, silt, and clay percentages plotted on the three axes. The triangle is divided into 12 textural classes, each representing a specific range of particle proportions. The classes are: sand, loamy sand, sandy loam, loam, silt, silt loam, sandy clay loam, clay loam, silty clay loam, sandy clay, silty clay, and clay. By plotting the percentages of sand, silt, and clay in a soil sample on the triangle, the texture can be determined.
Textural Classes and Their Characteristics
Each textural class has distinct characteristics that affect soil behavior and plant growth. For example, sandy soils have high water infiltration rates but low water-holding capacity, while clay soils have low infiltration rates but high water-holding capacity. Loamy soils, on the other hand, have a balanced mix of sand, silt, and clay, making them suitable for a wide range of crops.
| Textural Class | Sand (%) | Silt (%) | Clay (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sand | 90-100 | 0-10 | 0-10 |
| Loamy Sand | 70-90 | 10-30 | 0-20 |
| Sandy Loam | 50-70 | 30-50 | 0-20 |
| Loam | 30-50 | 30-50 | 10-30 |

Determining Soil Texture
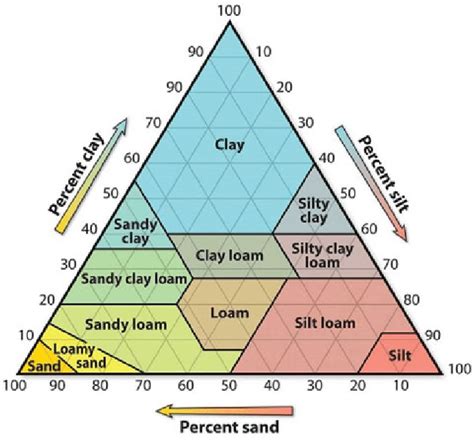
Soil texture can be determined using various methods, including the feel method, sedimentation method, and hydrometer method. The feel method involves manually estimating the texture by feeling the soil’s grittiness, smoothness, and stickiness. The sedimentation method involves measuring the settling rates of sand, silt, and clay particles in a water column. The hydrometer method involves measuring the density of a soil-water suspension using a hydrometer.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Method
Each method has its advantages and limitations. The feel method is simple and quick but requires experience and skill. The sedimentation method is accurate but time-consuming and requires specialized equipment. The hydrometer method is rapid and accurate but requires careful calibration and maintenance of the equipment.
In conclusion, the soil texture triangle is a fundamental concept in soil science that provides a framework for understanding the physical and chemical properties of soils. By determining the texture of a soil, professionals can predict its behavior and make informed decisions for management practices. While various methods are available for determining soil texture, each has its advantages and limitations, and the choice of method depends on the specific application and resources available.
What is the soil texture triangle, and how is it used?
+The soil texture triangle is a graphical representation of the proportion of sand, silt, and clay particles in a soil sample. It is used to determine the texture of a soil, which affects its physical and chemical properties and behavior.
How do I determine the soil texture of a sample?
+Soil texture can be determined using various methods, including the feel method, sedimentation method, and hydrometer method. The choice of method depends on the specific application and resources available.
What are the advantages and limitations of each method?
+Each method has its advantages and limitations. The feel method is simple and quick but requires experience and skill. The sedimentation method is accurate but time-consuming and requires specialized equipment. The hydrometer method is rapid and accurate but requires careful calibration and maintenance of the equipment.
Meta Description: Learn about the soil texture triangle and its importance in understanding soil properties and behavior. Discover how to determine soil texture using various methods and their advantages and limitations.