Trigonometry, a branch of mathematics that deals with the relationships between the sides and angles of triangles, is fundamental in various fields such as physics, engineering, and navigation. Among its numerous applications, the concept of limits, particularly special trig limits, plays a crucial role. These special limits are essential in calculus, as they help in understanding the behavior of trigonometric functions and their derivatives. In this article, we will delve into the world of special trig limits, exploring their definitions, derivations, and practical applications.
Key Points
- Understanding the concept of limits in trigonometry, especially for sine and cosine functions.
- Derivation and application of the limit of sin(x)/x as x approaches 0.
- Exploring the limit of (1 - cos(x))/x as x approaches 0 and its relevance to calculus.
- Practical applications of special trig limits in physics, engineering, and other disciplines.
- Importance of these limits in the development of trigonometric identities and derivatives.
Introduction to Special Trig Limits

The concept of a limit in mathematics refers to the value that a function approaches as the input (or independent variable) gets arbitrarily close to a certain point. In trigonometry, special limits are those that involve trigonometric functions and are crucial for understanding the behavior of these functions as the angle approaches certain values, typically 0 or π/2. The two most significant special trig limits are the limit of sin(x)/x as x approaches 0 and the limit of (1 - cos(x))/x as x approaches 0.
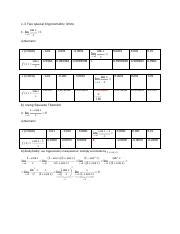
Derivation of sin(x)/x as x approaches 0
The limit of sin(x)/x as x approaches 0 is a fundamental concept in calculus, and its derivation involves understanding the geometry of the unit circle and the definition of the sine function. This limit is crucial because it represents the instantaneous rate of change of the sine function at x = 0. Through geometric arguments and the squeeze theorem, it can be shown that this limit equals 1. The squeeze theorem states that if a function f(x) is squeezed between two functions g(x) and h(x), and if the limits of g(x) and h(x) as x approaches a certain value are equal, then the limit of f(x) as x approaches that same value must also equal that value.
| Function | Limit as x approaches 0 |
|---|---|
| sin(x)/x | 1 |
| (1 - cos(x))/x | 0 |
Practical Applications of Special Trig Limits

Special trig limits have numerous practical applications across various disciplines. In physics, the limit of sin(x)/x as x approaches 0 is used in the derivation of the formula for the period of a simple pendulum. This limit is also essential in the study of wave phenomena, where the behavior of sine and cosine functions as their arguments approach 0 is critical. In engineering, these limits are applied in the design of electronic circuits, particularly in the analysis of filters and oscillators. Furthermore, in navigation and surveying, understanding the limits of trigonometric functions helps in calculating distances and angles with high precision.
Limit of (1 - cos(x))/x as x approaches 0
This limit, though less straightforward than sin(x)/x, is equally important. It can be derived using the half-angle formula for cosine and the limit of sin(x)/x. The result of this limit is 0, which might seem intuitive given the behavior of the cosine function near x = 0. However, its derivation requires careful manipulation of trigonometric identities and an understanding of the behavior of these functions as x approaches 0.
These special trig limits are not only foundational in calculus but also underscore the intricate relationships between different mathematical concepts. They demonstrate how mathematical derivations, which might seem abstract, have tangible applications in our understanding of the physical world. As such, grasping these concepts is essential for anyone delving into the realms of calculus, physics, or engineering.
What is the significance of the limit of sin(x)/x as x approaches 0 in calculus?
+This limit is crucial because it represents the instantaneous rate of change of the sine function at x = 0 and is fundamental in the derivation of many trigonometric identities and derivatives.
How are special trig limits applied in physics and engineering?
+Special trig limits are applied in the study of wave phenomena, the design of electronic circuits, the calculation of work and energy, and in navigation and surveying, among other applications.
What is the importance of understanding the limit of (1 - cos(x))/x as x approaches 0?
+Understanding this limit is essential for comprehending the behavior of the cosine function near x = 0 and has implications in calculus, particularly in the derivation of trigonometric identities and in the analysis of physical systems.
In conclusion, special trig limits are a cornerstone of calculus and have far-reaching implications in various fields. Their derivation and application not only demonstrate the elegance of mathematical reasoning but also highlight the interconnectedness of mathematical concepts and their practical applications. As we continue to explore and understand these limits, we deepen our insight into the fundamental laws that govern our universe, enabling us to solve complex problems and innovate with precision and creativity.