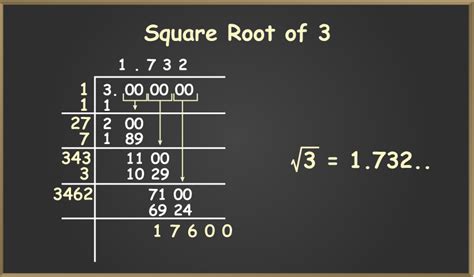
The square root of 3, denoted as √3, is an irrational number that has been a subject of interest in mathematics for centuries. It is an essential element in various mathematical concepts, including geometry, trigonometry, and algebra. The value of √3 is approximately 1.732, but it is a non-repeating, non-terminating decimal. In this article, we will explore five ways to understand and work with the square root of 3, highlighting its significance and applications in different areas of mathematics.
Key Points
- The square root of 3 is an irrational number, approximately equal to 1.732.
- It has numerous applications in geometry, particularly in the study of equilateral triangles and hexagons.
- √3 is a fundamental element in trigonometry, especially in the context of 30-60-90 triangles.
- The square root of 3 appears in various algebraic expressions and equations, often requiring simplification or factorization.
- Understanding the properties and applications of √3 is crucial for problem-solving in mathematics and other fields, such as physics and engineering.
Geometric Significance of Square Root 3

In geometry, the square root of 3 plays a vital role in the study of equilateral triangles and hexagons. The altitude of an equilateral triangle, for instance, is calculated using the formula h = (√3)/2 * s, where s is the length of the side. This demonstrates the intrinsic connection between the square root of 3 and the geometric properties of these shapes. Moreover, the internal angles of an equilateral triangle are all 60 degrees, which is closely related to the value of √3 in trigonometric functions.
Trigonometric Applications of Square Root 3
In trigonometry, the square root of 3 is a fundamental element in the context of 30-60-90 triangles. The sine, cosine, and tangent of 60 degrees are all related to √3, with the values being sin(60°) = √3/2, cos(60°) = 1⁄2, and tan(60°) = √3. These relationships are essential for solving problems involving right triangles and wave patterns in physics and engineering.
| Trigonometric Function | Value at 60° |
|---|---|
| Sine | √3/2 |
| Cosine | 1/2 |
| Tangent | √3 |
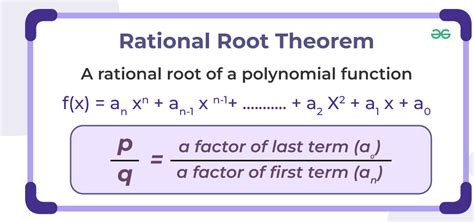
Algebraic Expressions and Equations Involving Square Root 3

In algebra, the square root of 3 appears in various expressions and equations, often requiring simplification or factorization. For example, the expression (√3 + 1)(√3 - 1) can be simplified using the difference of squares formula to (√3)^2 - 1^2 = 3 - 1 = 2. This demonstrates the importance of understanding the properties of √3 in algebraic manipulations.
Problem-Solving Strategies with Square Root 3
When working with problems involving the square root of 3, it is essential to have a range of strategies at your disposal. These may include simplifying expressions, factoring equations, and applying trigonometric identities. By combining these techniques with a deep understanding of the properties and applications of √3, you can develop a robust approach to problem-solving in mathematics and other fields.
What is the approximate value of the square root of 3?
+The approximate value of the square root of 3 is 1.732.
What are some common applications of the square root of 3 in geometry?
+The square root of 3 has numerous applications in geometry, particularly in the study of equilateral triangles and hexagons. It is used to calculate altitudes, side lengths, and internal angles of these shapes.
How is the square root of 3 related to trigonometric functions?
+The square root of 3 is a fundamental element in trigonometry, especially in the context of 30-60-90 triangles. The sine, cosine, and tangent of 60 degrees are all related to √3, with the values being sin(60°) = √3/2, cos(60°) = 1/2, and tan(60°) = √3.
In conclusion, the square root of 3 is a fascinating mathematical concept with far-reaching implications in various fields. By exploring its geometric significance, trigonometric applications, and algebraic expressions, we can gain a deeper understanding of this essential element and its role in problem-solving. Whether you are a student, teacher, or professional, developing a strong foundation in the properties and applications of √3 can provide a valuable foundation for further mathematical exploration and discovery.