Calculating the square root of 106, denoted as √106, can be approached in several ways, each with its own methodology and level of precision. The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 16 is 4 because 4 multiplied by 4 equals 16. However, not all numbers have a whole number as their square root, and 106 is one such number. Here, we will explore five different methods to calculate √106, focusing on both exact and approximate methods.
Method 1: Using a Calculator
The most straightforward method to find √106 is by using a calculator. Most calculators have a square root function, often denoted by the symbol “√” or a button labeled “sqrt.” To calculate √106 using a calculator, simply enter 106 and press the square root button. This method provides an approximate value quickly and easily. The result will be approximately 10.30, but the exact calculation can yield a more precise result, such as 10.29563014, depending on the calculator’s precision.
Understanding Calculator Precision
Calculators can provide results with varying levels of precision, depending on their capabilities. Some calculators, especially those designed for advanced mathematical calculations or scientific use, can display more decimal places than others, offering a more precise result.
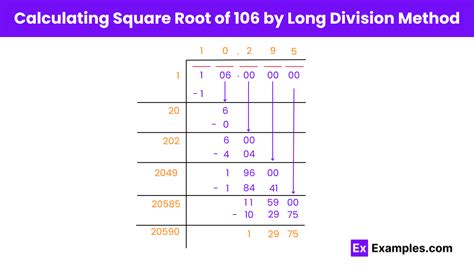
Method 2: Long Division Method

The long division method for finding square roots is an older, more labor-intensive approach that was used before the widespread availability of electronic calculators. This method involves a series of steps that essentially guess and check, refining the guess until a sufficiently precise answer is obtained. It starts with making an initial guess for the square root, then dividing the number (in this case, 106) by this guess, and averaging the result with the guess. This process is repeated with the new value until the desired level of precision is achieved.
Step-by-Step Long Division Example
Let’s start with an initial guess of 10 for √106. We divide 106 by 10, getting 10.6. The average of 10 and 10.6 is 10.3. We then divide 106 by 10.3, getting approximately 10.29. Averaging 10.3 and 10.29 gives us 10.295, which is closer to the actual square root of 106. This process can be continued for even greater precision.
Method 3: Using Algebraic Manipulation
For numbers that are not perfect squares, algebraic manipulation can sometimes simplify the calculation or provide an exact expression for the square root. However, for a number like 106, which does not have an obvious factorization that simplifies its square root, this method may not yield a straightforward numerical answer without resorting to approximation techniques.
Expression as a Radical
In some cases, square roots can be expressed exactly using radical notation. For example, the square root of 100 is 10, and the square root of 6 can be expressed as √6. Thus, √106 could be thought of in relation to √100 and √6, but since 106 is not a product of 100 and 6 in a manner that simplifies its square root, we look at it as a separate entity, √106.
Method 4: Using the Babylonian Method
The Babylonian method is an ancient algorithm for computing the square root of a number. It is an iterative method that uses successive approximations to find the square root. The formula for this method is (x_{n+1} = \frac{1}{2}(x_n + \frac{S}{x_n})), where (S) is the number for which we are finding the square root (106 in this case), and (x_n) is the current estimate of the square root.
Applying the Babylonian Method
Starting with an initial guess, say (x_0 = 10), we apply the formula iteratively. For (x_0 = 10), (x_1 = \frac{1}{2}(10 + \frac{106}{10}) = \frac{1}{2}(10 + 10.6) = 10.3). Continuing this process with (x_1 = 10.3), we calculate (x_2 = \frac{1}{2}(10.3 + \frac{106}{10.3})), which gives a more precise value.
Method 5: Using a Computer Program or Script
In today’s digital age, another method to calculate the square root of 106 is by using a computer program or script. Most programming languages have built-in functions for mathematical operations, including calculating square roots. For example, in Python, one can use the math.sqrt() function to find the square root of a number.
Python Example
In Python, calculating the square root of 106 can be as simple as importing the math module and using the sqrt function: import math; print(math.sqrt(106)). This will output the square root of 106 to a high degree of precision.
Key Points
- The square root of 106 can be calculated using various methods, including calculators, long division, algebraic manipulation, the Babylonian method, and computer programs.
- Each method has its own level of precision and complexity, ranging from quick approximations to more labor-intensive calculations.
- The long division and Babylonian methods allow for iterative refinement of the square root value.
- Computer programs and calculators provide quick and precise calculations, leveraging built-in mathematical functions.
- Understanding the different methods for calculating square roots can provide insight into mathematical concepts and historical calculation techniques.
What is the most accurate method for calculating the square root of 106?
+The most accurate method depends on the tools available and the desired level of precision. For most purposes, using a calculator or a computer program will provide the most accurate and quickest result.
How does the Babylonian method compare to the long division method in terms of efficiency?
+The Babylonian method is generally more efficient and converges faster to the actual square root than the long division method, making it a preferred choice for iterative calculations.
Can the square root of 106 be expressed as a simple fraction or decimal?
+No, the square root of 106 is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation goes on indefinitely without repeating.