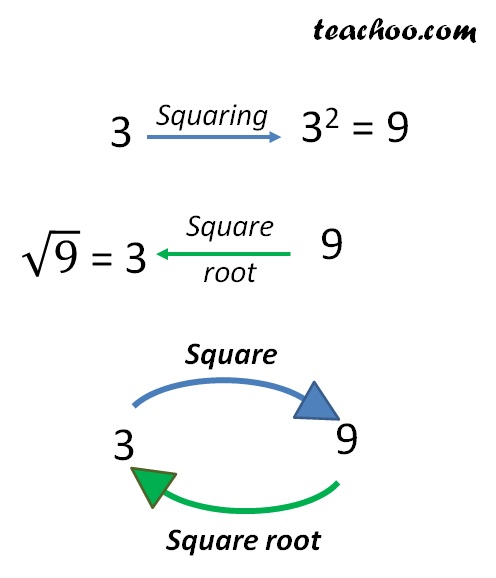
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For instance, the square root of 16 is 4, because 4 multiplied by 4 equals 16. Finding square roots is a fundamental operation in mathematics, and there are several methods to achieve this, each with its own set of applications and advantages. Below, we explore five primary methods for finding square roots, highlighting their procedures, benefits, and the contexts in which they are most appropriately used.
Understanding the Importance of Square Roots
Before diving into the methods, it’s essential to understand why square roots are important. They are crucial in various mathematical operations, including algebra, geometry, and calculus. Moreover, square roots have numerous real-world applications, such as in physics, engineering, and finance. The ability to find square roots efficiently is, therefore, a fundamental skill in many fields.
1. Using a Calculator
The most straightforward method to find a square root is by using a calculator. Almost all calculators have a square root button, denoted by the symbol √. This method is quick, easy, and highly accurate, making it the preferred choice for most calculations, especially in exams or professional settings where speed and precision are critical. For example, to find the square root of 25 using a calculator, you would simply type “√25” and the calculator would display “5” as the result.
Manual Calculation Methods

While calculators offer convenience, understanding manual methods for finding square roots is essential for a deeper comprehension of mathematics and for situations where calculators are not available. The following methods are commonly used for manual calculations.
2. Prime Factorization
Prime factorization involves breaking down a number into its prime factors and then finding the square root. This method is particularly useful for perfect squares. For instance, to find the square root of 36, you would first factorize 36 into its prime factors: 36 = 2 * 2 * 3 * 3. Then, you would group the factors in pairs: (2*2) * (3*3), which simplifies to 2*3 = 6. Therefore, the square root of 36 is 6. This method can be time-consuming for larger numbers but provides a clear understanding of the mathematical principles involved.
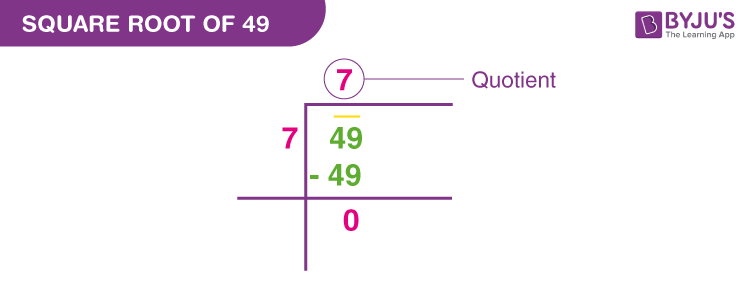
3. Long Division Method
The long division method for finding square roots is a bit complex but can be used for both perfect and imperfect squares. It involves a series of steps where the number is divided by a series of perfect squares, and the remainders are used to find the next digit of the square root. This method requires patience and practice to master but can be very effective for finding square roots manually. It’s a method often taught in schools to help students understand the concept of square roots more deeply.
4. Babylonian Method
The Babylonian method, also known as Heron’s method, is an ancient algorithm for computing the square root of a number. It is an iterative method that refines an initial guess for the square root until it is accurate enough. The formula for this method is x_{n+1} = (x_n + S/x_n) / 2, where S is the number for which you are finding the square root, and x_n is the current estimate of the square root. This method is surprisingly efficient and can be used to find square roots to a high degree of accuracy with just a few iterations.
5. Estimation and Refinement
Estimation and refinement is a simple, intuitive method that involves making an initial guess for the square root and then refining it. For example, to find the square root of 40, you might start by noting that the square root of 36 is 6 and the square root of 49 is 7. Since 40 is between 36 and 49, its square root must be between 6 and 7. You could then try 6.5 as a guess, square it to get 42.25, and realize that the square root of 40 must be slightly less than 6.5. This process can be repeated until a satisfactory level of accuracy is achieved.
Key Points
- The choice of method for finding a square root depends on the context, the tools available, and the desired level of accuracy.
- Calculators provide the quickest and most accurate results but may not always be available.
- Manual methods, such as prime factorization, long division, the Babylonian method, and estimation, offer a deeper understanding of mathematical principles and can be essential in certain situations.
- Understanding square roots is crucial for various mathematical operations and real-world applications.
- Practice and familiarity with different methods can enhance proficiency in finding square roots.
| Method | Description | Accuracy | Speed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calculator | Using a calculator's square root function | High | Fast |
| Prime Factorization | Breaking down a number into prime factors | High for perfect squares | Varies |
| Long Division | A series of divisions to find the square root | High | Slow |
| Babylonian Method | An iterative algorithm for refining an estimate | Very High | Fast with iterations |
| Estimation and Refinement | Making an initial guess and refining it | Varies | Fast for initial estimates |
In conclusion, finding square roots is a versatile operation that can be approached through various methods, each suited to different contexts and requirements. Whether using a calculator for speed and accuracy, or manual methods for a deeper understanding of mathematical principles, being proficient in finding square roots can significantly enhance one's mathematical and problem-solving capabilities.
What is the most accurate method for finding square roots?
+The most accurate method for finding square roots is often considered to be the Babylonian method, due to its iterative nature that refines estimates to a high degree of accuracy with minimal iterations.
When should I use the prime factorization method?
+The prime factorization method is particularly useful for finding the square roots of perfect squares, as it allows for a straightforward calculation by grouping prime factors into pairs.
Is there a method for finding square roots without a calculator that is both fast and accurate?
+Yes, the Babylonian method can be both fast and accurate for finding square roots without a calculator. It involves an initial guess and then iterative refinements, making it efficient and precise with practice.
How do I choose the best method for finding square roots in different situations?
+The choice of method depends on the availability of tools, the desired level of accuracy, and the time available for the calculation. For quick estimates, estimation and refinement or using a calculator might be best. For precise calculations without a calculator, the Babylonian method or long division could be more appropriate.
Are there any real-world applications of square roots?
+Yes, square roots have numerous real-world applications in physics, engineering, finance, and more. For example, in physics, the trajectory of projectiles can be calculated using square roots, and in finance, square roots are used in models for pricing options.