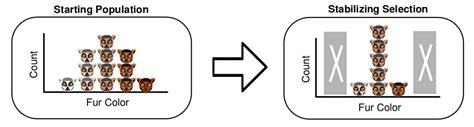
Stabilizing selection, a fundamental concept in evolutionary biology, refers to the process by which natural selection acts to reduce genetic variation in a population, thereby maintaining the average trait value. This phenomenon occurs when individuals with extreme trait values, either higher or lower than the mean, have lower fitness compared to those with trait values closer to the population mean. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of stabilizing selection, exploring its mechanisms, examples, and implications for population dynamics.
Key Points
- Stabilizing selection reduces genetic variation by favoring individuals with average trait values.
- This process is driven by the decreased fitness of individuals with extreme trait values.
- Examples of stabilizing selection include optimal foraging behaviors and temperature regulation in organisms.
- Stabilizing selection can lead to the maintenance of genetic polymorphism within a population.
- The strength and direction of stabilizing selection can be influenced by environmental factors.
Understanding Stabilizing Selection
Stabilizing selection is often contrasted with directional selection, which favors one extreme of a trait over the other, leading to an increase in the average trait value. In contrast, stabilizing selection acts to maintain the status quo, ensuring that the population’s average trait value remains relatively constant. This is achieved through the differential survival and reproduction of individuals based on their trait values. For instance, in a population of birds, individuals with beak sizes that are too large or too small may have difficulty foraging for food, while those with average beak sizes are better adapted to their environment.
Mechanisms of Stabilizing Selection
The mechanisms underlying stabilizing selection are multifaceted and can be attributed to various factors, including environmental pressures, genetic constraints, and demographic processes. One key mechanism involves the trade-off between different components of fitness, such as survival and reproduction. For example, in a population of mammals, individuals with high reproductive rates may have lower survival rates due to increased energy expenditure, while those with lower reproductive rates may have higher survival rates but reduced overall fitness. This trade-off can lead to stabilizing selection, as individuals with intermediate reproductive rates may have the highest overall fitness.
| Selection Type | Description | Effect on Trait Value |
|---|---|---|
| Directional Selection | Favors one extreme of a trait | Increases average trait value |
| Stabilizing Selection | Favors average trait value | Maintains average trait value |
| Disruptive Selection | Favors both extremes of a trait | Increases variation in trait value |
Examples of Stabilizing Selection
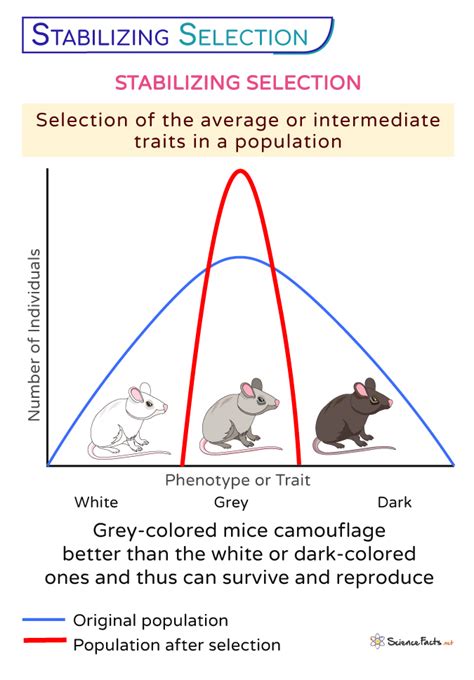
Stabilizing selection can be observed in various biological systems, ranging from simple organisms to complex ecosystems. One classic example is the evolution of the peppered moth in England. Prior to the Industrial Revolution, the moths had a light-colored, speckled appearance, allowing them to blend in with lichen-covered tree bark. However, with the increase in air pollution, the trees became darker, and a genetic variation in the moth population, resulting in dark-colored individuals, became more common. This led to an example of directional selection, as the dark-colored moths were better camouflaged on the dark tree trunks. However, in areas where the trees remained light-colored, stabilizing selection acted to maintain the original light-colored trait, as individuals with intermediate colors were better adapted to their environment.
Implications of Stabilizing Selection
The implications of stabilizing selection are far-reaching, influencing population dynamics, species evolution, and ecosystem functioning. By reducing genetic variation, stabilizing selection can lead to a decrease in the population’s ability to adapt to changing environments. However, it can also maintain genetic polymorphism, allowing populations to respond to future selection pressures. Furthermore, stabilizing selection can have significant effects on the evolution of species interactions, such as predator-prey relationships, where the maintenance of optimal trait values can influence the dynamics of these interactions.
What is the primary mechanism driving stabilizing selection?
+The primary mechanism driving stabilizing selection is the decreased fitness of individuals with extreme trait values, leading to the favoring of individuals with average trait values.
Can stabilizing selection lead to the loss of genetic variation?
+Yes, stabilizing selection can lead to a reduction in genetic variation, as individuals with extreme trait values are selected against, reducing the overall genetic diversity of the population.
What is the difference between directional and stabilizing selection?
+Directional selection favors one extreme of a trait, leading to an increase in the average trait value, while stabilizing selection favors the average trait value, maintaining the status quo.
In conclusion, stabilizing selection plays a crucial role in shaping the evolution of populations, maintaining the average trait value, and reducing genetic variation. By understanding the mechanisms and implications of stabilizing selection, we can gain insights into the complex dynamics of evolutionary processes and the intricate relationships between organisms and their environments. As we continue to explore the intricacies of stabilizing selection, we may uncover new perspectives on the evolution of species and the functioning of ecosystems, ultimately deepening our appreciation for the fascinating world of biology.