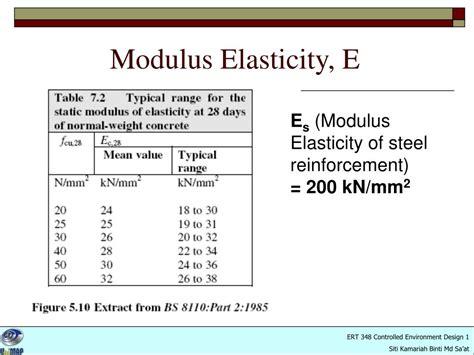
The modulus of elasticity, also known as Young's modulus, is a fundamental property of materials that describes their ability to withstand stress and strain. In the context of steel, the modulus of elasticity is a critical parameter that engineers and designers use to calculate the deformation of steel structures under various loads. The steel modulus of elasticity value is typically denoted by the symbol E and is measured in units of pascals (Pa) or gigapascals (GPa).
In general, the modulus of elasticity of steel is around 200 GPa, which is significantly higher than many other materials. This high value indicates that steel is a relatively stiff material that can withstand substantial stresses without deforming excessively. However, it's essential to note that the actual value of the modulus of elasticity can vary depending on the specific type of steel, its composition, and the manufacturing process used to produce it.
Key Points
- The steel modulus of elasticity value is approximately 200 GPa.
- This value can vary depending on the type of steel, its composition, and manufacturing process.
- Understanding the modulus of elasticity is crucial for designing and analyzing steel structures.
- Steel's high modulus of elasticity makes it a popular choice for construction and engineering applications.
- Accurate calculation of the modulus of elasticity is essential for ensuring the safety and reliability of steel structures.
Factors Influencing the Modulus of Elasticity of Steel
The modulus of elasticity of steel is influenced by several factors, including the type of steel, its chemical composition, and the manufacturing process. For example, carbon steel, which is one of the most common types of steel, typically has a modulus of elasticity around 200-210 GPa. In contrast, stainless steel, which contains a higher percentage of chromium and nickel, can have a slightly lower modulus of elasticity, ranging from 190-200 GPa.
In addition to the type of steel, the chemical composition can also affect the modulus of elasticity. For instance, the presence of alloying elements such as manganese, silicon, and chromium can increase the modulus of elasticity, while the presence of impurities such as sulfur and phosphorus can decrease it. The manufacturing process, including the rolling and heat treatment conditions, can also impact the modulus of elasticity.
Experimental Methods for Determining the Modulus of Elasticity
There are several experimental methods available for determining the modulus of elasticity of steel, including tensile testing, bending testing, and ultrasonic testing. Tensile testing, which involves stretching a steel specimen to failure, is one of the most common methods used to determine the modulus of elasticity. This method provides a direct measurement of the steel’s ability to withstand stress and strain.
Bending testing, which involves applying a load to a steel beam and measuring its deflection, is another method used to determine the modulus of elasticity. This method is particularly useful for determining the modulus of elasticity of steel beams and plates. Ultrasonic testing, which involves measuring the speed of sound waves through the steel, is a non-destructive method that can be used to determine the modulus of elasticity.
| Steel Type | Modulus of Elasticity (GPa) |
|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | 200-210 |
| Stainless Steel | 190-200 |
| Alloy Steel | 195-205 |
| High-Strength Steel | 205-215 |
Practical Applications of the Modulus of Elasticity

The modulus of elasticity has numerous practical applications in the design and analysis of steel structures. For example, it is used to calculate the deflection of steel beams and plates under various loads, as well as the stress and strain in steel members subject to tension, compression, and bending. The modulus of elasticity is also used to determine the natural frequency of steel structures, which is critical for ensuring their stability and resistance to vibration.
In addition to its use in the design and analysis of steel structures, the modulus of elasticity is also used in the development of new steel products and materials. For instance, researchers use the modulus of elasticity to evaluate the properties of new steel alloys and to optimize their composition and manufacturing process.
Limitations and Challenges
While the modulus of elasticity is a fundamental property of steel, there are several limitations and challenges associated with its measurement and application. One of the main challenges is the variability in the modulus of elasticity values reported in the literature, which can be attributed to differences in the testing methods, specimen preparation, and data analysis. Additionally, the modulus of elasticity can be affected by various factors, such as temperature, humidity, and loading rate, which can impact its accuracy and reliability.
To address these challenges, researchers and engineers use various techniques, such as statistical analysis and machine learning algorithms, to improve the accuracy and reliability of the modulus of elasticity values. Furthermore, the development of new testing methods and instruments, such as advanced ultrasonic testing and digital image correlation, has enabled more precise and efficient measurement of the modulus of elasticity.
What is the typical value of the modulus of elasticity for steel?
+The typical value of the modulus of elasticity for steel is around 200 GPa.
What factors can influence the modulus of elasticity of steel?
+The modulus of elasticity of steel can be influenced by factors such as the type of steel, chemical composition, and manufacturing process.
What are the practical applications of the modulus of elasticity in steel design and analysis?
+The modulus of elasticity is used to calculate the deflection of steel beams and plates, stress and strain in steel members, and natural frequency of steel structures.
In conclusion, the steel modulus of elasticity value is a critical parameter that plays a vital role in the design and analysis of steel structures. Understanding the factors that influence the modulus of elasticity, as well as its practical applications, is essential for ensuring the safety and reliability of these structures. By addressing the limitations and challenges associated with the measurement and application of the modulus of elasticity, researchers and engineers can continue to develop new steel products and materials that meet the demands of modern construction and engineering applications.