Student mental health has become a pressing concern in educational institutions worldwide. The World Health Organization (WHO) reports that approximately 50% of mental health issues start by the age of 14, but most cases go untreated. The prevalence of mental health problems among students is a complex issue, influenced by a combination of factors including academic pressure, social media, and societal expectations. As a result, it is essential to address this issue through a multifaceted approach that involves educators, policymakers, and mental health professionals.
The impact of mental health issues on students' academic performance and overall well-being cannot be overstated. Research has shown that students experiencing mental health problems are more likely to struggle with academic responsibilities, leading to decreased grades, increased absenteeism, and higher dropout rates. Furthermore, untreated mental health issues can have long-term consequences, including increased risk of substance abuse, chronic diseases, and even suicidal behaviors. Therefore, it is crucial to prioritize student mental health and provide accessible, evidence-based support services to promote their overall well-being.
Key Points
- Student mental health is a significant concern, with 50% of mental health issues starting by age 14
- Academic pressure, social media, and societal expectations contribute to mental health problems among students
- Untreated mental health issues can lead to decreased academic performance, increased absenteeism, and higher dropout rates
- Providing accessible, evidence-based support services is crucial to promoting student mental health and overall well-being
- Collaboration between educators, policymakers, and mental health professionals is essential to address student mental health issues effectively
Causes and Risk Factors
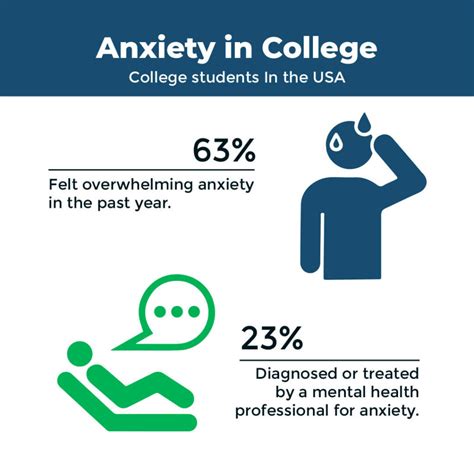
The causes of mental health problems among students are diverse and multifaceted. Academic pressure is a significant contributor, with students often feeling overwhelmed by the demands of their coursework, assignments, and exams. Social media also plays a role, as it can create unrealistic expectations and promote comparison, leading to decreased self-esteem and increased stress levels. Additionally, societal expectations and the pressure to succeed can exacerbate mental health issues, particularly among students from marginalized or underrepresented groups.
Socio-Economic Factors
Socio-economic factors, such as poverty, inequality, and lack of access to resources, can also contribute to mental health problems among students. Students from low-income backgrounds may face additional stressors, including food insecurity, housing instability, and limited access to healthcare, which can exacerbate mental health issues. Furthermore, students from marginalized communities may experience discrimination, stigma, and social isolation, which can further compound their mental health problems.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Academic Pressure | Overwhelming demands of coursework, assignments, and exams |
| Social Media | Unrealistic expectations, comparison, and decreased self-esteem |
| Socio-Economic Factors | Poverty, inequality, lack of access to resources, and discrimination |

Consequences of Untreated Mental Health Issues

The consequences of untreated mental health issues among students can be severe and long-lasting. Research has shown that students experiencing mental health problems are more likely to experience decreased academic performance, increased absenteeism, and higher dropout rates. Furthermore, untreated mental health issues can lead to increased risk of substance abuse, chronic diseases, and even suicidal behaviors. Therefore, it is crucial to prioritize student mental health and provide accessible, evidence-based support services to promote their overall well-being.
Early Intervention and Support
Early intervention and support are critical in addressing student mental health issues. Schools and educational institutions can play a vital role in promoting student mental health by providing accessible, evidence-based support services, such as counseling, therapy, and peer support groups. Additionally, educators can help identify early warning signs of mental health problems, such as changes in behavior, mood, or academic performance, and refer students to appropriate support services.
In conclusion, student mental health is a pressing concern that requires a multifaceted approach to address. By acknowledging the complex interplay of factors contributing to mental health issues, prioritizing early intervention and support, and providing accessible, evidence-based support services, we can promote student mental health and overall well-being. As educators, policymakers, and mental health professionals, it is our responsibility to work together to create a supportive and inclusive environment that fosters the mental health and well-being of all students.
What are the most common mental health issues affecting students?
+The most common mental health issues affecting students include anxiety, depression, substance abuse, and eating disorders.
How can educators and policymakers support student mental health?
+Edcuators and policymakers can support student mental health by providing accessible, evidence-based support services, promoting early intervention and support, and creating a supportive and inclusive environment that fosters mental health and well-being.
What are the consequences of untreated mental health issues among students?
+The consequences of untreated mental health issues among students can include decreased academic performance, increased absenteeism, higher dropout rates, and increased risk of substance abuse, chronic diseases, and suicidal behaviors.



