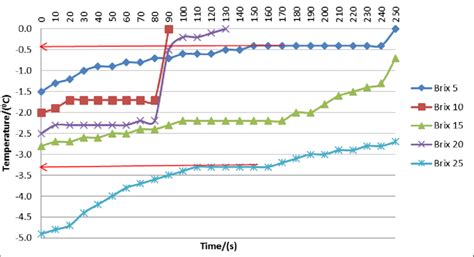
The phenomenon of sucrose melting is a complex process that has garnered significant attention in the realms of food science and materials engineering. At its core, sucrose, commonly known as table sugar, undergoes a phase transition from a solid to a liquid state when subjected to increasing temperatures. This process, while seemingly straightforward, is influenced by a multitude of factors including the purity of the sucrose, the presence of impurities, and the rate of heating. Understanding the sucrose melting time is crucial for various industrial applications, particularly in the manufacturing of foods, beverages, and pharmaceuticals, where precise control over the physical state of sucrose is necessary.
Historically, the study of sucrose melting has been approached from a thermodynamic perspective, focusing on the relationship between temperature, entropy, and the Gibbs free energy of the system. The melting point of sucrose, approximately 160°C to 180°C, is not a fixed value but rather a range that can vary based on the conditions under which the sucrose is heated. This variability stems from the complex interplay of intermolecular forces within the sucrose crystal lattice, which must be overcome for the solid to melt. The process of melting is also accompanied by the absorption of latent heat, further complicating the dynamics of the phase transition.
Key Points
- Sucrose melting is a complex process influenced by purity, impurities, and heating rate.
- The melting point of sucrose ranges from approximately 160°C to 180°C.
- Understanding sucrose melting time is crucial for industrial applications in food, beverage, and pharmaceutical manufacturing.
- The process involves overcoming intermolecular forces within the sucrose crystal lattice and absorbing latent heat.
- Precise control over sucrose's physical state is necessary for various manufacturing processes.
The Science Behind Sucrose Melting
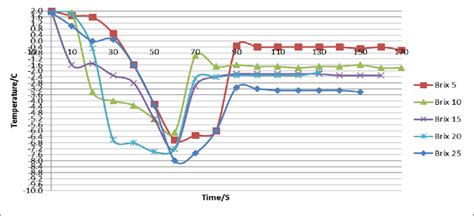
From a scientific standpoint, the melting of sucrose can be analyzed through the lens of thermodynamics and kinetics. The thermodynamic approach provides insights into the equilibrium properties of the system, including the melting point and the heat of fusion. However, the kinetics of melting, which deals with the rates of phase transition, is equally important, especially in processes where the heating rate can significantly influence the final product’s quality and consistency.
Factors Influencing Sucrose Melting Time
Several factors can influence the melting time of sucrose, including its purity, the presence of moisture or other impurities, and the method of heating. High-purity sucrose tends to have a more consistent and predictable melting behavior compared to sucrose contaminated with impurities. The presence of water, in particular, can significantly lower the melting point of sucrose due to the formation of a eutectic mixture, where the mixture’s melting point is lower than that of either component alone. The heating method, whether it be through conduction, convection, or radiation, also plays a critical role, as it affects the rate at which heat is transferred to the sucrose.
| Factor | Influence on Melting Time |
|---|---|
| Purity of Sucrose | High purity: more consistent melting behavior |
| Presence of Impurities | Moisture and other impurities can lower the melting point |
| Heating Method | Affects the rate of heat transfer and thus the melting time |
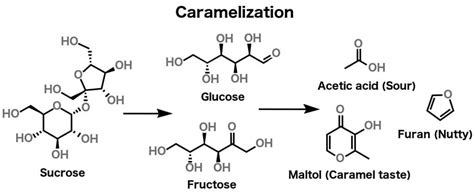
Applications and Implications

The understanding and control of sucrose melting time have significant implications for various industries. In food manufacturing, precise control over the melting of sucrose is critical for producing consistent products, such as candies, chocolates, and baked goods. In pharmaceutical applications, sucrose is used as an excipient in tablet formulations, where its melting behavior can affect the drug’s release profile. Furthermore, research into sucrose melting can provide insights into the broader category of carbohydrate phase transitions, contributing to advancements in materials science and biotechnology.
Future Perspectives
Looking forward, advancements in understanding sucrose melting will likely be driven by interdisciplinary research combining insights from food science, materials engineering, and physical chemistry. The development of new technologies and methodologies for controlling and predicting the melting behavior of sucrose will be crucial, especially as industries seek more efficient, sustainable, and quality-oriented production processes. Moreover, exploring the potential of sucrose and its derivatives in novel applications, such as biodegradable materials and pharmaceutical carriers, presents exciting avenues for future research and development.
What is the typical melting point range of sucrose?
+The typical melting point range of sucrose is approximately 160°C to 180°C, though this can vary based on the purity of the sucrose and the presence of impurities.
How does the presence of moisture affect the melting point of sucrose?
+The presence of moisture can significantly lower the melting point of sucrose by forming a eutectic mixture, where the melting point of the mixture is lower than that of pure sucrose.
What are some industrial applications where understanding sucrose melting time is crucial?
+Understanding sucrose melting time is crucial in the manufacturing of foods, beverages, and pharmaceuticals, where precise control over the physical state of sucrose is necessary for producing consistent and high-quality products.