Sulfur, a yellow, brittle, nonmetallic element, is one of the most fascinating and versatile substances in the periodic table. With its unique properties and widespread applications, sulfur has been a crucial component in various industries, from chemistry and pharmaceuticals to agriculture and energy. In this article, we will delve into the world of sulfur, exploring its history, properties, and uses, as well as some interesting and lesser-known facts about this essential element.
Introduction to Sulfur
Sulfur is the 16th most abundant element in the Earth’s crust, making up about 0.034% of the planet’s soil and rocks. It is found naturally in its elemental form, as well as in the form of sulfide and sulfate minerals. Sulfur has been known and utilized by humans for thousands of years, with ancient civilizations using it for various purposes, including medicine, matches, and gunpowder. Today, sulfur is an essential component in the production of numerous products, including fertilizers, pesticides, and pharmaceuticals.
Key Points
- Sulfur is a yellow, brittle, nonmetallic element with a unique smell and taste.
- It is the 16th most abundant element in the Earth's crust and is found naturally in its elemental form, as well as in the form of sulfide and sulfate minerals.
- Sulfur has been known and utilized by humans for thousands of years, with ancient civilizations using it for various purposes, including medicine, matches, and gunpowder.
- Today, sulfur is an essential component in the production of numerous products, including fertilizers, pesticides, and pharmaceuticals.
- Sulfur has a number of unique properties, including its ability to form a wide range of compounds and its high reactivity with other elements.
Physical and Chemical Properties of Sulfur

Sulfur is a yellow, brittle, nonmetallic element with a unique smell and taste. It has a melting point of 112.8°C and a boiling point of 444.6°C, making it one of the few elements that is solid at room temperature. Sulfur is also highly reactive, forming a wide range of compounds with other elements, including oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon. Its high reactivity and ability to form complex molecules make sulfur an essential component in many industrial processes.
Sulfur Compounds and Their Applications
Sulfur forms a wide range of compounds, including sulfides, sulfates, and sulfonates. These compounds have numerous applications in various industries, including agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and energy. For example, sulfur dioxide (SO2) is used as a preservative in food and wine, while sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is used in the production of fertilizers and pesticides. Sulfur-based compounds are also used in the production of pharmaceuticals, such as antibiotics and antifungals.
| Compound | Application |
|---|---|
| Sulfur dioxide (SO2) | Preservative in food and wine |
| Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) | Production of fertilizers and pesticides |
| Sulfonates | Production of pharmaceuticals, such as antibiotics and antifungals |

Environmental and Health Impacts of Sulfur
While sulfur is an essential component in many industrial processes, it can also have negative environmental and health impacts. The burning of fossil fuels, such as coal and oil, releases sulfur dioxide (SO2) into the atmosphere, contributing to air pollution and acid rain. Sulfur dioxide can also have negative health impacts, including respiratory problems and cardiovascular disease. Additionally, sulfur-based compounds can be toxic to aquatic life, making it essential to monitor and regulate their use in industrial processes.
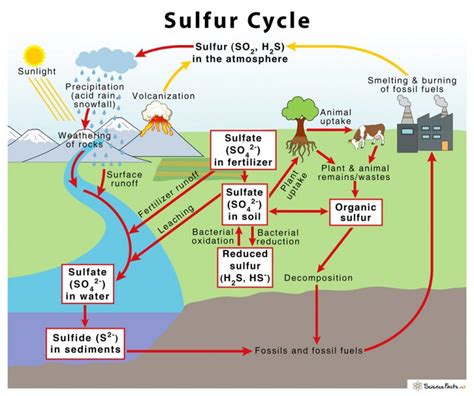
Sulfur in the Environment
Sulfur is a naturally occurring element in the environment, and it plays a crucial role in many ecosystem processes. However, human activities, such as the burning of fossil fuels and the use of sulfur-based fertilizers, have increased the amount of sulfur in the environment, leading to negative impacts on ecosystems. For example, acid rain, which is caused by the release of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere, can have devastating effects on forests, lakes, and wildlife.
What are the main uses of sulfur?
+Sulfur is used in the production of numerous products, including fertilizers, pesticides, and pharmaceuticals. It is also used in the production of matches, gunpowder, and other explosives.
What are the environmental impacts of sulfur?
+The burning of fossil fuels, such as coal and oil, releases sulfur dioxide (SO2) into the atmosphere, contributing to air pollution and acid rain. Sulfur-based compounds can also be toxic to aquatic life, making it essential to monitor and regulate their use in industrial processes.
What are the health impacts of sulfur?
+Sulfur dioxide can have negative health impacts, including respiratory problems and cardiovascular disease. Additionally, sulfur-based compounds can be toxic to humans, making it essential to handle them with care and follow proper safety protocols.
In conclusion, sulfur is a fascinating and versatile element that plays a crucial role in many industrial processes. Its unique properties and ability to form a wide range of compounds make it an essential component in the production of numerous products. However, it is also important to note that sulfur can have negative environmental and health impacts, making it essential to monitor and regulate its use in industrial processes. By understanding the properties, uses, and impacts of sulfur, we can work to minimize its negative effects and maximize its benefits.