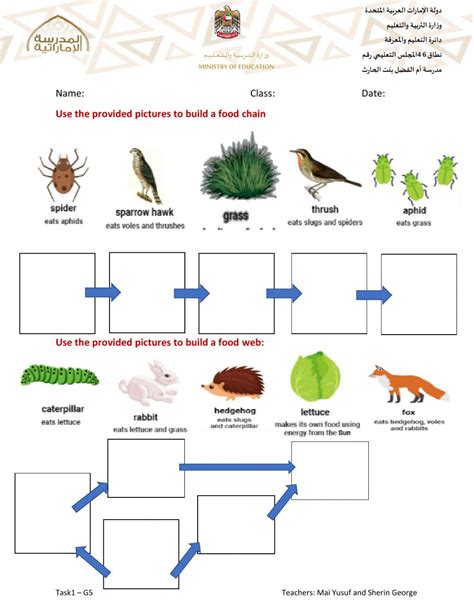
The Sundaland region, comprising the Malay Peninsula, Indonesian Archipelago, and surrounding areas, is home to a diverse array of flora and fauna. The food chain in this region is complex and fascinating, with various species playing crucial roles in maintaining the delicate balance of the ecosystem. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the Sundaland food chain, exploring five key ways it functions.
Key Points
- The Sundaland food chain is characterized by a diverse array of species, including mangroves, proboscis monkeys, and saltwater crocodiles.
- Primary producers, such as phytoplankton and seagrasses, form the base of the food chain, providing energy and nutrients for higher-trophic level species.
- Herbivores, like the proboscis monkey, play a vital role in dispersing seeds and maintaining forest diversity.
- Carnivores, including the saltwater crocodile and clouded leopard, regulate prey populations and maintain the balance of the ecosystem.
- Decomposers, such as fungi and bacteria, break down organic matter, recycling nutrients and maintaining soil fertility.
Primary Production and Energy Flow

The Sundaland food chain begins with primary producers, such as phytoplankton, seagrasses, and mangroves. These species form the base of the food chain, converting sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. Phytoplankton, for example, are microscopic plants that drift in the water column, producing organic compounds that support the growth of zooplankton and other herbivores. Seagrasses and mangroves, on the other hand, provide habitat and food for a variety of species, from fish and invertebrates to birds and mammals.
Trophic Level Interactions
As energy flows through the food chain, it is transferred from one trophic level to the next. Herbivores, like the proboscis monkey, feed on primary producers, while carnivores, such as the saltwater crocodile, prey on herbivores. This process of energy transfer is inefficient, with only about 10% of energy being passed from one trophic level to the next. However, this inefficiency allows for the coexistence of diverse species, each playing a unique role in the ecosystem.
| Trophic Level | Species Example | Energy Source |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Producer | Phytoplankton | Sunlight |
| Herbivore | Proboscis Monkey | Seagrasses and Mangroves |
| Carnivore | Saltwater Crocodile | Herbivores (e.g., Proboscis Monkey) |
Predator-Prey Dynamics
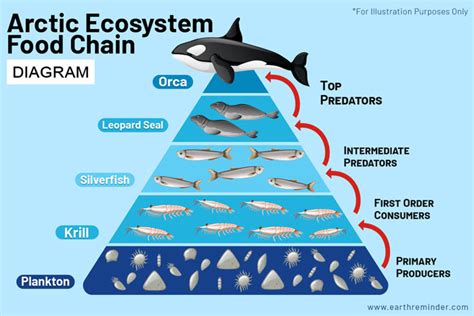
Predator-prey dynamics play a crucial role in regulating populations and maintaining the balance of the Sundaland ecosystem. The saltwater crocodile, for example, is an apex predator that preys on a variety of species, from fish and crustaceans to birds and mammals. This predation pressure helps to regulate prey populations, preventing any one species from dominating the ecosystem. In turn, the presence of predators like the saltwater crocodile influences the behavior and ecology of prey species, such as the proboscis monkey, which must adapt to avoid predation.
Decomposition and Nutrient Cycling
Decomposers, such as fungi and bacteria, play a vital role in breaking down organic matter and recycling nutrients in the Sundaland ecosystem. These microorganisms decompose dead plant and animal material, releasing nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus back into the environment. This process of nutrient cycling is essential for maintaining soil fertility and supporting the growth of primary producers, which in turn support the entire food chain.
What is the role of primary producers in the Sundaland food chain?
+Primary producers, such as phytoplankton, seagrasses, and mangroves, form the base of the food chain, converting sunlight into energy through photosynthesis and providing energy and nutrients for higher-trophic level species.
How do predators influence prey populations in the Sundaland ecosystem?
+Predators, such as the saltwater crocodile, regulate prey populations through predation pressure, preventing any one species from dominating the ecosystem and influencing the behavior and ecology of prey species.
What is the importance of decomposers in the Sundaland food chain?
+Decomposers, such as fungi and bacteria, break down organic matter and recycle nutrients, maintaining soil fertility and supporting the growth of primary producers, which in turn support the entire food chain.
In conclusion, the Sundaland food chain is a complex and fascinating system, with various species playing crucial roles in maintaining the delicate balance of the ecosystem. By understanding the intricacies of this food chain, we can better appreciate the importance of conservation and management efforts aimed at preserving the region’s biodiversity and ecosystem health.