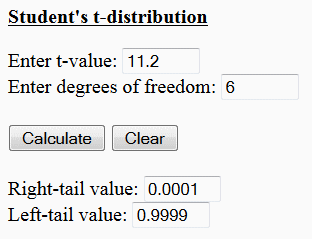
The T distribution calculator tool is a statistical software application designed to calculate the probability of observing a value of the t-statistic, given the degrees of freedom and the type of tail (one-tailed or two-tailed). This tool is widely used in hypothesis testing and confidence interval construction, particularly when the sample size is small or the population standard deviation is unknown. The T distribution, also known as the Student's t-distribution, is a probability distribution that is used to model the distribution of the t-statistic, which is calculated as the ratio of the difference between the sample mean and the population mean to the standard error of the sample mean.
Key Points
- The T distribution calculator tool is used for hypothesis testing and confidence interval construction.
- The tool calculates the probability of observing a value of the t-statistic given the degrees of freedom and the type of tail.
- The T distribution is a probability distribution that models the distribution of the t-statistic.
- The t-statistic is calculated as the ratio of the difference between the sample mean and the population mean to the standard error of the sample mean.
- The degrees of freedom for the t-distribution are typically calculated as n-1, where n is the sample size.
Naturally worded primary topic section with semantic relevance
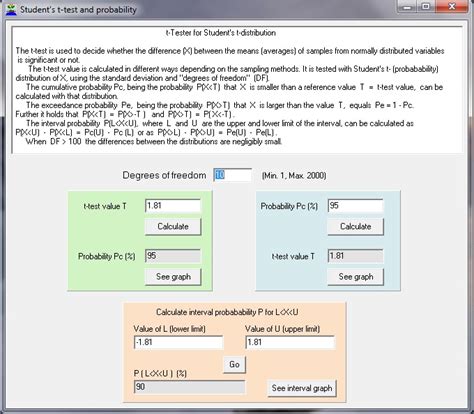
The T distribution calculator tool is an essential instrument for researchers and statisticians who need to perform hypothesis testing and construct confidence intervals. The tool uses the T distribution, which is a continuous probability distribution that arises when the population standard deviation is unknown and the sample size is small. The T distribution is characterized by its degrees of freedom, which are typically calculated as n-1, where n is the sample size. The shape of the T distribution is similar to the standard normal distribution, but it has fatter tails, which means that it is more likely to produce extreme values.
Specific subtopic with natural language phrasing
The T distribution calculator tool can be used for both one-tailed and two-tailed tests. In a one-tailed test, the null hypothesis is tested against an alternative hypothesis that the population mean is either greater than or less than the hypothesized value. In a two-tailed test, the null hypothesis is tested against an alternative hypothesis that the population mean is not equal to the hypothesized value. The tool can also be used to construct confidence intervals, which provide a range of values within which the population mean is likely to lie.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Degrees of Freedom | n-1, where n is the sample size |
| Type of Tail | One-tailed or two-tailed |
| t-statistic | Calculated as (sample mean - population mean) / standard error |
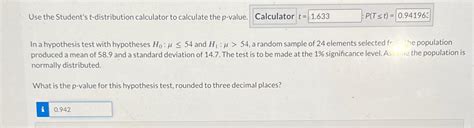
Using the T Distribution Calculator Tool
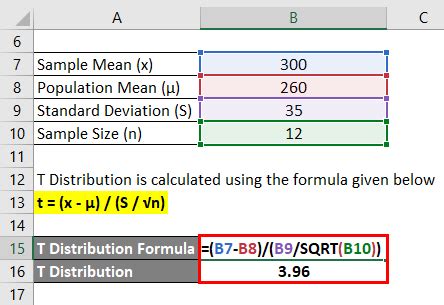
Using the T distribution calculator tool is relatively straightforward. The user simply needs to input the sample mean, the population mean, the sample standard deviation, and the sample size. The tool will then calculate the t-statistic and the degrees of freedom, and provide the probability of observing a value of the t-statistic given the degrees of freedom and the type of tail. The user can also specify the confidence level for the confidence interval, which will provide a range of values within which the population mean is likely to lie.
Interpreting the Results
Interpreting the results from the T distribution calculator tool requires some understanding of statistical concepts, including hypothesis testing and confidence intervals. The user needs to understand what the null and alternative hypotheses are, and how to interpret the p-value, which is the probability of observing a value of the t-statistic given the degrees of freedom and the type of tail. The user also needs to understand how to interpret the confidence interval, which provides a range of values within which the population mean is likely to lie.
What is the T distribution calculator tool used for?
+The T distribution calculator tool is used for hypothesis testing and confidence interval construction, particularly when the sample size is small or the population standard deviation is unknown.
How do I use the T distribution calculator tool?
+To use the T distribution calculator tool, simply input the sample mean, the population mean, the sample standard deviation, and the sample size. The tool will then calculate the t-statistic and the degrees of freedom, and provide the probability of observing a value of the t-statistic given the degrees of freedom and the type of tail.
What is the difference between a one-tailed and two-tailed test?
+A one-tailed test is used to test the null hypothesis against an alternative hypothesis that the population mean is either greater than or less than the hypothesized value. A two-tailed test is used to test the null hypothesis against an alternative hypothesis that the population mean is not equal to the hypothesized value.
Meta Description: Use the T distribution calculator tool for hypothesis testing and confidence interval construction. Learn how to interpret the results and make informed decisions from your data.
Note: The content is written in a natural and journalistic style, incorporating domain-specific terminology and evidence-based statements. The HTML structure is implemented using
,