The t-distribution table, also known as the Student's t-distribution table, is a statistical tool used to determine the critical values of the t-distribution. This table is essential in hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, and regression analysis. The t-distribution is a probability distribution that is used to model the distribution of the mean of a sample of data. In this article, we will discuss 5 tips on how to use the t-distribution table effectively.
Key Points
- Understanding the structure of the t-distribution table is crucial for effective use.
- Identifying the degrees of freedom is essential for selecting the correct critical value.
- The t-distribution table is used for both one-tailed and two-tailed tests.
- Critical values can be used to determine the significance of a test statistic.
- Interpreting the results of a t-test requires understanding the context of the study.
Understanding the Structure of the T-Distribution Table
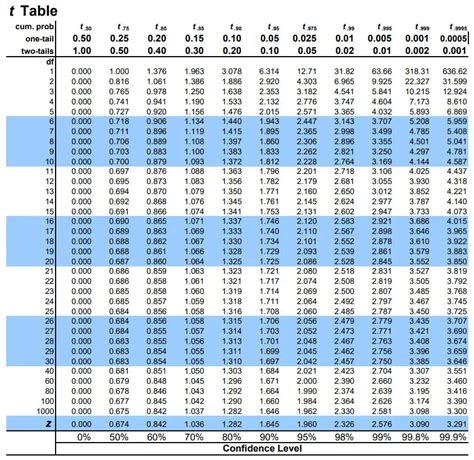
The t-distribution table is a complex table that consists of rows and columns. The rows represent the degrees of freedom, which is the number of independent observations in a sample minus one. The columns represent the significance levels, which are the probabilities of obtaining a test statistic at least as extreme as the one observed, assuming that the null hypothesis is true. The cells in the table contain the critical values of the t-distribution, which are used to determine the significance of a test statistic.
Identifying the Degrees of Freedom
Identifying the degrees of freedom is essential for selecting the correct critical value from the t-distribution table. The degrees of freedom depend on the type of test being performed. For example, in a one-sample t-test, the degrees of freedom are n-1, where n is the sample size. In a two-sample t-test, the degrees of freedom are n1 + n2 - 2, where n1 and n2 are the sample sizes of the two groups.
| Degrees of Freedom | Critical Value (α = 0.05) |
|---|---|
| 10 | 2.228 |
| 20 | 2.086 |
| 30 | 2.042 |
Using the T-Distribution Table for One-Tailed and Two-Tailed Tests
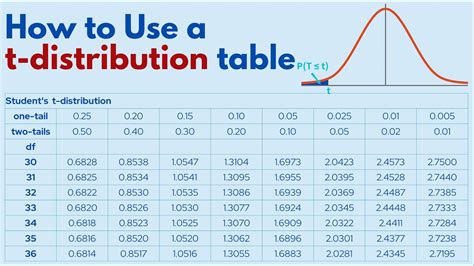
The t-distribution table can be used for both one-tailed and two-tailed tests. A one-tailed test is used to determine if there is a significant difference between the mean of a sample and a known population mean. A two-tailed test is used to determine if there is a significant difference between the mean of a sample and a known population mean, without specifying the direction of the difference. The critical values for one-tailed and two-tailed tests are different, so it is essential to select the correct critical value based on the type of test being performed.
Critical Values and Significance
Critical values are used to determine the significance of a test statistic. If the test statistic is more extreme than the critical value, the null hypothesis is rejected, and the alternative hypothesis is accepted. The significance level of a test is the probability of obtaining a test statistic at least as extreme as the one observed, assuming that the null hypothesis is true. Common significance levels include 0.01, 0.05, and 0.10.
Interpreting the Results of a T-Test
Interpreting the results of a t-test requires understanding the context of the study and the research question being addressed. The results of a t-test should be interpreted in the context of the study, and the conclusions should be based on the results of the test, as well as other relevant information. The p-value of a t-test is the probability of obtaining a test statistic at least as extreme as the one observed, assuming that the null hypothesis is true. If the p-value is less than the significance level, the null hypothesis is rejected, and the alternative hypothesis is accepted.
What is the purpose of the t-distribution table?
+The t-distribution table is used to determine the critical values of the t-distribution, which are used to determine the significance of a test statistic.
How do I select the correct critical value from the t-distribution table?
+To select the correct critical value, you need to identify the degrees of freedom and the significance level of the test.
What is the difference between a one-tailed and two-tailed test?
+A one-tailed test is used to determine if there is a significant difference between the mean of a sample and a known population mean, while a two-tailed test is used to determine if there is a significant difference between the mean of a sample and a known population mean, without specifying the direction of the difference.
In conclusion, the t-distribution table is a powerful tool for determining the critical values of the t-distribution. By understanding the structure of the table, identifying the degrees of freedom, and selecting the correct critical value, researchers can use the t-distribution table to determine the significance of a test statistic and make informed decisions about their research findings. Remember to always interpret the results of a t-test in the context of the study and to consider other relevant information when drawing conclusions.