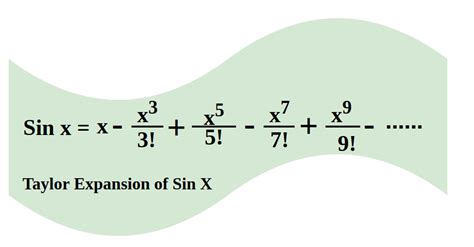
The Taylor expansion of the sine function, denoted as sin(x), is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in the realm of calculus. It provides a way to approximate the value of sin(x) for any given x using an infinite series. This expansion is named after James Gregory and Brook Taylor, who introduced it in the 17th and 18th centuries, respectively. The Taylor series expansion of sin(x) is given by the formula: sin(x) = x - x^3/3! + x^5/5! - x^7/7! +..., where "!" denotes factorial, the product of all positive integers up to that number. Here, we'll explore five ways the Taylor expansion of sin(x) can be utilized or understood, highlighting its significance in mathematics and beyond.
Introduction to Taylor Expansion of Sin(x)
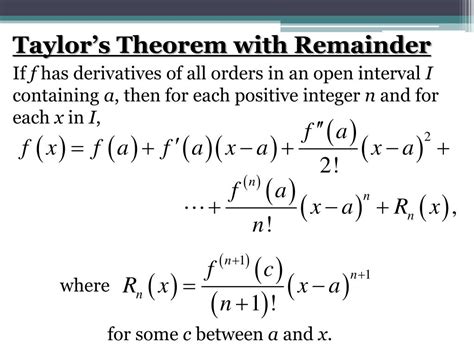
The Taylor expansion of sin(x) around x = 0, also known as the Maclaurin series, is a powerful tool for understanding the behavior of the sine function. It allows for the approximation of sin(x) at any point x by summing up the terms of the series. The more terms included in the sum, the more accurate the approximation will be. This concept is crucial in various fields, including physics, engineering, and computer science, where precise calculations of trigonometric functions are often required.
Mathematical Derivation and Accuracy
The derivation of the Taylor series for sin(x) involves the use of derivatives and the definition of a Taylor series. By calculating the derivatives of sin(x) at x = 0 and applying the Taylor series formula, one can derive the series x - x^3⁄3! + x^5⁄5! - x^7⁄7! +…. The accuracy of the approximation depends on the number of terms used and the value of x. For values of x close to 0, even a few terms can provide a very accurate approximation. However, as x moves away from 0, more terms are needed to achieve the same level of accuracy.
| Number of Terms | Approximation Accuracy |
|---|---|
| 1 term | Low, only accurate for x very close to 0 |
| 3 terms | Medium, accurate for small values of x |
| 5 terms | High, accurate for a wider range of x values |
Applications in Physics and Engineering
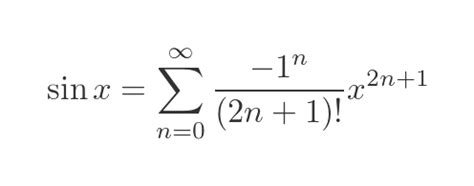
In physics and engineering, the Taylor expansion of sin(x) is used in various applications, including the study of wave patterns, oscillations, and signal processing. For instance, in the analysis of simple harmonic motion, the sine function is pivotal, and its Taylor expansion can be used to model and predict the behavior of oscillating systems. Additionally, in electrical engineering, the Taylor series expansion is crucial for understanding and designing filters and circuits that process sinusoidal signals.
Computational Implementation
From a computational perspective, the Taylor expansion of sin(x) can be implemented in programming languages to calculate the sine of an angle. This approach can be particularly useful in situations where the standard library functions for trigonometric operations are not available or when custom implementation is required for educational purposes. However, it’s worth noting that for most practical applications, the built-in functions for calculating sin(x) in programming languages are highly optimized and should be used for accuracy and efficiency.
Key Points
- The Taylor expansion of sin(x) provides a method for approximating the sine function using an infinite series.
- The series is derived from the definition of a Taylor series and the derivatives of sin(x) at x = 0.
- The accuracy of the approximation depends on the number of terms used and the value of x.
- The Taylor expansion has significant applications in physics, engineering, and computer science.
- It offers a fundamental understanding of the sine function and its behavior around x = 0.
Historical Context and Development
The concept of the Taylor series, including the expansion of sin(x), has a rich historical background. Developed by James Gregory and Brook Taylor in the 17th and 18th centuries, respectively, it laid the foundation for significant advancements in calculus and mathematical analysis. The understanding and application of Taylor series expansions, including that of sin(x), have evolved over time, contributing to the development of modern mathematics and its applications in science and technology.
Evolutionary Developments and Modern Applications
In modern times, the Taylor expansion of sin(x) continues to play a crucial role in various fields. With the advent of computational tools and programming languages, the application of Taylor series has become more accessible and widespread. Furthermore, the development of new mathematical tools and techniques has expanded the scope of Taylor series applications, including areas such as numerical analysis, signal processing, and machine learning. The evolutionary development of the Taylor series concept, including the expansion of sin(x), underscores its enduring significance in the mathematical sciences.
What is the Taylor expansion of sin(x) used for?
+The Taylor expansion of sin(x) is used for approximating the sine function, understanding its behavior, and applying it in various mathematical and scientific contexts, including physics, engineering, and computer science.
How is the Taylor series of sin(x) derived?
+The Taylor series of sin(x) is derived by calculating the derivatives of sin(x) at x = 0 and applying the Taylor series formula, resulting in the series x - x^3/3! + x^5/5! - x^7/7! +....
What determines the accuracy of the Taylor expansion approximation of sin(x)?
+The accuracy of the Taylor expansion approximation of sin(x) is determined by the number of terms used in the series and the value of x. More terms and values of x closer to 0 result in a more accurate approximation.
In conclusion, the Taylor expansion of sin(x) is a foundational concept in mathematics with profound implications and applications across various disciplines. Its derivation, application, and historical development underscore its significance as a tool for understanding and approximating the sine function. As mathematics and its applications continue to evolve, the importance of the Taylor expansion of sin(x) will endure, providing a basis for further exploration and innovation in the sciences and beyond.