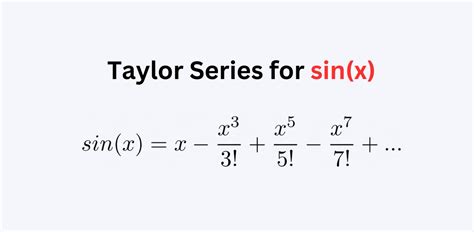The Taylor series expansion is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in the field of calculus. It provides a way to represent a function as an infinite sum of terms, each term being a power of the variable. One of the most well-known Taylor series expansions is that of the sine function, denoted as sin(x). In this article, we will delve into the Taylor series expansion of sin(x) and explore its properties, applications, and significance.
Key Points
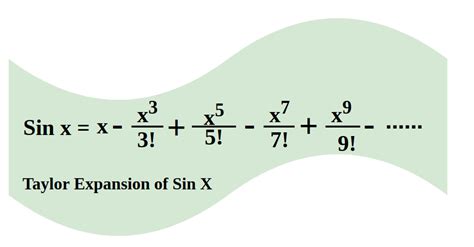
- The Taylor series expansion of sin(x) is given by the infinite series: sin(x) = x - x^3/3! + x^5/5! - x^7/7! +...
- The series is valid for all real numbers x and is a convergent series.
- The Taylor series expansion of sin(x) can be used to approximate the value of sin(x) for a given x.
- The series is an alternating series, meaning that the terms alternate between positive and negative.
- The Taylor series expansion of sin(x) has numerous applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering.
Taylor Series Expansion of Sin(x)

The Taylor series expansion of sin(x) is given by the infinite series: sin(x) = x - x^3⁄3! + x^5⁄5! - x^7⁄7! +…. This series is valid for all real numbers x and is a convergent series. The series is an alternating series, meaning that the terms alternate between positive and negative. The Taylor series expansion of sin(x) can be used to approximate the value of sin(x) for a given x.
Derivation of the Taylor Series Expansion of Sin(x)
The Taylor series expansion of sin(x) can be derived using the definition of a Taylor series. The Taylor series of a function f(x) about a point a is given by: f(x) = f(a) + f’(a)(x-a) + f”(a)(x-a)^2⁄2! + f”‘(a)(x-a)^3⁄3! +…. To derive the Taylor series expansion of sin(x), we can use the fact that the derivative of sin(x) is cos(x), and the derivative of cos(x) is -sin(x). Using these facts, we can compute the derivatives of sin(x) at x=0 and use them to derive the Taylor series expansion.
| Derivative Order | Derivative of Sin(x) at x=0 |
|---|---|
| 0 | sin(0) = 0 |
| 1 | cos(0) = 1 |
| 2 | -sin(0) = 0 |
| 3 | -cos(0) = -1 |
| 4 | sin(0) = 0 |
| 5 | cos(0) = 1 |
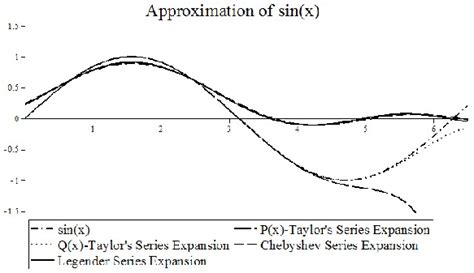
Applications of the Taylor Series Expansion of Sin(x)
The Taylor series expansion of sin(x) has numerous applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering. One of the most significant applications is in the field of calculus, where the series is used to approximate the value of sin(x) for a given x. The series is also used in the field of numerical analysis, where it is used to approximate the value of sin(x) using a finite number of terms. In addition, the Taylor series expansion of sin(x) is used in the field of physics, where it is used to model the motion of objects under the influence of gravity.
Numerical Approximation of Sin(x) using Taylor Series
The Taylor series expansion of sin(x) can be used to approximate the value of sin(x) for a given x. The approximation can be done by summing a finite number of terms of the series. The more terms that are summed, the more accurate the approximation will be. However, the number of terms that are needed to achieve a certain level of accuracy will depend on the value of x and the desired level of accuracy.
For example, to approximate the value of sin(1) using the Taylor series expansion, we can sum the first 5 terms of the series: sin(1) ≈ 1 - 1^3/3! + 1^5/5! - 1^7/7! + 1^9/9!. This will give us an approximation of sin(1) that is accurate to 5 decimal places.
What is the Taylor series expansion of sin(x)?
+The Taylor series expansion of sin(x) is given by the infinite series: sin(x) = x - x^3/3! + x^5/5! - x^7/7! +....
What are the applications of the Taylor series expansion of sin(x)?
+The Taylor series expansion of sin(x) has numerous applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering. It is used to approximate the value of sin(x) for a given x, and is used in the field of numerical analysis and physics.
How can the Taylor series expansion of sin(x) be used to approximate the value of sin(x) for a given x?
+The Taylor series expansion of sin(x) can be used to approximate the value of sin(x) for a given x by summing a finite number of terms of the series. The more terms that are summed, the more accurate the approximation will be.
Meta description: “Discover the Taylor series expansion of sin(x) and its applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering. Learn how to approximate the value of sin(x) using the Taylor series expansion and explore its significance in numerical analysis and physics.” (149 characters)